The safety and effects of the beta-blocker, nadolol, in mild asthma: an open-label pilot study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2007.07.002. Epub 2007 Jul 17.
Supria Singh, Rami El-Wali, Michael Flashner, Amie E Franklin, William J Garner, Burton F Dickey, Sergio Parra, Stephen Ruoss, Felix Shardonofsky, Brian J O'Connor, Clive Page, Richard A Bond
Affiliations
- PMID: 17703976
- PMCID: PMC2254137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pupt.2007.07.002
Clinical Trial
The safety and effects of the beta-blocker, nadolol, in mild asthma: an open-label pilot study
Nicola A Hanania et al. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2008.
Abstract
Beta-blockers are currently contraindicated in asthma because their acute administration may be associated with worsening bronchospasm. However, their effects and safety with their chronic administration are not well evaluated. The rationale for this pilot study was based on the paradigm shift that was observed with the use of beta-blockers in congestive heart failure, which once contraindicated because of their acute detrimental effects, have now been shown to reduce mortality with their chronic use. We hypothesized that certain beta-blockers may also be safe and useful in chronic asthma therapy. In this prospective, open-label, pilot study, we evaluated the safety and effects of escalating doses of the beta-blocker, nadolol, administered over 9 weeks to 10 subjects with mild asthma. Dose escalation was performed on a weekly basis based on pre-determined safety, lung function, asthma control and hemodynamic parameters. The primary objective was to evaluate safety and secondary objectives were to evaluate effects on airway hyperresponsiveness, and indices of respiratory function. The escalating administration of nadolol was well tolerated. In 8 out of the 10 subjects, 9 weeks of nadolol treatment produced a significant, dose-dependent increase in PC20 that reached 2.1 doubling doses at 40 mg (P<0.0042). However, there was also a dose-independent 5% reduction in mean FEV1 over the study period (P<0.01). We conclude that in most patients with mild asthma, the dose-escalating administration of the beta-blocker, nadolol, is well tolerated and may have beneficial effects on airway hyperresponsiveness. Our findings warrant further testing in future larger trials.
Figures
Figure 1. Schematic description of study protocol
V = Visit, ACQ= Asthma Control Questionnaire Score, PEFR = peak expiratory flow rates, PC20: provocative concentration of methacholine producing a 20% fall in FEV1, HR = heart rate, BP = Blood pressure.
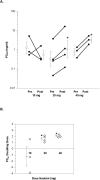
Figure 2A & 2B. The effect of chronic treatment with nadolol on the PC20 methacholine in mild asthmatic patients
A. Data shown as pre- and post-treatment with final nadolol doses of 10, 20, and 40 mg. Mean values ± SEM are also shown. Comparisons between pre- and post-treatment with nadolol were done using paired t-test. *P<0.05. B. Data for each patient shown as the doubling dose in PC20 methacholine values between baseline and after treatment relative to final doses of nadolol of 10, 20, and 40 mg. Mean values ± SEM are also shown.
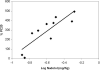
Figure 3. Correlation Between Nadolol Dose and Change in PC20
Correlation between nadolol dose log (mg/Kg) versus the percentage of change in PC20 as compared with baseline levels for each patient. Least squares linear regression correlation: r = 0.86; p=0.0016
Similar articles
- Chronic exposure to beta-blockers attenuates inflammation and mucin content in a murine asthma model.
Nguyen LP, Omoluabi O, Parra S, Frieske JM, Clement C, Ammar-Aouchiche Z, Ho SB, Ehre C, Kesimer M, Knoll BJ, Tuvim MJ, Dickey BF, Bond RA. Nguyen LP, et al. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008 Mar;38(3):256-62. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0279RC. Epub 2007 Dec 20. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18096872 Free PMC article. - Oral Nadolol for the Treatment of Infantile Hemangiomas: A Single-Institution Retrospective Cohort Study.
Randhawa HK, Sibbald C, Garcia Romero MT, Pope E. Randhawa HK, et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Sep-Oct;32(5):690-5. doi: 10.1111/pde.12655. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 26215612 - Beta-blocker underuse in secondary prevention of myocardial infarction.
Everly MJ, Heaton PC, Cluxton RJ Jr. Everly MJ, et al. Ann Pharmacother. 2004 Feb;38(2):286-93. doi: 10.1345/aph.1C472. Epub 2003 Dec 30. Ann Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 14742768 Review. - Adverse respiratory effect of acute β-blocker exposure in asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Morales DR, Jackson C, Lipworth BJ, Donnan PT, Guthrie B. Morales DR, et al. Chest. 2014 Apr;145(4):779-786. doi: 10.1378/chest.13-1235. Chest. 2014. PMID: 24202435 Review.
Cited by
- Effects of hydrocortisone on acute β-adrenoceptor blocker and histamine induced bronchoconstriction.
Short PM, Williamson PA, Lipworth BJ. Short PM, et al. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 May;73(5):717-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.04143.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22077869 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Cardiovascular diseases or type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic airway diseases: mutual pharmacological interferences.
Cazzola M, Rogliani P, Ora J, Calzetta L, Matera MG. Cazzola M, et al. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2023 May 31;14:20406223231171556. doi: 10.1177/20406223231171556. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2023. PMID: 37284143 Free PMC article. Review. - Nonrespiratory Comorbidities in Asthma.
Cardet JC, Bulkhi AA, Lockey RF. Cardet JC, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021 Nov;9(11):3887-3897. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2021.08.027. Epub 2021 Sep 4. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021. PMID: 34492402 Free PMC article. Review. - β2 Agonists.
Billington CK, Penn RB, Hall IP. Billington CK, et al. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;237:23-40. doi: 10.1007/164_2016_64. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27878470 Free PMC article. Review. - Clinical implications of the intrinsic efficacy of beta-adrenoceptor drugs in asthma: full, partial and inverse agonism.
Hanania NA, Dickey BF, Bond RA. Hanania NA, et al. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2010 Jan;16(1):1-5. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0b013e328333def8. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2010. PMID: 19887938 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Lipworth BJ. Airway subsensitivity with long-acting beta 2-agonists. Is there cause for concern? Drug Saf. 1997;16:295–308. - PubMed
- Salpeter SR, Buckley NS, Ormiston TM, Salpeter EE. Meta-analysis: effect of long-acting beta-agonists on severe asthma exacerbations and asthma-related deaths. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:904–912. - PubMed
- Abramson MJ, Walters J, Walters EH. Adverse effects of beta-agonists: are they clinically relevant? Am J Respir Med. 2003;2:287–297. - PubMed
- Cockcroft DW, McParland CP, Britto SA, et al. Regular inhaled salbutamol and airway responsiveness to allergen. Lancet. 1993;342:833–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical