PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses - PubMed (original) (raw)
PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses
Shaun Purcell et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2007 Sep.
Abstract
Whole-genome association studies (WGAS) bring new computational, as well as analytic, challenges to researchers. Many existing genetic-analysis tools are not designed to handle such large data sets in a convenient manner and do not necessarily exploit the new opportunities that whole-genome data bring. To address these issues, we developed PLINK, an open-source C/C++ WGAS tool set. With PLINK, large data sets comprising hundreds of thousands of markers genotyped for thousands of individuals can be rapidly manipulated and analyzed in their entirety. As well as providing tools to make the basic analytic steps computationally efficient, PLINK also supports some novel approaches to whole-genome data that take advantage of whole-genome coverage. We introduce PLINK and describe the five main domains of function: data management, summary statistics, population stratification, association analysis, and identity-by-descent estimation. In particular, we focus on the estimation and use of identity-by-state and identity-by-descent information in the context of population-based whole-genome studies. This information can be used to detect and correct for population stratification and to identify extended chromosomal segments that are shared identical by descent between very distantly related individuals. Analysis of the patterns of segmental sharing has the potential to map disease loci that contain multiple rare variants in a population-based linkage analysis.
Figures
Figure A1.
Example transmissions and corresponding IBD states. For two haploid genomes,
_C_1
and
_C_2
, the figure illustrates four (of many) possible patterns of transmission and the corresponding IBD states at two positions, U and V. The text describes how consideration of these possible scenarios leads to the specification of transition matrices for IBD state along the chromosome.
Figure 1.
MDS and classification of Asian HapMap individuals. MDS reveals in each panel two clear clusters that correspond to CHB (left) and JPT (right) HapMap populations. The figure’s three panels differ only in the color scheme, which represents classification according to PPC thresholds of 0.01 (A), 0.001 (B), and 0.0001 (C).
Figure 2.
Example segment shared IBD between two HapMap CEU offspring individuals and their parents. The main set of plots show the multipoint estimate of IBD sharing,
P(_Z_=1)
, for a 25-Mb region of chromosome 9, for the pairs of individuals between two families (CEPH1375 and CEPH1341). The region was selected because the two offspring (NA10863 and NA06991) showed sharing in this region, shown in plot a. The three other segments shared between seemingly unrelated individuals are shown—that is, between the offspring in one family and a parent in the other family (two plots labeled b and c) and between those two parents (plot d). The lower-left diagram illustrates the region shared; this extended haplotype spans multiple haplotype blocks and recombination hotspots in the full phase II data. The lower-right diagram depicts the pattern of gene flow for this particular region—that is, a segment of the original common chromosome (dark rectangles) appears in the two families as shown.
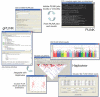
Figure 3.
Schema of integration of PLINK, gPLINK, and Haploview. PLINK is the main C/C++ WGAS analytic engine that can run either as a stand-alone tool (from the command line or via shell scripting) or in conjunction with gPLINK, a Java-based graphical user interface (GUI). gPLINK also offers a simple project management framework to track PLINK analyses and facilitates integration with Haploview. It is easy to configure these tools, such that the whole-genome data and PLINK analyses (i.e., the computationally expensive aspects of this process) can reside on a remote server, but all initiation and viewing of results is done locally—for example, on a user’s laptop, connected to the whole-genome data via the Internet, by use of gPLINK’s secure shell networking.
Similar articles
- PLINK: Key Functions for Data Analysis.
Slifer SH. Slifer SH. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2018 Apr;97(1):e59. doi: 10.1002/cphg.59. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 30040203 - Inference of relationships in population data using identity-by-descent and identity-by-state.
Stevens EL, Heckenberg G, Roberson ED, Baugher JD, Downey TJ, Pevsner J. Stevens EL, et al. PLoS Genet. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002287. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002287. Epub 2011 Sep 22. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21966277 Free PMC article. - Second-generation PLINK: rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets.
Chang CC, Chow CC, Tellier LC, Vattikuti S, Purcell SM, Lee JJ. Chang CC, et al. Gigascience. 2015 Feb 25;4:7. doi: 10.1186/s13742-015-0047-8. eCollection 2015. Gigascience. 2015. PMID: 25722852 Free PMC article. - Application of genome-wide SNP data for uncovering pairwise relationships and quantitative trait loci.
Sham PC, Cherny SS, Purcell S. Sham PC, et al. Genetica. 2009 Jun;136(2):237-43. doi: 10.1007/s10709-008-9349-4. Epub 2009 Jan 7. Genetica. 2009. PMID: 19127410 Review. - Linkage analysis and the study of Mendelian disease in the era of whole exome and genome sequencing.
Teare MD, Santibañez Koref MF. Teare MD, et al. Brief Funct Genomics. 2014 Sep;13(5):378-83. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elu024. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Brief Funct Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25024279 Review.
Cited by
- Genetic Predisposition to Prediabetes in the Kazakh Population.
Svyatova G, Berezina G, Murtazaliyeva A, Dyussupov A, Belyayeva T, Faizova R, Dyussupova A. Svyatova G, et al. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 28;46(10):10913-10922. doi: 10.3390/cimb46100648. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39451528 Free PMC article. - SMARTER-database: a tool to integrate SNP array datasets for sheep and goat breeds.
Cozzi P, Manunza A, Ramirez-Diaz J, Tsartsianidou V, Gkagkavouzis K, Peraza P, Johansson AM, Arranz JJ, Freire F, Kusza S, Biscarini F, Peters L, Tosser-Klopp G, Ciappesoni G, Triantafyllidis A, Rupp R, Servin B, Stella A. Cozzi P, et al. GigaByte. 2024 Oct 21;2024:gigabyte139. doi: 10.46471/gigabyte.139. eCollection 2024. GigaByte. 2024. PMID: 39473492 Free PMC article. - Socio-demographic and genetic risk factors for drug adherence and persistence across 5 common medication classes.
Cordioli M, Corbetta A, Kariis HM, Jukarainen S, Vartiainen P, Kiiskinen T, Ferro M; FinnGen; Estonian Biobank Research Team; Perola M, Niemi M, Ripatti S, Lehto K, Milani L, Ganna A. Cordioli M, et al. Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 23;15(1):9156. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53556-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39443518 Free PMC article. - African origin haplotype protective for Alzheimer's disease in _APOE_ε4 carriers: exploring potential mechanisms.
Bertholim-Nasciben L, Nuytemans K, Van Booven D, Rajabli F, Moura S, Ramirez AM, Dykxhoorn DM, Wang L, Scott WK, Davis DA, Vontell RT, McInerney KF, Cuccaro ML, Byrd GS, Haines JL, Gearing M, Adams LD, Pericak-Vance MA; ADSP; Young JI, Griswold AJ, Vance JM. Bertholim-Nasciben L, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 27:2024.10.24.619909. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.24.619909. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39484566 Free PMC article. Preprint. - SNP-Based and Kmer-Based eQTL Analysis Using Transcriptome Data.
Ge M, Li C, Zhang Z. Ge M, et al. Animals (Basel). 2024 Oct 11;14(20):2941. doi: 10.3390/ani14202941. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457872 Free PMC article.
References
Web Resources
- Haploview, http://www.broad.mit.edu/mpg/haploview/
- HapMap, http://www.hapmap.org/
- PLINK and gPLINK, http://pngu.mgh.harvard.edu/purcell/plink/
- Queue portal at the Coriell Institute, https://queue.coriell.org/q/
References
- Hirschhorn JN, Lohmueller K, Byrne E, Hirschhorn K (2002) A comprehensive review of genetic association studies. Genet Med 4:45–61 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 EY012562/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 MH73806-01A1/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004171/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- EY-12562/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 MH073806/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials