Genetic interactions between DNA demethylation and methylation in Arabidopsis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Genetic interactions between DNA demethylation and methylation in Arabidopsis
Jon Penterman et al. Plant Physiol. 2007 Dec.
Abstract
DNA demethylation in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) is mediated by DNA glycosylases of the DEMETER family. Three DEMETER-LIKE (DML) proteins, REPRESSOR OF SILENCING1 (ROS1), DML2, and DML3, function to protect genes from potentially deleterious methylation. In Arabidopsis, much of the DNA methylation is directed by RNA interference (RNAi) pathways and used to defend the genome from transposable elements and their remnants, repetitive sequences. Here, we investigated the relationship between DML demethylation and RNAi-mediated DNA methylation. We found that genic regions demethylated by DML enzymes are enriched for small interfering RNAs and generally contain sequence repeats, transposons, or both. The most common class of small interfering RNAs was 24 nucleotides long, suggesting a role for an RNAi pathway that depends on RNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE2 (RDR2). We show that ROS1 removes methylation that has multiple, independent origins, including de novo methylation directed by RDR2-dependent and -independent RNAi pathways. Interestingly, in rdr2 and drm2 mutant plants, we found that genes demethylated by ROS1 accumulate CG methylation, and we propose that this hypermethylation is due to the ROS1 down-regulation that occurs in these mutant backgrounds. Our observations support the hypothesis that DNA demethylation by DML enzymes is one mechanism by which Arabidopsis genes are protected from genome defense pathways.
Figures
Figure 1.
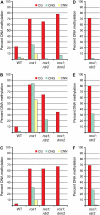
DML-target loci have features associated with DNA methylation. A, Percentage of DML-target genes and intergenic loci with siRNAs, transposons and repetitive elements, or both. B, Percentage of DML-target loci with 20-, 21-, 22-, 23-, and 24-nucleotide siRNAs.
Figure 2.
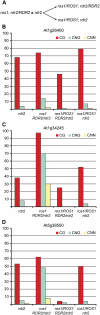
ROS1 removes DNA methylation established and maintained by the PolIV/RDR2/DCL3/AGO4 pathway and DRM2. A to F, Percentage of methylation at At1g26400 (A and D), At1g34245 (B and E), and At5g38550 (C and F) in wild-type, ros1-3, ros1-3; rdr2-1, and ros1-3; drm2-1 plants. The ros1-3; rdr2-1 genotype in A to C was generated by selfing a ros1-3; rdr2-1 F2 line, and the ros1-3; rdr2-1 genotype in D to F was generated by selfing a ros1-3; RDR2/rdr2-1 plant. The ros1-3; drm2-1 F3 plant was generated by selfing a ros1-3; drm2-1 F2 line.
Figure 3.
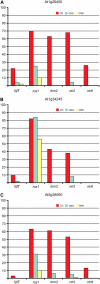
ROS1-target loci are hypermethylated in rdr2-1 and drm2-1 mutant plants. A to C, Percentage of methylation at At1g26400 (A), At1g34245 (B), and At5g38550 (C) in wild-type, ros1-3, rdr2-1, drm2-1, and rdr6-11 plants.
Figure 4.
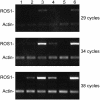
ROS1 expression is down-regulated in rdr2-1 and drm2-1 mutants. Shown is the expression of ROS1 and ACTIN11 (Actin) in ros1-3, rdr2-1, ros1-3/ROS1; rdr2-1/RDR2, ros1-3/ROS1; rdr2-1, drm2-1, and rdr6-11 plants (lanes 1–6, respectively).
Figure 5.
RDR2 is required for ROS1 DNA demethylation. A, Inheritance of hypermethylated loci by siblings that differ in the absence or presence of an RDR2 allele. B to D, Percentage of methylation at At1g26400, At1g34245, and At5g38550 in the parental genotypes (rdr2 and ros1-3; RDR2/rdr2-1) and their progeny (ROS1/ros1-3; RDR2/rdr2-1 and ROS1/ros1-3; rdr2-1). Eight to 10 clones from the parents were sequenced, and 17 to 20 clones from the progeny were sequenced.
Similar articles
- DNA demethylation in the Arabidopsis genome.
Penterman J, Zilberman D, Huh JH, Ballinger T, Henikoff S, Fischer RL. Penterman J, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Apr 17;104(16):6752-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701861104. Epub 2007 Apr 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17409185 Free PMC article. - DEMETER plays a role in DNA demethylation and disease response in somatic tissues of Arabidopsis.
Schumann U, Lee JM, Smith NA, Zhong C, Zhu JK, Dennis ES, Millar AA, Wang MB. Schumann U, et al. Epigenetics. 2019 Nov;14(11):1074-1087. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2019.1631113. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 31189415 Free PMC article. - DNA demethylases target promoter transposable elements to positively regulate stress responsive genes in Arabidopsis.
Le TN, Schumann U, Smith NA, Tiwari S, Au PC, Zhu QH, Taylor JM, Kazan K, Llewellyn DJ, Zhang R, Dennis ES, Wang MB. Le TN, et al. Genome Biol. 2014 Sep 17;15(9):458. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0458-3. Genome Biol. 2014. PMID: 25228471 Free PMC article. - DNA demethylation: a lesson from the garden.
Ikeda Y, Kinoshita T. Ikeda Y, et al. Chromosoma. 2009 Feb;118(1):37-41. doi: 10.1007/s00412-008-0183-3. Epub 2008 Oct 7. Chromosoma. 2009. PMID: 18839198 Review. - RNA-directed DNA methylation and Pol IVb in Arabidopsis.
Matzke M, Kanno T, Huettel B, Daxinger L, Matzke AJ. Matzke M, et al. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:449-59. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.028. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381327 Review.
Cited by
- Regulation and function of DNA methylation in plants and animals.
He XJ, Chen T, Zhu JK. He XJ, et al. Cell Res. 2011 Mar;21(3):442-65. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.23. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21321601 Free PMC article. Review. - The developmental regulator PKL is required to maintain correct DNA methylation patterns at RNA-directed DNA methylation loci.
Yang R, Zheng Z, Chen Q, Yang L, Huang H, Miki D, Wu W, Zeng L, Liu J, Zhou JX, Ogas J, Zhu JK, He XJ, Zhang H. Yang R, et al. Genome Biol. 2017 May 31;18(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1226-y. Genome Biol. 2017. PMID: 28569170 Free PMC article. - Role of Epigenetic Factors in Response to Stress and Establishment of Somatic Memory of Stress Exposure in Plants.
Kovalchuk I. Kovalchuk I. Plants (Basel). 2023 Oct 24;12(21):3667. doi: 10.3390/plants12213667. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37960024 Free PMC article. Review. - Double-edged sword: The evolutionary consequences of the epigenetic silencing of transposable elements.
Choi JY, Lee YCG. Choi JY, et al. PLoS Genet. 2020 Jul 16;16(7):e1008872. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008872. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32673310 Free PMC article. Review. - Active DNA Demethylation in Plants.
Parrilla-Doblas JT, Roldán-Arjona T, Ariza RR, Córdoba-Cañero D. Parrilla-Doblas JT, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 21;20(19):4683. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194683. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31546611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bender J (2004) DNA methylation and epigenetics. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55 41–68 - PubMed
- Cao X, Jacobsen SE (2002) Role of the arabidopsis DRM methyltransferases in de novo DNA methylation and gene silencing. Curr Biol 12 1138–1144 - PubMed
- Chan SW, Henderson IR, Jacobsen SE (2005) Gardening the genome: DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Rev Genet 6 351–360 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials