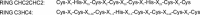Pellino proteins: novel players in TLR and IL-1R signalling - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Pellino proteins: novel players in TLR and IL-1R signalling
Reinout Schauvliege et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2007 May-Jun.
Abstract
Members of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) and interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) family play important roles in immunity and inflammation. They initiate common intracellular signalling cascades leading to the activation of nuclear factor-?B (NF-?B) and other transcription factors that stimulate the expression of a variety of genes that shape an appropriate immune response. TLR/IL-1R signalling involves multiple proteinprotein interactions, but the mechanisms that regulate these interactions are still largely unclear. In this context, Pellino proteins have been suggested to function as evolutionary conserved scaffold proteins in TLR/IL-1R signalling. However, recently Pellino proteins were also proposed to function as novel ubiquitin ligases for IL-1R associated kinase 1 (IRAK-1). Here we review our current knowledge on the expression, biological role and mechanism of action of Pellino proteins in TLR/IL-1R-induced signalling.
Figures
1
Schematic overview of LPS-induced MyD88-dependent signalling leading to IKK and MAPK activation. Upon LPS-binding (mediated by MD-2 and CD14) to TLR4 and subsequent TLR4 clustering, Mal, MyD88, IRAK-1, Tollip and IRAK-4 are recruited to the cytoplasmic part of the receptor via TLR4/MyD88 TIR–TIR interactions (1). IRAK-4 phosphorylates IRAK-1 (2), leading to IRAK-1 activity and autophosphorylation (3). Tollip is also phosphorylated by IRAK-1 and leaves the receptor complex (Complex I) (4). IRAK-1 interacts with TRAF6 and the TRAF6 adaptor protein TIFA (5). IRAK-1/TRAF6/TIFA leave the receptor complex (6) and associate with the preformed (but inactive) TAK1/TAB1/TAB2 complex (7), resulting in the formation of Complex II. There, TAK1 and TAB1 are phosphorylated after which TRAF6/TAK1/TAB1/TAB2 migrate back to the cytosol (8), while IRAK-1 remains at the membrane and is most likely degraded by the proteasome (9). TIFA promotes the oligomerization and activation of TRAF6, leading to TRAF6 K63-linked polyubiquitination and subsequent TAK1 activation (10). TAK1 is then responsible for the downstream activation of IKK as well as MAPK pathways (11). Pellino proteins associate with IRAK-1, TRAF6 and TAK1 in Complex II and III, and become phosphorylated by IRAK-1 (12). Pellino-1 and -2 also induce IRAK-1 polyubiquitination (13). DD = Death Domain, KD = active kinase domain, KD*= inactive kinase domain, RING = RING domain, FHA = Forkhead Associated domain, Ub = Ubiquitin, Zf = Zinc-finger, TRAF = TRAF domain and P = phosphorylation. For more information, see text.
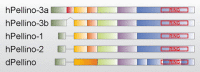
2
Schematic alignment of some representative Pellino proteins. Different exons of a particular Pellino are marked in a different colour, and homologous exons in various Pellino sequences are indicated in the same colour. The RING-like domain in the C-terminal part of every Pellino is boxed in red. (h) = human; (d) =Drosophila. For more information, see text.
3
Alignment of the mammalian Pellino-RING (CHC2CHC2) consensus sequence with the C3HC4 RING consensus sequence, which was adopted from [37].
Similar articles
- Pellino proteins are more than scaffold proteins in TLR/IL-1R signalling: a role as novel RING E3-ubiquitin-ligases.
Schauvliege R, Janssens S, Beyaert R. Schauvliege R, et al. FEBS Lett. 2006 Aug 21;580(19):4697-702. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.07.046. Epub 2006 Jul 24. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 16884718 - Pellino 2 is critical for Toll-like receptor/interleukin-1 receptor (TLR/IL-1R)-mediated post-transcriptional control.
Kim TW, Yu M, Zhou H, Cui W, Wang J, DiCorleto P, Fox P, Xiao H, Li X. Kim TW, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 20;287(30):25686-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.352625. Epub 2012 Jun 5. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22669975 Free PMC article. - Smad7 and Smad6 bind to discrete regions of Pellino-1 via their MH2 domains to mediate TGF-beta1-induced negative regulation of IL-1R/TLR signaling.
Lee YS, Kim JH, Kim ST, Kwon JY, Hong S, Kim SJ, Park SH. Lee YS, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Mar 19;393(4):836-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.094. Epub 2010 Feb 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20171181 - The Pellino family: IRAK E3 ligases with emerging roles in innate immune signalling.
Moynagh PN. Moynagh PN. Trends Immunol. 2009 Jan;30(1):33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2008.10.001. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Trends Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19022706 Review. - TLR-4, IL-1R and TNF-R signaling to NF-kappaB: variations on a common theme.
Verstrepen L, Bekaert T, Chau TL, Tavernier J, Chariot A, Beyaert R. Verstrepen L, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Oct;65(19):2964-78. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8064-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18535784 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Pellino-1 confers chemoresistance in lung cancer cells by upregulating cIAP2 through Lys63-mediated polyubiquitination.
Jeon YK, Kim CK, Koh J, Chung DH, Ha GH. Jeon YK, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 5;7(27):41811-41824. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9619. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27248820 Free PMC article. - Innate immunity and the regulation and mobilization of keratinocyte stem cells: are the old players playing a new game?
Singh A, Morris RJ. Singh A, et al. Exp Dermatol. 2012 Sep;21(9):660-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2012.01566.x. Exp Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 22897573 Free PMC article. Review. - Toll-like Receptors and the Control of Immunity.
Fitzgerald KA, Kagan JC. Fitzgerald KA, et al. Cell. 2020 Mar 19;180(6):1044-1066. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.041. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32164908 Free PMC article. Review. - Identification of a prognostic 28-gene expression signature for gastric cancer with lymphatic metastasis.
Zhang C, Jing LW, Li ZT, Chang ZW, Liu H, Zhang QM, Zhang QY. Zhang C, et al. Biosci Rep. 2019 May 2;39(5):BSR20182179. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182179. Print 2019 May 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30971501 Free PMC article. - TGR5 activation attenuates neuroinflammation via Pellino3 inhibition of caspase-8/NLRP3 after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats.
Liang H, Matei N, McBride DW, Xu Y, Zhou Z, Tang J, Luo B, Zhang JH. Liang H, et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Feb 2;18(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02087-1. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 33531049 Free PMC article.
References
- Dunne A, O'Neill LA. The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: signal transduction during inflam-mation and host defense. Sci STKE. 2003;171:re3. - PubMed
- Beutler B, Jiang Z, Georgel P, Crozat K, Croker B, Rutschmann S, Du X, Hoebe K. Genetic analysis of host resistance: toll-like receptor signaling and immunity at large. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:353–89. - PubMed
- Dunne A, O'Neill LA. Adaptor usage and Toll-like receptor signaling specificity. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:3330–5. - PubMed
- Janssens S, Beyaert R. A universal role for MyD88 in TLR/IL-1R-mediated signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 2002;27:474–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources