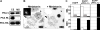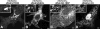Rab32 regulates melanosome transport in Xenopus melanophores by protein kinase a recruitment - PubMed (original) (raw)
Rab32 regulates melanosome transport in Xenopus melanophores by protein kinase a recruitment
Minjong Park et al. Curr Biol. 2007.
Abstract
Intracellular transport is essential for cytoplasm organization, but mechanisms regulating transport are mostly unknown. In Xenopus melanophores, melanosome transport is regulated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA). Melanosome aggregation is triggered by melatonin, whereas dispersion is induced by melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). The action of hormones is mediated by cAMP: High cAMP in MSH-treated cells stimulates PKA, whereas low cAMP in melatonin-treated cells inhibits it. PKA activity is typically restricted to specific cell compartments by A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs). Recently, Rab32 has been implicated in protein trafficking to melanosomes and shown to function as an AKAP on mitochondria. Here, we tested the hypothesis that Rab32 is involved in regulation of melanosome transport by PKA. We demonstrated that Rab32 is localized to the surface of melanosomes in a GTP-dependent manner and binds to the regulatory subunit RIIalpha of PKA. Both RIIalpha and Cbeta subunits of PKA are required for transport regulation and are recruited to melanosomes by Rab32. Overexpression of wild-type Rab32, but not mutants unable to bind PKA or melanosomes, inhibits melanosome aggregation by melatonin. Therefore, in melanophores, Rab32 is a melanosome-specific AKAP that is essential for regulation of melanosome transport.
Figures
Figure 1. PKA Cβ/RIIα Regulates Melanosome Transport
(A) PKA C and RIIα are localized to melanosomes. Xenopus melanophore extract (CE) and purified melanosome fraction (MS) were probed with antibodies against PKA subunit isoforms. PKA C and RIIα, but not RIα, are present in melanosome fraction. (B) PKA Cβ overexpression blocks melanosome aggregation by melatonin. The left panel is a bright-field image showing melanosome distribution before melatonin stimulation. The black arrow indicates a cell expressing EGFP-xPKA Cβ (inset) and the black arrowhead indicates a control cell. The right panel shows the distribution of melanosomes after 40 minutes of melatonin stimulation. EGFP-xPKA Cβ overexpression in a transfected cell (black arrow) completely blocks pigment aggregation. Bars, 10 μm. This figure represents two frames from Supplementary Movie 1. (C) Xenopus melanophores were transiently transfected with EGFP, EGFP-xPKA Cα, or EGFP-xPKA Cβ. Transfected cells were treated with melatonin or MSH and scored into three groups (aggregated, partially dispersed, and dispersed). In each experiment, aggregated, partially dispersed, and dispersed cells are shown as white, gray, and black bars, respectively. n=100 for each condition. The experiment was repeated three times.
Figure 2. Rab32 is Localized to Melanosomes
mCherry-_x_Rab32 is localized to melanosomes. Xenopus melanophores were transfected with mCherry-_x_Rab32 for 24 hr. The left panel shows the distribution of the mCherry-_x_Rab32 fusion protein, the middle panel shows in bright-field distribution of melanosomes, and the right panel shows the bright field image merged with the distribution of mCherry-_x_Rab32 fusion proteins. Melanosomes are decorated with mCherry-_x_Rab32 (right panel inset), indicating that the mCherry-_x_Rab32 fusion protein is localized to melanosomes. Bars, 5 μm.
Figure 3. Localization of _x_Rab32 mutants
Xenopus melanophores were transfected with mCherry-_x_Rab32T36N (mimicking the GDP-bound state of the protein) (A), mCherry-_x_Rab32Q82L (mimicking the GTP-bound state of the protein) (B), mCherry-_x_Rab32L186P (a mutant defective in PKA binding) (C), and mCherry-_x_Rab32ΔCC (lacking C-terminal cysteines) (D) for 24 hr. mCherry-_x_Rab32Q82L and mCherry-_x_Rab32L186P are localized to melanosomes (B and C insets, respectively), whereas, mCherry-_x_Rab32T36N and mCherry-_x_Rab32ΔCC are not (A and D inset, respectively). Bars, 5 μm in main images and 1 μm in insets.
Figure 4. Xenopus Rab32 is an A-Kinase Anchoring Protein
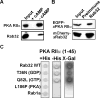
(A) PKA RIIα binds Xenopus Rab32. Xenopus melanophore extracts were incubated with cAMP-agarose resin in the presence of 75 mM cAMP (+ cAMP) or in the absence cAMP (- cAMP). cAMP-agarose resin was washed and eluted with 75mM cAMP. The Western blot was performed using PKA RIIα and _x_Rab32 antibodies. The cAMP agarose resin binds RIIα and also pulls down _x_Rab32. This interaction is abolished in the presence of 75 mM cAMP. (B) Rab32 binds to PKA RIIα in vivo. Extracts from cells coexpressing EGFP-_x_PKA RIIα and mCherry-_x_Rab32 were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Rab32 antibody or preimmune IgG. Precipitates were probed using anti-PKA RIIα antibody or anti-Rab32 and developed using HRP-protein A. Note that Rab32 antibody but not the preimmune IgG pulls down PKA RIIα. Inputs are 5% of cell extracts from sample. (C) Two-hybrid analysis of Rab32-RIIα binding. _x_Rab32 bait constructs (lacking C-terminal cysteins to prevent membrane binding) were tested against the indicated prey constructs in the yeast two-hybrid system for the ability to grow on minimal media in the presence (+His), or absence (-His) of histidine. The Rab32- PKA RIIα interaction was also tested with high-stringency (SD/-Trp/-Leu/-His/-Ade/X-α-Gal) plates. Growth on minimal media in the absence of histidine or α-galactosidase activity represents a positive interaction.
Figure 5. _x_Rab32 is Involved in Regulation of Melanosome Transport
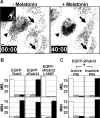
(A) _x_Rab32 blocks melanosome aggregation by melatonin. The left panel is a bright-field image showing melanosome distribution before melatonin stimulation. The black arrows indicate EGFP-_x_Rab32 transfected cells (inset) and the black arrowhead indicates a control cell. The right panel shows the distribution of melanosomes after 40 minutes of melatonin stimulation. EGFP-_x_Rab32 overexpression in transfected cells (black arrows) completely blocks pigment aggregation by melatonin. Bars, 10 μm. This figure represents frames from Supplementary Movie 3. (B) Recruitment of PKA by _x_Rab32 to melanosomes is essential for inhibition. Xenopus melanophores were transiently transfected with EGFP-Rab9, EGFP-_x_Rab32, or EGFP _x_Rab32L186P. Transfected cells were treated with melatonin or MSH and scored into three groups (aggregated, partially dispersed, and dispersed). In each experiment, aggregated, partially dispersed, and dispersed cells are shown as white, gray, and black bars, respectively. n=100 for each condition. The experiment was repeated three times. (C) _x_Rab32 regulates melanosome movement upstream of PKA. Xenopus melanophores were cotransfected with EGFP-_x_Rab32 and constructs pNP210 or pNP211 encoding HA-epitope tagged active or inactive PKA inhibitor, PKI, respectively. Transfected cells were treated with melatonin or MSH, fixed, immunostained for HA and scored into three groups (aggregated, partially dispersed, and dispersed). In each experiment, aggregated, partially dispersed, and dispersed cells are shown as white, gray, and black bars, respectively. n=100 for each condition. The experiment was repeated three times.
Similar articles
- Regulation of bidirectional melanosome transport by organelle bound MAP kinase.
Deacon SW, Nascimento A, Serpinskaya AS, Gelfand VI. Deacon SW, et al. Curr Biol. 2005 Mar 8;15(5):459-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.12.074. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15753041 - Light modulates the melanophore response to alpha-MSH in Xenopus laevis: an analysis of the signal transduction crosstalk mechanisms involved.
Isoldi MC, Provencio I, Castrucci AM. Isoldi MC, et al. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2010 Jan 1;165(1):104-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2009.06.014. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 19539625 - Acoustic detection of melanosome transport in Xenopus laevis melanophores.
Frost R, Norström E, Bodin L, Langhammer C, Sturve J, Wallin M, Svedhem S. Frost R, et al. Anal Biochem. 2013 Apr 1;435(1):10-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2012.12.004. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Anal Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23262280 - Melatonin, melatonin receptors and melanophores: a moving story.
Sugden D, Davidson K, Hough KA, Teh MT. Sugden D, et al. Pigment Cell Res. 2004 Oct;17(5):454-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.2004.00185.x. Pigment Cell Res. 2004. PMID: 15357831 Review. - Cell type-specific Rab32 and Rab38 cooperate with the ubiquitous lysosome biogenesis machinery to synthesize specialized lysosome-related organelles.
Bultema JJ, Di Pietro SM. Bultema JJ, et al. Small GTPases. 2013 Jan-Mar;4(1):16-21. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.22349. Epub 2012 Dec 17. Small GTPases. 2013. PMID: 23247405 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- VARP is recruited on to endosomes by direct interaction with retromer, where together they function in export to the cell surface.
Hesketh GG, Pérez-Dorado I, Jackson LP, Wartosch L, Schäfer IB, Gray SR, McCoy AJ, Zeldin OB, Garman EF, Harbour ME, Evans PR, Seaman MNJ, Luzio JP, Owen DJ. Hesketh GG, et al. Dev Cell. 2014 Jun 9;29(5):591-606. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.04.010. Epub 2014 May 22. Dev Cell. 2014. PMID: 24856514 Free PMC article. - Asymmetric organelle positioning during epithelial polarization of C. elegans intestinal cells.
Brandt JN, Voss L, Rambo FM, Nicholson K, Thein JR, Fairchild L, Seabrook L, Lewis D, Guevara-Hernandez L, White ML, Sax L, Eichten V, Harper L, Hermann GJ. Brandt JN, et al. Dev Biol. 2022 Jan;481:75-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2021.09.007. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 34597675 Free PMC article. - Notochord vacuoles are lysosome-related organelles that function in axis and spine morphogenesis.
Ellis K, Bagwell J, Bagnat M. Ellis K, et al. J Cell Biol. 2013 Mar 4;200(5):667-79. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201212095. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23460678 Free PMC article. - Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology.
Hutagalung AH, Novick PJ. Hutagalung AH, et al. Physiol Rev. 2011 Jan;91(1):119-49. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00059.2009. Physiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21248164 Free PMC article. Review. - A-kinase anchoring proteins: from protein complexes to physiology and disease.
Carnegie GK, Means CK, Scott JD. Carnegie GK, et al. IUBMB Life. 2009 Apr;61(4):394-406. doi: 10.1002/iub.168. IUBMB Life. 2009. PMID: 19319965 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Daniolos A, Lerner AB, Lerner MR. Action of light on frog pigment cells in culture. Pigment cell research. 1990;3:38–43. sponsored by the European Society for Pigment Cell Research and the International Pigment Cell Society. - PubMed
- Wong W, Scott JD. AKAP signalling complexes: focal points in space and time. Nature reviews. 2004;5:959–970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources