Genome-wide detection and characterization of positive selection in human populations - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2007 Oct 18;449(7164):913-8.
doi: 10.1038/nature06250.
Patrick Varilly, Ben Fry, Jason Lohmueller, Elizabeth Hostetter, Chris Cotsapas, Xiaohui Xie, Elizabeth H Byrne, Steven A McCarroll, Rachelle Gaudet, Stephen F Schaffner, Eric S Lander; International HapMap Consortium; Kelly A Frazer, Dennis G Ballinger, David R Cox, David A Hinds, Laura L Stuve, Richard A Gibbs, John W Belmont, Andrew Boudreau, Paul Hardenbol, Suzanne M Leal, Shiran Pasternak, David A Wheeler, Thomas D Willis, Fuli Yu, Huanming Yang, Changqing Zeng, Yang Gao, Haoran Hu, Weitao Hu, Chaohua Li, Wei Lin, Siqi Liu, Hao Pan, Xiaoli Tang, Jian Wang, Wei Wang, Jun Yu, Bo Zhang, Qingrun Zhang, Hongbin Zhao, Hui Zhao, Jun Zhou, Stacey B Gabriel, Rachel Barry, Brendan Blumenstiel, Amy Camargo, Matthew Defelice, Maura Faggart, Mary Goyette, Supriya Gupta, Jamie Moore, Huy Nguyen, Robert C Onofrio, Melissa Parkin, Jessica Roy, Erich Stahl, Ellen Winchester, Liuda Ziaugra, David Altshuler, Yan Shen, Zhijian Yao, Wei Huang, Xun Chu, Yungang He, Li Jin, Yangfan Liu, Yayun Shen, Weiwei Sun, Haifeng Wang, Yi Wang, Ying Wang, Xiaoyan Xiong, Liang Xu, Mary M Y Waye, Stephen K W Tsui, Hong Xue, J Tze-Fei Wong, Luana M Galver, Jian-Bing Fan, Kevin Gunderson, Sarah S Murray, Arnold R Oliphant, Mark S Chee, Alexandre Montpetit, Fanny Chagnon, Vincent Ferretti, Martin Leboeuf, Jean-François Olivier, Michael S Phillips, Stéphanie Roumy, Clémentine Sallée, Andrei Verner, Thomas J Hudson, Pui-Yan Kwok, Dongmei Cai, Daniel C Koboldt, Raymond D Miller, Ludmila Pawlikowska, Patricia Taillon-Miller, Ming Xiao, Lap-Chee Tsui, William Mak, You Qiang Song, Paul K H Tam, Yusuke Nakamura, Takahisa Kawaguchi, Takuya Kitamoto, Takashi Morizono, Atsushi Nagashima, Yozo Ohnishi, Akihiro Sekine, Toshihiro Tanaka, Tatsuhiko Tsunoda, Panos Deloukas, Christine P Bird, Marcos Delgado, Emmanouil T Dermitzakis, Rhian Gwilliam, Sarah Hunt, Jonathan Morrison, Don Powell, Barbara E Stranger, Pamela Whittaker, David R Bentley, Mark J Daly, Paul I W de Bakker, Jeff Barrett, Yves R Chretien, Julian Maller, Steve McCarroll, Nick Patterson, Itsik Pe'er, Alkes Price, Shaun Purcell, Daniel J Richter, Pardis Sabeti, Richa Saxena, Stephen F Schaffner, Pak C Sham, Patrick Varilly, David Altshuler, Lincoln D Stein, Lalitha Krishnan, Albert Vernon Smith, Marcela K Tello-Ruiz, Gudmundur A Thorisson, Aravinda Chakravarti, Peter E Chen, David J Cutler, Carl S Kashuk, Shin Lin, Gonçalo R Abecasis, Weihua Guan, Yun Li, Heather M Munro, Zhaohui Steve Qin, Daryl J Thomas, Gilean McVean, Adam Auton, Leonardo Bottolo, Niall Cardin, Susana Eyheramendy, Colin Freeman, Jonathan Marchini, Simon Myers, Chris Spencer, Matthew Stephens, Peter Donnelly, Lon R Cardon, Geraldine Clarke, David M Evans, Andrew P Morris, Bruce S Weir, Tatsuhiko Tsunoda, Todd A Johnson, James C Mullikin, Stephen T Sherry, Michael Feolo, Andrew Skol, Houcan Zhang, Changqing Zeng, Hui Zhao, Ichiro Matsuda, Yoshimitsu Fukushima, Darryl R Macer, Eiko Suda, Charles N Rotimi, Clement A Adebamowo, Ike Ajayi, Toyin Aniagwu, Patricia A Marshall, Chibuzor Nkwodimmah, Charmaine D M Royal, Mark F Leppert, Missy Dixon, Andy Peiffer, Renzong Qiu, Alastair Kent, Kazuto Kato, Norio Niikawa, Isaac F Adewole, Bartha M Knoppers, Morris W Foster, Ellen Wright Clayton, Jessica Watkin, Richard A Gibbs, John W Belmont, Donna Muzny, Lynne Nazareth, Erica Sodergren, George M Weinstock, David A Wheeler, Imtaz Yakub, Stacey B Gabriel, Robert C Onofrio, Daniel J Richter, Liuda Ziaugra, Bruce W Birren, Mark J Daly, David Altshuler, Richard K Wilson, Lucinda L Fulton, Jane Rogers, John Burton, Nigel P Carter, Christopher M Clee, Mark Griffiths, Matthew C Jones, Kirsten McLay, Robert W Plumb, Mark T Ross, Sarah K Sims, David L Willey, Zhu Chen, Hua Han, Le Kang, Martin Godbout, John C Wallenburg, Paul L'Archevêque, Guy Bellemare, Koji Saeki, Hongguang Wang, Daochang An, Hongbo Fu, Qing Li, Zhen Wang, Renwu Wang, Arthur L Holden, Lisa D Brooks, Jean E McEwen, Mark S Guyer, Vivian Ota Wang, Jane L Peterson, Michael Shi, Jack Spiegel, Lawrence M Sung, Lynn F Zacharia, Francis S Collins, Karen Kennedy, Ruth Jamieson, John Stewart
Affiliations
- PMID: 17943131
- PMCID: PMC2687721
- DOI: 10.1038/nature06250
Genome-wide detection and characterization of positive selection in human populations
Pardis C Sabeti et al. Nature. 2007.
Abstract
With the advent of dense maps of human genetic variation, it is now possible to detect positive natural selection across the human genome. Here we report an analysis of over 3 million polymorphisms from the International HapMap Project Phase 2 (HapMap2). We used 'long-range haplotype' methods, which were developed to identify alleles segregating in a population that have undergone recent selection, and we also developed new methods that are based on cross-population comparisons to discover alleles that have swept to near-fixation within a population. The analysis reveals more than 300 strong candidate regions. Focusing on the strongest 22 regions, we develop a heuristic for scrutinizing these regions to identify candidate targets of selection. In a complementary analysis, we identify 26 non-synonymous, coding, single nucleotide polymorphisms showing regional evidence of positive selection. Examination of these candidates highlights three cases in which two genes in a common biological process have apparently undergone positive selection in the same population:LARGE and DMD, both related to infection by the Lassa virus, in West Africa;SLC24A5 and SLC45A2, both involved in skin pigmentation, in Europe; and EDAR and EDA2R, both involved in development of hair follicles, in Asia.
Figures
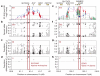
Figure 1. Localizing SLC24A5 and EDAR signals of selection
a–d, SLC24A5. a, Strong evidence for positive selection in CEU samples at a chromosome 15 locus: XP-EHH between CEU and JPT + CHB (blue), CEU and YRI (red), and YRI and JPT + CHB (grey). SNPs are classified as having low probability (bordered diamonds) and high probability (filled diamonds) potential for function. SNPs were filtered to identify likely targets of selection on the basis of the frequency of derived alleles (b), differences between populations (c) and differences between populations for high-frequency derived alleles (less than 20% in non-selected populations) (d). The number of SNPs that passed each filter is given in the top left corner in red. The threonine to alanine candidate polymorphism in SLC24A5 is the clear outlier. e–h, EDAR. e, Similar evidence for positive selection in JPT + CHB at a chromosome 2 locus: XP-EHH between CEU and JPT + CHB (blue), between YRI and JPT + CHB (red), and between CEU and YRI (grey); iHS in JPT + CHB (green). A valine to alanine polymorphism in EDAR passes all filters: the frequency of derived alleles (f), differences between populations (g) and differences between populations for high-frequency derived alleles (less than 20% in non-selected populations) (h). Three other functional changes, a D→E change in SULT1C2 and two SNPs associated with RANBP2 expression (Methods), have also become common in the selected population.
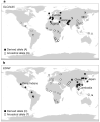
Figure 2. Global distribution of SLC24A5 A111T and EDAR V370A
Worldwide allele-frequency distributions for candidate polymorphisms with the strongest evidence for selection. a, SLC24A5 A111T is common in Europe, Northern Africa and Pakistan, but rare or absent elsewhere. b, EDAR V370A is common in Asia and the Americas, but absent in Europe and Africa.
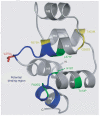
Figure 3. Structural model of the EDAR death domain
Ribbon representation of a homology model of the EDAR death domain (DD), based on the alignment of the EDAR DD amino acid sequence (EDAR residues 356–431), with multiple known DD structures. The helices are labelled H1 to H6. Residues in blue (the H1–H2 and H5–H6 loops, residues 370–376 and 419–425, respectively) correspond to the homologous residues in Tube that interact with Pelle in the Tube-DD–Pelle-DD structure. These EDAR-DD residues therefore form a potential region of interaction with a DD-containing EDAR-interacting protein, such as EDARADD. The V370A polymorphic residue (red) is located prominently within this potential binding region in the H1–H2 loop. Seven of the thirteen known mis-sense mutations in EDAR that lead to hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (HED) in humans are located in the EDAR-DD: the only four mutations in EDAR that lead to the dominant transmission of HED (green) and three recessive mutations (yellow). Four of these mutations, R375H, L377F, R420Q and I418T are located in the vicinity of the predicted interaction interface.
Similar articles
- Population differentiation as an indicator of recent positive selection in humans: an empirical evaluation.
Xue Y, Zhang X, Huang N, Daly A, Gillson CJ, Macarthur DG, Yngvadottir B, Nica AC, Woodwark C, Chen Y, Conrad DF, Ayub Q, Mehdi SQ, Li P, Tyler-Smith C. Xue Y, et al. Genetics. 2009 Nov;183(3):1065-77. doi: 10.1534/genetics.109.107722. Epub 2009 Sep 7. Genetics. 2009. PMID: 19737746 Free PMC article. - MC1R diversity in Northern Island Melanesia has not been constrained by strong purifying selection and cannot explain pigmentation phenotype variation in the region.
Norton HL, Werren E, Friedlaender J. Norton HL, et al. BMC Genet. 2015 Oct 19;16:122. doi: 10.1186/s12863-015-0277-x. BMC Genet. 2015. PMID: 26482799 Free PMC article. - A whole genome long-range haplotype (WGLRH) test for detecting imprints of positive selection in human populations.
Zhang C, Bailey DK, Awad T, Liu G, Xing G, Cao M, Valmeekam V, Retief J, Matsuzaki H, Taub M, Seielstad M, Kennedy GC. Zhang C, et al. Bioinformatics. 2006 Sep 1;22(17):2122-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl365. Epub 2006 Jul 15. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16845142 - Positive natural selection in the human lineage.
Sabeti PC, Schaffner SF, Fry B, Lohmueller J, Varilly P, Shamovsky O, Palma A, Mikkelsen TS, Altshuler D, Lander ES. Sabeti PC, et al. Science. 2006 Jun 16;312(5780):1614-20. doi: 10.1126/science.1124309. Science. 2006. PMID: 16778047 Review. - Molecular genetics of human pigmentation diversity.
Sturm RA. Sturm RA. Hum Mol Genet. 2009 Apr 15;18(R1):R9-17. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp003. Hum Mol Genet. 2009. PMID: 19297406 Review.
Cited by
- Positive selection in the chromosome 16 VKORC1 genomic region has contributed to the variability of anticoagulant response in humans.
Patillon B, Luisi P, Blanché H, Patin E, Cann HM, Génin E, Sabbagh A. Patillon B, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e53049. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053049. Epub 2012 Dec 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23285254 Free PMC article. - The Counteracting Effects of Demography on Functional Genomic Variation: The Roma Paradigm.
Font-Porterias N, Caro-Consuegra R, Lucas-Sánchez M, Lopez M, Giménez A, Carballo-Mesa A, Bosch E, Calafell F, Quintana-Murci L, Comas D. Font-Porterias N, et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Jun 25;38(7):2804-2817. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab070. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33713133 Free PMC article. - BGVD: An Integrated Database for Bovine Sequencing Variations and Selective Signatures.
Chen N, Fu W, Zhao J, Shen J, Chen Q, Zheng Z, Chen H, Sonstegard TS, Lei C, Jiang Y. Chen N, et al. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2020 Apr;18(2):186-193. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2019.03.007. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32540200 Free PMC article. - Ancestry, admixture and fitness in Colombian genomes.
Rishishwar L, Conley AB, Wigington CH, Wang L, Valderrama-Aguirre A, Jordan IK. Rishishwar L, et al. Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 21;5:12376. doi: 10.1038/srep12376. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26197429 Free PMC article. - Spatial structure alters the site frequency spectrum produced by hitchhiking.
Min J, Gupta M, Desai MM, Weissman DB. Min J, et al. Genetics. 2022 Nov 1;222(3):iyac139. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac139. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 36094352 Free PMC article.
References
- Sabeti PC, et al. Positive natural selection in the human lineage. Science. 2006;312:1614–1620. - PubMed
- Graf J, Hodgson R, van Daal A. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the MATP gene are associated with normal human pigmentation variation. Hum. Mutat. 2005;25:278–284. - PubMed
- Lamason RL, et al. SLC24A5, a putative cation exchanger, affects pigmentation in zebrafish and humans. Science. 2005;310:1782–1786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 077008/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 077011/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 077046/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 081682/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials