The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): gene structure and function annotation - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D1009-14.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm965. Epub 2007 Nov 5.
Christopher Wilks, Philippe Lamesch, Tanya Z Berardini, Margarita Garcia-Hernandez, Hartmut Foerster, Donghui Li, Tom Meyer, Robert Muller, Larry Ploetz, Amie Radenbaugh, Shanker Singh, Vanessa Swing, Christophe Tissier, Peifen Zhang, Eva Huala
Affiliations
- PMID: 17986450
- PMCID: PMC2238962
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm965
The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): gene structure and function annotation
David Swarbreck et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan.
Abstract
The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR, http://arabidopsis.org) is the model organism database for the fully sequenced and intensively studied model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Data in TAIR is derived in large part from manual curation of the Arabidopsis research literature and direct submissions from the research community. New developments at TAIR include the addition of the GBrowse genome viewer to the TAIR site, a redesigned home page, navigation structure and portal pages to make the site more intuitive and easier to use, the launch of several TAIR web services and a new genome annotation release (TAIR7) in April 2007. A combination of manual and computational methods were used to generate this release, which contains 27,029 protein-coding genes, 3889 pseudogenes or transposable elements and 1123 ncRNAs (32,041 genes in all, 37,019 gene models). A total of 681 new genes and 1002 new splice variants were added. Overall, 10,098 loci (one-third of all loci from the previous TAIR6 release) were updated for the TAIR7 release.
Figures
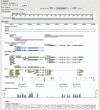
Figure 1.
TAIR GBrowse. The TAIR GBrowse tool allows navigation of the five A. thaliana nuclear chromosomes plus the mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes. A 10 kb region including AT4G39680 and AT4G39690 is shown (coding regions in dark blue and UTRs in light blue). Selected tracks shown here include cDNAs (dark green), ESTs (light green for forward orientation and light brown for reverse), T-DNA and transposon insertions (orange triangles), polymorphisms (yellow diamonds) and the VISTA plot showing sequence similarity with poplar. Additional tracks (data not shown) include CDS segments, markers and GC content. All elements shown in GBrowse can be clicked on to access the TAIR detail page for that object.
Similar articles
- The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): improved gene annotation and new tools.
Lamesch P, Berardini TZ, Li D, Swarbreck D, Wilks C, Sasidharan R, Muller R, Dreher K, Alexander DL, Garcia-Hernandez M, Karthikeyan AS, Lee CH, Nelson WD, Ploetz L, Singh S, Wensel A, Huala E. Lamesch P, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(Database issue):D1202-10. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1090. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22140109 Free PMC article. - Using the Arabidopsis information resource (TAIR) to find information about Arabidopsis genes.
Lamesch P, Dreher K, Swarbreck D, Sasidharan R, Reiser L, Huala E. Lamesch P, et al. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2010 Jun;Chapter 1:1.11.1-1.11.51. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0111s30. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20521243 - Using the Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) to Find Information About Arabidopsis Genes.
Reiser L, Subramaniam S, Li D, Huala E. Reiser L, et al. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2017 Dec 8;60:1.11.1-1.11.45. doi: 10.1002/cpbi.36. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 29220077 - TAIR: a resource for integrated Arabidopsis data.
Garcia-Hernandez M, Berardini TZ, Chen G, Crist D, Doyle A, Huala E, Knee E, Lambrecht M, Miller N, Mueller LA, Mundodi S, Reiser L, Rhee SY, Scholl R, Tacklind J, Weems DC, Wu Y, Xu I, Yoo D, Yoon J, Zhang P. Garcia-Hernandez M, et al. Funct Integr Genomics. 2002 Nov;2(6):239-53. doi: 10.1007/s10142-002-0077-z. Epub 2002 Oct 3. Funct Integr Genomics. 2002. PMID: 12444417 Review. - Anno genominis XX: 20 years of Arabidopsis genomics.
Provart NJ, Brady SM, Parry G, Schmitz RJ, Queitsch C, Bonetta D, Waese J, Schneeberger K, Loraine AE. Provart NJ, et al. Plant Cell. 2021 May 31;33(4):832-845. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koaa038. Plant Cell. 2021. PMID: 33793861 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- NUCLEAR FACTOR Y transcription factors have both opposing and additive roles in ABA-mediated seed germination.
Kumimoto RW, Siriwardana CL, Gayler KK, Risinger JR, Siefers N, Holt BF 3rd. Kumimoto RW, et al. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59481. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059481. Epub 2013 Mar 19. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23527203 Free PMC article. - An evolutionary network of genes present in the eukaryote common ancestor polls genomes on eukaryotic and mitochondrial origin.
Thiergart T, Landan G, Schenk M, Dagan T, Martin WF. Thiergart T, et al. Genome Biol Evol. 2012;4(4):466-85. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evs018. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Genome Biol Evol. 2012. PMID: 22355196 Free PMC article. - Transcriptomic profiles of poplar (Populus simonii × P. nigra) cuttings during adventitious root formation.
Yu Y, Meng N, Chen S, Zhang H, Liu Z, Wang Y, Jing Y, Wang Y, Chen S. Yu Y, et al. Front Genet. 2022 Sep 8;13:968544. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.968544. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36160010 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide survey of cold stress regulated alternative splicing in Arabidopsis thaliana with tiling microarray.
Leviatan N, Alkan N, Leshkowitz D, Fluhr R. Leviatan N, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Jun 11;8(6):e66511. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066511. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23776682 Free PMC article. - SpliceGrapher: detecting patterns of alternative splicing from RNA-Seq data in the context of gene models and EST data.
Rogers MF, Thomas J, Reddy AS, Ben-Hur A. Rogers MF, et al. Genome Biol. 2012 Jan 31;13(1):R4. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-1-r4. Genome Biol. 2012. PMID: 22293517 Free PMC article.
References
- Wilkinson MD, Links M. BioMOBY: an open source biological web services proposal. Brief Bioinform. 2002;3:331–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous