'Classical' but not 'other' mutations of EGFR kinase domain are associated with clinical outcome in gefitinib-treated patients with non-small cell lung cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
'Classical' but not 'other' mutations of EGFR kinase domain are associated with clinical outcome in gefitinib-treated patients with non-small cell lung cancer
A G Pallis et al. Br J Cancer. 2007.
Abstract
'Classical' mutations in the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain (exons 18, 19 and 21) have been associated with sensitivity to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in patients with NSCLC. The aim of the current study was to evaluate whether other than the classical G719X, DEL19 and L858R mutations of EGFR confer sensitivity to TKIs. Genomic DNA was extracted from microdissected formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumour tissue from 86 patients treated with gefitinib. Exons 18, 19 and 21 were amplified and subjected to direct sequencing. Eleven (13%) patients harboured the classical exon's 18, 19 and 21 mutations, while 14 (16%) had 'other' variants. There was a significantly higher percentage of 'never-smoker' patients with 'classical' EGFR mutations (P=0.002). Among patients with 'classical' mutations 3 patients achieved PR and 7 SD, while in the 'other' mutations group 10 patients had SD as best response. In the wild-type group, there were 3 patients with PR and 25 with SD. Median TTP was 16, 64 (P=0.002) and 21 weeks and median survival was 36, 78 and 67 weeks for patients with wild-type, 'classical' and 'other' EGFR mutations, respectively. The clinical relevance of 'other' EGFR mutation variants remains uncertain and requires further assessment in a prospective study.
Figures
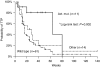
Figure 1
Kaplan–Meier curve of time to tumour progression (TTP) of wild-type EGFR patients group, ‘classical’ and ‘other’ mutations group. *_P_-value between ‘classical’ and wild type.
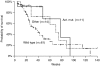
Figure 2
Kaplan–Meier survival curve of wild-type EGFR patients group, ‘classical’ and ‘other’ mutations group.
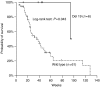
Figure 3
Kaplan–Meier survival curve of patients with the ‘classical’ DEL19 mutation and wild-type EGFR.
Similar articles
- Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in plasma DNA samples predict tumor response in Chinese patients with stages IIIB to IV non-small-cell lung cancer.
Bai H, Mao L, Wang HS, Zhao J, Yang L, An TT, Wang X, Duan CJ, Wu NM, Guo ZQ, Liu YX, Liu HN, Wang YY, Wang J. Bai H, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2009 Jun 1;27(16):2653-9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.3930. Epub 2009 May 4. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19414683 Clinical Trial. - Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in a series of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients and response rate to EGFR-specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
Martínez-Navarro EM, Rebollo J, González-Manzano R, Sureda M, Evgenyeva E, Valenzuela B, Fernández FJ, Forteza J, Brugarolas A. Martínez-Navarro EM, et al. Clin Transl Oncol. 2011 Nov;13(11):812-8. doi: 10.1007/s12094-011-0739-1. Clin Transl Oncol. 2011. PMID: 22082647 - Relative abundance of EGFR mutations predicts benefit from gefitinib treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.
Zhou Q, Zhang XC, Chen ZH, Yin XL, Yang JJ, Xu CR, Yan HH, Chen HJ, Su J, Zhong WZ, Yang XN, An SJ, Wang BC, Huang YS, Wang Z, Wu YL. Zhou Q, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2011 Aug 20;29(24):3316-21. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.3757. Epub 2011 Jul 25. J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21788562 - A comprehensive review of uncommon EGFR mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
Tu HY, Ke EE, Yang JJ, Sun YL, Yan HH, Zheng MY, Bai XY, Wang Z, Su J, Chen ZH, Zhang XC, Dong ZY, Wu SP, Jiang BY, Chen HJ, Wang BC, Xu CR, Zhou Q, Mei P, Luo DL, Zhong WZ, Yang XN, Wu YL. Tu HY, et al. Lung Cancer. 2017 Dec;114:96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29173773 Review. - [Afatinib as first-line therapy in mutation-positive EGFR. Results by type of mutation].
Vidal ÓJ. Vidal ÓJ. Med Clin (Barc). 2016 Apr;146 Suppl 1:12-8. doi: 10.1016/S0025-7753(16)30258-5. Med Clin (Barc). 2016. PMID: 27426243 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
- Clinicopathologic and molecular features of epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation and c-MET amplification in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant Chinese non-small cell lung cancer.
Chen HJ, Mok TS, Chen ZH, Guo AL, Zhang XC, Su J, Wu YL. Chen HJ, et al. Pathol Oncol Res. 2009 Dec;15(4):651-8. doi: 10.1007/s12253-009-9167-8. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Pathol Oncol Res. 2009. PMID: 19381876 - Efficacy of gefitinib for non-adenocarcinoma non-small-cell lung cancer patients harboring epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: a pooled analysis of published reports.
Shukuya T, Takahashi T, Kaira R, Ono A, Nakamura Y, Tsuya A, Kenmotsu H, Naito T, Kaira K, Murakami H, Endo M, Takahashi K, Yamamoto N. Shukuya T, et al. Cancer Sci. 2011 May;102(5):1032-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01887.x. Epub 2011 Feb 28. Cancer Sci. 2011. PMID: 21272159 Free PMC article. - HER family kinase domain mutations promote tumor progression and can predict response to treatment in human breast cancer.
Boulbes DR, Arold ST, Chauhan GB, Blachno KV, Deng N, Chang WC, Jin Q, Huang TH, Hsu JM, Brady SW, Bartholomeusz C, Ladbury JE, Stone S, Yu D, Hung MC, Esteva FJ. Boulbes DR, et al. Mol Oncol. 2015 Mar;9(3):586-600. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2014.10.011. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Mol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25435280 Free PMC article. - DNA-Mutation Inventory to Refine and Enhance Cancer Treatment (DIRECT): a catalog of clinically relevant cancer mutations to enable genome-directed anticancer therapy.
Yeh P, Chen H, Andrews J, Naser R, Pao W, Horn L. Yeh P, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Apr 1;19(7):1894-901. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1894. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23344264 Free PMC article. - Clinical outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations: pooled analysis.
Paz-Ares L, Soulières D, Melezínek I, Moecks J, Keil L, Mok T, Rosell R, Klughammer B. Paz-Ares L, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2010 Jan;14(1-2):51-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00991.x. Epub 2009 Dec 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20015198 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Altman GD (1991) Practical Statistics for Medical Research. London, UK: Chapman and Hall
- Argiris A, Mittal N, Masters G (2003) Gefitinib (ZD1839) as first line, compassionate use therapy in patients with advanced NSCLC. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22; Abstract 2729
- Bell DW, Lynch TJ, Haserlat SM, Harris PL, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Sgroi DC, Muir B, Riemenschneider MJ, Iacona RB, Krebs AD, Johnson DH, Giaccone G, Herbst RS, Manegold C, Fukuoka M, Kris MG, Baselga J, Ochs JS, Haber DA (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and gene amplification in non-small-cell lung cancer: molecular analysis of the IDEAL/INTACT gefitinib trials. J Clin Oncol 23: 8081–8092 - PubMed
- Calvo E, Baselga J (2006) Ethnic differences in response to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Clin Oncol 24: 2158–2163 - PubMed
- Carney DN (2002) Lung cancer – time to move on from chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 346: 126–128 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous