WormBase 2007 - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D612-7.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm975. Epub 2007 Nov 8.
Igor Antoshechkin, Tamberlyn Bieri, Darin Blasiar, Carol Bastiani, Payan Canaran, Juancarlos Chan, Wen J Chen, Paul Davis, Jolene Fernandes, Tristan J Fiedler, Michael Han, Todd W Harris, Ranjana Kishore, Raymond Lee, Sheldon McKay, Hans-Michael Müller, Cecilia Nakamura, Philip Ozersky, Andrei Petcherski, Gary Schindelman, Erich M Schwarz, Will Spooner, Mary Ann Tuli, Kimberly Van Auken, Daniel Wang, Xiaodong Wang, Gary Williams, Karen Yook, Richard Durbin, Lincoln D Stein, John Spieth, Paul W Sternberg
Affiliations
- PMID: 17991679
- PMCID: PMC2238927
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm975
WormBase 2007
Anthony Rogers et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan.
Abstract
WormBase (www.wormbase.org) is the major publicly available database of information about Caenorhabditis elegans, an important system for basic biological and biomedical research. Derived from the initial ACeDB database of C. elegans genetic and sequence information, WormBase now includes the genomic, anatomical and functional information about C. elegans, other Caenorhabditis species and other nematodes. As such, it is a crucial resource not only for C. elegans biologists but the larger biomedical and bioinformatics communities. Coverage of core areas of C. elegans biology will allow the biomedical community to make full use of the results of intensive molecular genetic analysis and functional genomic studies of this organism. Improved search and display tools, wider cross-species comparisons and extended ontologies are some of the features that will help scientists extend their research and take advantage of other nematode species genome sequences.
Figures
Figure 1.
Syntenic alignments of C. elegans, C. briggsae and C. remanei.
Figure 2.
Expression details of ife-4 shown in genome browser. Cartoon worms show approximate expression location. Mouse over pop-up window (left-center box) gives more details and original image. SAGE tags shown as blue/pink triangles with tag sequence and count. Sequences used in microarray experiments shown as horizontal, orange bar which can be clicked for more details. Gene exons displayed as pink boxes.
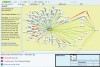
Figure 3.
N-Browse can be accessed via the icon on the Gene page (inset). Gene information (left panel) is taken from WormBase. Each gene in the main network window can be clicked to expand the network. Interaction types are colour-coded and can be switched dynamically on or off with the check boxes (lower panel). Search and navigation tools are provided in the top bar.
Similar articles
- Using WormBase: A Genome Biology Resource for Caenorhabditis elegans and Related Nematodes.
Grove C, Cain S, Chen WJ, Davis P, Harris T, Howe KL, Kishore R, Lee R, Paulini M, Raciti D, Tuli MA, Van Auken K, Williams G; WormBase Consortium. Grove C, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1757:399-470. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7737-6_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29761466 Free PMC article. - WormBase: a multi-species resource for nematode biology and genomics.
Harris TW, Chen N, Cunningham F, Tello-Ruiz M, Antoshechkin I, Bastiani C, Bieri T, Blasiar D, Bradnam K, Chan J, Chen CK, Chen WJ, Davis P, Kenny E, Kishore R, Lawson D, Lee R, Muller HM, Nakamura C, Ozersky P, Petcherski A, Rogers A, Sabo A, Schwarz EM, Van Auken K, Wang Q, Durbin R, Spieth J, Sternberg PW, Stein LD. Harris TW, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jan 1;32(Database issue):D411-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh066. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 14681445 Free PMC article. - WormBase 2016: expanding to enable helminth genomic research.
Howe KL, Bolt BJ, Cain S, Chan J, Chen WJ, Davis P, Done J, Down T, Gao S, Grove C, Harris TW, Kishore R, Lee R, Lomax J, Li Y, Muller HM, Nakamura C, Nuin P, Paulini M, Raciti D, Schindelman G, Stanley E, Tuli MA, Van Auken K, Wang D, Wang X, Williams G, Wright A, Yook K, Berriman M, Kersey P, Schedl T, Stein L, Sternberg PW. Howe KL, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D774-80. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1217. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26578572 Free PMC article. - WormBase: methods for data mining and comparative genomics.
Harris TW, Stein LD. Harris TW, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2006;351:31-50. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-151-7:31. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16988424 Review. - Mining nematode genome data for novel drug targets.
Foster JM, Zhang Y, Kumar S, Carlow CK. Foster JM, et al. Trends Parasitol. 2005 Mar;21(3):101-4. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2004.12.002. Trends Parasitol. 2005. PMID: 15734654 Review.
Cited by
- Emerging molecular knowledge on Radopholus similis, an important nematode pest of banana.
Haegeman A, Elsen A, De Waele D, Gheysen G. Haegeman A, et al. Mol Plant Pathol. 2010 May;11(3):315-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2010.00614.x. Mol Plant Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20447280 Free PMC article. - The Caenorhabditis elegans intermediate-size transcriptome shows high degree of stage-specific expression.
Wang Y, Chen J, Wei G, He H, Zhu X, Xiao T, Yuan J, Dong B, He S, Skogerbø G, Chen R. Wang Y, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jul;39(12):5203-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr102. Epub 2011 Mar 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21378118 Free PMC article. - The Protein Feature Ontology: a tool for the unification of protein feature annotations.
Reeves GA, Eilbeck K, Magrane M, O'Donovan C, Montecchi-Palazzi L, Harris MA, Orchard S, Jimenez RC, Prlic A, Hubbard TJ, Hermjakob H, Thornton JM. Reeves GA, et al. Bioinformatics. 2008 Dec 1;24(23):2767-72. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn528. Epub 2008 Oct 20. Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18936051 Free PMC article. - The UCSC Genome Browser Database: update 2009.
Kuhn RM, Karolchik D, Zweig AS, Wang T, Smith KE, Rosenbloom KR, Rhead B, Raney BJ, Pohl A, Pheasant M, Meyer L, Hsu F, Hinrichs AS, Harte RA, Giardine B, Fujita P, Diekhans M, Dreszer T, Clawson H, Barber GP, Haussler D, Kent WJ. Kuhn RM, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan;37(Database issue):D755-61. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn875. Epub 2008 Nov 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 18996895 Free PMC article. - MetaBase--the wiki-database of biological databases.
Bolser DM, Chibon PY, Palopoli N, Gong S, Jacob D, Del Angel VD, Swan D, Bassi S, González V, Suravajhala P, Hwang S, Romano P, Edwards R, Bishop B, Eargle J, Shtatland T, Provart NJ, Clements D, Renfro DP, Bhak D, Bhak J. Bolser DM, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(Database issue):D1250-4. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1099. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22139927 Free PMC article.
References
- TIGR. Brugia Malayi Genome Sequencing Project. 2005. [cited; Available from: http://www.tigr.org/tdb/e2k1/bma1/.
- BioMart. [cited; Available from: http://www.biomart.org/].
- Matera AG, Terns RM, Terns MP. Non-coding RNAs: lessons from the small nuclear and small nucleolar RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:209–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials