Th17 cells: effector T cells with inflammatory properties - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Th17 cells: effector T cells with inflammatory properties
Thomas Korn et al. Semin Immunol. 2007 Dec.
Abstract
Upon activation, naïve CD4(+) T cells differentiate into effector T cells with specific effector functions and cytokine profiles. The Th1/Th2 paradigm has recently been reevaluated to include a third population of T helper cells, producing IL-17 and designated Th17. The differentiation of Th17 cells requires the coordinate and specific action of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 and the immunosuppressive cytokine TGF-beta. In addition, the IL-12 family member IL-23 is involved in the maintenance of these cells. Analogous to other T helper cell subsets, Th17 commitment is initiated by sequential involvement of STAT molecules, i.e. STAT3 downstream of cytokine receptors, and specific transcription factors, i.e. ROR-gammat. Recent data also support the existence of a complex network of cytokines regulating Th17 cells. Clearly, the specific effector functions of Th17 cells expand beyond previously described effects of Th1 and Th2 immunity, with specific roles in host defense against certain pathogens and in organ-specific autoimmunity. The potential dynamics of Th17 cell populations and their interplay with other inflammatory cells in the induction of tissue inflammation in host defense and organ-specific autoimmunity are discussed.
Figures
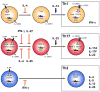
Figure 1. Differentiation and effector cytokines of T helper cell subsets
Th1, Th17, and Th2 cells constitute different T helper cell subsets with different cytokine signatures. The induction of the various T helper cell subsets requires different cytokine stimuli to induce distinct transcriptional programs. Other cytokines are necessary to stabilize the transcriptional phenotype (For details see text). Cross-inhibition of Th17 cell development by Th1 and Th2 associated cytokines has been shown in vitro and in vivo.
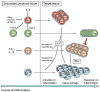
Figure 2. Development of tissue inflammation driven by Th17 cells
Antigen specific T cells are primed in secondary lymphoid tissue and driven into the Th17 developmental pathway in the presence of IL-6 and TGF-β. Sources of TGF-β are other T cells like Foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells (Treg) or Th3 cells. Similarly, antigen specific T cells are committed to the Th1 subset in the presence of IFN-γ and IL-12. Activated Th17 cells are among the first to infiltrate the target organ. By induction of chemokines, secondary waves of inflammatory cells like mononuclear cells and Th1 cells are attracted into the inflamed tissue. Both IL-17 produced by Th17 cells and IFN-γ produced by Th1 cells may act on myeloid cells to induce their effector functions that eventually lead to tissue damage. Whereas Th17 cells are prone to apoptosis, Th1 cells might finally be suppressed by T-reg cells that accumulate in the target organ and thus induce the resolution of inflammation.
Similar articles
- Targeting the development and effector functions of TH17 cells.
Ghilardi N, Ouyang W. Ghilardi N, et al. Semin Immunol. 2007 Dec;19(6):383-93. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.10.016. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Semin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18083530 Review. - Th17 cells: from precursors to players in inflammation and infection.
Awasthi A, Kuchroo VK. Awasthi A, et al. Int Immunol. 2009 May;21(5):489-98. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxp021. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Int Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19261692 Free PMC article. Review. - Interplay between effector Th17 and regulatory T cells.
Awasthi A, Murugaiyan G, Kuchroo VK. Awasthi A, et al. J Clin Immunol. 2008 Nov;28(6):660-70. doi: 10.1007/s10875-008-9239-7. Epub 2008 Sep 23. J Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18810613 - IL-17 and Th17 Cells.
Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. Korn T, et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:485-517. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132710. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19132915 Review. - Th17: the third member of the effector T cell trilogy.
Bettelli E, Korn T, Kuchroo VK. Bettelli E, et al. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Dec;19(6):652-7. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.07.020. Epub 2007 Sep 4. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17766098 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Altered immunoregulation in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of regulatory T cells and proinflammatory Th17 cells and therapeutic implications.
Alunno A, Manetti M, Caterbi S, Ibba-Manneschi L, Bistoni O, Bartoloni E, Valentini V, Terenzi R, Gerli R. Alunno A, et al. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:751793. doi: 10.1155/2015/751793. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 25918479 Free PMC article. Review. - The serum IL-6 profile and Treg/Th17 peripheral cell populations in patients with type 1 diabetes.
Ryba-Stanisławowska M, Skrzypkowska M, Myśliwska J, Myśliwiec M. Ryba-Stanisławowska M, et al. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:205284. doi: 10.1155/2013/205284. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23533301 Free PMC article. - Induction of Th17 cell differentiation by B-1 cells.
Wang Y, Rothstein TL. Wang Y, et al. Front Immunol. 2012 Sep 11;3:281. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00281. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22973276 Free PMC article. - Serum Interleukins as Potential Prognostic Biomarkers in HBV-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure.
Zhang L, Hu J, Gou C, Jin H, Zhang C, Liu Y, Wang Y, Wang X. Zhang L, et al. Mediators Inflamm. 2022 Sep 8;2022:7794890. doi: 10.1155/2022/7794890. eCollection 2022. Mediators Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 36117587 Free PMC article. Review. - The Relationship between Cancer and Paraoxonase 1.
Medina-Díaz IM, Ponce-Ruíz N, Rojas-García AE, Zambrano-Zargoza JF, Bernal-Hernández YY, González-Arias CA, Barrón-Vivanco BS, Herrera-Moreno JF. Medina-Díaz IM, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Mar 31;11(4):697. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040697. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453382 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–73. - PubMed
- Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996;383:787–93. - PubMed
- Cua DJ, Sherlock J, Chen Y, Murphy CA, Joyce B, Seymour B, Lucian L, To W, Kwan S, Churakova T, Zurawski S, Wiekowski M, Lira SA, Gorman D, Kastelein RA, Sedgwick JD. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature. 2003;421:744–8. - PubMed
- Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ, Locksley RM, Stockinger B. TGFbeta in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity. 2006;24:179–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous