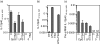Histone deacetylase inhibitors decrease Toll-like receptor-mediated activation of proinflammatory gene expression by impairing transcription factor recruitment - PubMed (original) (raw)
Histone deacetylase inhibitors decrease Toll-like receptor-mediated activation of proinflammatory gene expression by impairing transcription factor recruitment
Konrad A Bode et al. Immunology. 2007 Dec.
Abstract
Post-translational modifications of histone proteins are major mechanisms that modify chromatin structure and regulate gene expression in eukaryotes. Activation of histone acetyltransferases or inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDACs) is generally believed to allow chromatin to assume a more open state, permitting transcriptional activity. We report here the surprising observation that treatment of murine dendritic cells with the HDAC inhibitors trichostatin A (TSA) or suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) in non-apoptotic concentrations strongly inhibited induction of both interleukin-12 protein p40 (IL-12p40) mRNA and protein upon stimulation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs). Moreover, TLR-mediated up-regulation of costimulatory molecules was also inhibited. Up-regulation of tumour necrosis factor-alpha mRNA and protein in response to TLR agonists was only affected upon prolonged exposure to HDAC inhibitors and regulation of IL-1 beta was not affected. Similar effects were apparent in murine and human macrophages. Regarding the mode of action, HDAC inhibition increased the acetylation status at the IL-12p40 locus. Nevertheless, IL-12p40 chromatin remodelling, binding of Rel-A and IRF1 to the IL-12p40 promoter and transcriptional activation were abrogated. In contrast, HDAC inhibitors had no effects on upstream nuclear factor-kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. Thus HDACs positively regulate the expression of a subset of cytokine genes by enabling transcription factor recruitment.
Figures
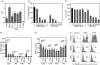
Figure 1
The HDAC inhibitors SAHA and TSA inhibit TLR-induced IL-12p40. (a) BMDCs were incubated with the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA (4 μ
m
) for 1 hr or stimulated with CpG-DNA (1 μ
m
) for the indicated time. ChIP assays were carried out from nuclear extracts with an anti-acetyl histone H4 antibody and acetylation of the IL-12p40 promoter was measured by quantitative PCR (one of three experiments). (b) BMDCs were preincubated for 1 hr with SAHA or TSA and stimulated with CpG-DNA (1 μ
m
) for 14 hr. Levels of IL-12p40 in culture supernatants were estimated by ELISA. (c) Additionally, cell viability was measured at 16 hr by MTT assay. (d, e) BMDCs were preincubated with SAHA (1 μ
m
) or TSA (10 n
m
) for 1 hr and stimulated with CpG-DNA (1 μ
m
), LPS (100 ng/ml), Pam3CSK4 (5 μg/ml) or poly(I : C) (50 μg/ml) for 8 hr. IL-12p40 (d) and TNF-α (e) were measured in the supernatant (mean + SEM, n = 3; ns: not significant). (f) BMDCs were preincubated with SAHA (1 μ
m
) or TSA (10 n
m
) for 1 hr and stimulated with CpG-DNA (1 μ
m
) or LPS (100 ng/ml). After 6 hr of incubation, cells were stained and analysed for intracytoplasmatic IL-12p40 by flow cytometry.
Figure 2
HDAC inhibitors diminish TLR-induced IL-12p40 transcription. (a) BMDCs were pretreated for 1 hr with TSA, then stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) or CpG-DNA (1 μ
m
). After 3 hr mRNA was isolated and expression of IL-12p40 was quantified by quantitative RT-PCR. The relative expression of IL-12p40 mRNA in comparison to the mRNA encoding the housekeeping gene β-actin is shown (mean + SEM, n = 4). (b) BMM were treated with medium, LPS (10 ng/ml), TSA (500 n
m
) or LPS + TSA. After 3 hr, mRNA was isolated and expression of IL-12p40 was estimated, relative to hprt, by quantitative RT-PCR. (c) Total RNA was isolated from BMDCs preincubated with TSA and stimulated with CpG or LPS. RT-PCR assays were performed using primer pairs that amplify pre-mRNA from intron sequences. The isolated cDNA was checked for contamination with genomic DNA applying a control cDNA preparation without reverse transcriptase (no RT) and also with primers against non-transcribed regions within the IL-12p40 promoter. Data are triplicates of quantitative RT-PCR results from one of three independent experiments (mean + SD).
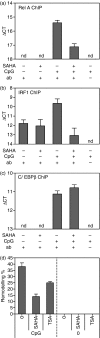
Figure 3
TLR-induced nucleosome remodelling and transcription factor recruitment is targeted by HDAC inhibitors. BMDCs were preincubated with SAHA (1 μ
m
) for 1 hr and stimulated with CpG-DNA (1 μ
m
) for 2 hr. ChIP assays were carried out from nuclear extracts with anti-RelA (a), anti-IRF1 (b), C/EBPβ (c), anti-IRF2 and anti-IRF7 (data not shown) antibodies and recruitment to the IL-12p40 promoter was measured by quantitative PCR using primers against (a, c) the known NF-κB binding site, and (b) a hypersensitive site in the IL-12p40 promoter 11 kb upstream of the TATA box. (d) BMDCs were preincubated with SAHA (1 μ
m
) or TSA (10 n
m
) for 1 hr and stimulated with CpG-DNA. Nuclear extracts were tested for restriction enzyme accessibility by ChART assay. Chromatin remodelling is plotted as a percentage of non-stimulated cells. Data are triplicates of PCR results from two independent experiments.
Figure 4
HDAC inhibitors do not affect upstream MAP kinase and NF-κB signalling. BMDCs were preincubated with TSA (50 n
m
) for 1 hr and stimulated with LPS (10 ng/ml) for the time indicated. Cell lysates were prepared and immunoblotting was performed using (a) phosphospecific antibodies against JNK, ERK and p38 as well as antibody against IκBα. Equivalent protein loading was checked using an antibody against β-actin. (b) Stimulated cells from above were also analysed by EMSA. Nuclear extracts were prepared and analysed for DNA-binding activities of NF-κB using an oligonucleotide with a canonical NF-κB-binding motif. Results are representative of three independent experiments.
Figure 5
SAHA and TSA differentially inhibit TLR-induced mRNA expression of various proinflammatory cytokines and affect regulation of costimulatory molecules. (a) BMDCs were preincubated with TSA (10 n
m
) for 1 hr and stimulated with CpG-DNA (1 μ
m
) for 3 hr. Messenger RNA expression of IFN-β, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β was quantified by quantitative RT-PCR. The relative expression of target genes in comparison to β-actin is shown. (b) BMM were treated with medium, LPS (10 ng/ml), TSA (500 n
m
) or LPS + TSA for 3 hr. Levels of IFN-β, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β mRNA were estimated by quantitative RT-PCR. The relative expression of target genes in comparison to hprt is shown. (c) HMDM were treated with medium, LPS (10 ng/ml) or LPS + TSA (500 n
m
) for 4 hr. Levels of IFN-β, IL-6 and IL-1β mRNA, relative to hprt mRNA, were estimated by quantitative RT-PCR. (d) BMDCs were stimulated with LPS in the presence of SAHA or TSA overnight. Expression of CD86, MHC-class II and CD40 was determined on CD11c+ cells by flow cytometry. Unstimulated (filled grey); LPS (black lines).
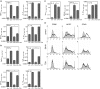
Figure 6
Longer pretreatment with HDAC inhibitors reveals additional effects on TLR-regulated gene expression. (a) BMDCs were preincubated with HDAC inhibitors SAHA or TSA for 1 or 3 hr and stimulated with CpG-DNA or LPS for an additional 3 hr. IL-12p40, TNF-α and IL-1β mRNA levels were quantified by quantitative RT-PCR. (b) BMDCs were pretreated as above with TSA or SAHA and further stimulated with CpG-DNA or LPS for 14 hr. TNF-α in culture supernatant was measured by ELISA (mean + SEM, n = 3).
Similar articles
- Differential effects of selective HDAC inhibitors on macrophage inflammatory responses to the Toll-like receptor 4 agonist LPS.
Halili MA, Andrews MR, Labzin LI, Schroder K, Matthias G, Cao C, Lovelace E, Reid RC, Le GT, Hume DA, Irvine KM, Matthias P, Fairlie DP, Sweet MJ. Halili MA, et al. J Leukoc Biol. 2010 Jun;87(6):1103-14. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0509363. Epub 2010 Mar 3. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20200406 - Protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 positively regulates TLR-induced IL-12p40 production in macrophages through inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.
Zhou D, Collins CA, Wu P, Brown EJ. Zhou D, et al. J Leukoc Biol. 2010 May;87(5):845-55. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0409289. Epub 2010 Feb 9. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20145200 - Deacetylase activity is required for STAT5-dependent GM-CSF functional activity in macrophages and differentiation to dendritic cells.
Sebastián C, Serra M, Yeramian A, Serrat N, Lloberas J, Celada A. Sebastián C, et al. J Immunol. 2008 May 1;180(9):5898-906. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.9.5898. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18424709 - Zn(II)-dependent histone deacetylase inhibitors: suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid and trichostatin A.
Codd R, Braich N, Liu J, Soe CZ, Pakchung AA. Codd R, et al. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;41(4):736-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.05.026. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18725319 Review. - Valproic acid: an old drug newly discovered as inhibitor of histone deacetylases.
Göttlicher M. Göttlicher M. Ann Hematol. 2004;83 Suppl 1:S91-2. doi: 10.1007/s00277-004-0850-2. Ann Hematol. 2004. PMID: 15124690 Review.
Cited by
- Histone deacetylases and NF-kB signaling coordinate expression of CX3CL1 in epithelial cells in response to microbial challenge by suppressing miR-424 and miR-503.
Zhou R, Gong AY, Chen D, Miller RE, Eischeid AN, Chen XM. Zhou R, et al. PLoS One. 2013 May 28;8(5):e65153. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065153. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23724129 Free PMC article. - Modified Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid Reduced Drug-Associated Immune Cell Death and Organ Damage under Lipopolysaccharide Inflammatory Challenge.
Truong N, Goodis CC, Cottingham AL, Shaw JR, Fletcher S, Pearson RM. Truong N, et al. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022 Oct 10;5(11):1128-1141. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.2c00119. eCollection 2022 Nov 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36407956 Free PMC article. - Epigenetic histone acetylation modulating prenatal Poly I:C induced neuroinflammation in the prefrontal cortex of rats: a study in a maternal immune activation model.
Su Y, Lian J, Chen S, Zhang W, Deng C. Su Y, et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Nov 28;16:1037105. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.1037105. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36519081 Free PMC article. - The Role of HDACs in the Response of Cancer Cells to Cellular Stress and the Potential for Therapeutic Intervention.
Alseksek RK, Ramadan WS, Saleh E, El-Awady R. Alseksek RK, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 24;23(15):8141. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158141. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897717 Free PMC article. Review. - Aging-dependent upregulation of IL-23p19 gene expression in dendritic cells is associated with differential transcription factor binding and histone modifications.
El Mezayen R, El Gazzar M, Myer R, High KP. El Mezayen R, et al. Aging Cell. 2009 Sep;8(5):553-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00502.x. Epub 2009 Jul 13. Aging Cell. 2009. PMID: 19624579 Free PMC article.
References
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
- Honda K, Taniguchi T. IRFs: master regulators of signalling by Toll-like receptors and cytosolic pattern-recognition receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:644–58. - PubMed
- O'Neill LA. How Toll-like receptors signal: what we know and what we don't know. Curr Opin Immunol. 2006;18:3–9. - PubMed
- Takeda K, Akira S. Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int Immunol. 2005;17:1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials