Laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery is effective in obese patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery is effective in obese patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
Vivien V Ng et al. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2007 Oct.
Abstract
Introduction: Obesity has long been regarded as a risk factor for the development of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD). It has been claimed that surgical efficacy of laparoscopic anti-reflux operations is decreased in obese patients. The aim of this study was to assess whether laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery is effective in obese patients with GORD compared to non-obese patients.
Patients and methods: A total of 366 patients (mean age 44 years; range, 12-86 years) underwent laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery between 1997-2003. Of these, 74 patients were considered obese; 58 patients had a body mass index (BMI) of 30-34 kg/m(2) and 16 were classified as morbidly obese with a BMI >or= 35 kg/m(2). Pre-operative symptomatic scoring, indications for surgery, pH studies, operative times and complications were compared between obese and non-obese patients. Symptomatic outcome and Visick score between the two groups were assessed at 6 weeks, 6 months and 1 year following surgery.
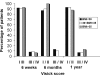
Results: Failure of medical treatment was the main reason for surgery in all groups. Operative time was longer in obese patients (mean time 93 min compared to 81 min; P = 0.0007), the main difficulty being gaining access because of their body habitus. All groups found the procedure to be effective in symptomatic outcome, 91% of obese patients compared to 92% of non-obese patients scored Visick I or II at 6 weeks' postoperatively. Similar Visick scoring was shown between the two groups at 6 months and 1 year, and in the morbidly obese group.
Conclusions: The outcome of laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery is similar between obese and non-obese patients with no trend towards a worse outcome in the obese or morbidly obese. Obesity should not be seen as a contra-indication, although it may be more technically challenging in this group of patients. Good results can be achieved in obese patients.
Figures
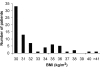
Figure 1
Distribution of patients with BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 (n = 74).
Figure 2
Follow-up Visick scores at 6 weeks, 6 months and 1 year
Similar articles
- The role of body mass index in determining clinical and quality of life outcomes after laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery.
Sanford Z, Jayaraman S, Weltz AS, Reza Zahiri H, Park A. Sanford Z, et al. Surg Endosc. 2020 Feb;34(2):646-657. doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-06811-0. Epub 2019 May 6. Surg Endosc. 2020. PMID: 31062159 - A prospective cross-sectional study of laparoscopic subtotal Lind fundoplication for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease--a durable and effective anti-reflux procedure.
Shapey IM, Agrawal S, Peacock A, Super P. Shapey IM, et al. Int J Surg. 2015 Jan;13:257-260. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.12.013. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Int J Surg. 2015. PMID: 25529280 - Outcomes after laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery related to obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Abdelrahman T, Latif A, Chan DS, Jones H, Farag M, Lewis WG, Havard T, Escofet X. Abdelrahman T, et al. Int J Surg. 2018 Mar;51:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.01.013. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Int J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29367036 Review. - Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication controls reflux symptoms and improves disease-specific quality of life in patients with class I and II obesity.
Martin Del Campo SE, Chaudhry UI, Kanji A, Suzo AJ, Perry KA. Martin Del Campo SE, et al. Surgery. 2017 Nov;162(5):1048-1054. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2017.07.006. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Surgery. 2017. PMID: 28827001 - Anti-reflux surgery in the laparoscopic era.
Lundell L. Lundell L. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2000 Oct;14(5):793-810. doi: 10.1053/bega.2000.0125. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2000. PMID: 11003810 Review.
Cited by
- The Impact of Obesity on Reflux Recurrence Following Laparoscopic Anti-reflux Surgery: An Evidence-Based Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Nadeem F, Singh A, Karim M, Khan A, Mirza S, Kabir SA. Nadeem F, et al. Cureus. 2024 Mar 26;16(3):e56981. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56981. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38665763 Free PMC article. Review. - Multi-society consensus conference and guideline on the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Slater BJ, Collings A, Dirks R, Gould JC, Qureshi AP, Juza R, Rodríguez-Luna MR, Wunker C, Kohn GP, Kothari S, Carslon E, Worrell S, Abou-Setta AM, Ansari MT, Athanasiadis DI, Daly S, Dimou F, Haskins IN, Hong J, Krishnan K, Lidor A, Litle V, Low D, Petrick A, Soriano IS, Thosani N, Tyberg A, Velanovich V, Vilallonga R, Marks JM. Slater BJ, et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Feb;37(2):781-806. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09817-3. Epub 2022 Dec 18. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 36529851 - The role of body mass index in determining clinical and quality of life outcomes after laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery.
Sanford Z, Jayaraman S, Weltz AS, Reza Zahiri H, Park A. Sanford Z, et al. Surg Endosc. 2020 Feb;34(2):646-657. doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-06811-0. Epub 2019 May 6. Surg Endosc. 2020. PMID: 31062159 - Safety and effectiveness of antireflux surgery in obese patients.
Tandon A, Rao R, Hotouras A, Nunes QM, Hartley M, Gunasekera R, Howes N. Tandon A, et al. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017 Sep;99(7):515-523. doi: 10.1308/rcsann.2017.0144. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017. PMID: 28853597 Free PMC article. Review. - Short- and Long-Term, 11-22 Years, Results after Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication in Obese versus Nonobese Patients.
Schietroma M, Piccione F, Clementi M, Cecilia EM, Sista F, Pessia B, Carlei F, Guadagni S, Amicucci G. Schietroma M, et al. J Obes. 2017;2017:7589408. doi: 10.1155/2017/7589408. Epub 2017 May 11. J Obes. 2017. PMID: 28584666 Free PMC article.
References
- Locke GR, 3rd, Talley NJ, Fett SL, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ., 3rd Risk factors associated with symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Med. 1999;106:642–9. - PubMed
- Wajed SA, Streets CG, Bremner CG, DeMeester TR. Elevated body mass disrupts the barrier to gastroesophageal reflux. Arch Surg. 2001;136:1014–8. discussion 1018–9. - PubMed
- Barak N, Ehrenpreis ED, Harrison JR, Sitrin MD. Gastro-esophageal reflux disease in obesity: pathophysiological and therapeutic considerations. Obes Rev. 2002;3:9–15. - PubMed
- Perez AR, Moncure AC, Rattner DW. Obesity adversely affects the outcome of antireflux operations. Surg Endosc. 2001;15:986–9. - PubMed
- Beauchamp G. Gastroesophageal reflux and obesity. Surg Clin North Am. 1983;63:869–76. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical