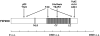FIP200, a key signaling node to coordinately regulate various cellular processes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
FIP200, a key signaling node to coordinately regulate various cellular processes
Boyi Gan et al. Cell Signal. 2008 May.
Abstract
A central question in cell biology is how various cellular processes are coordinately regulated in normal cell and how dysregulation of the normal signaling pathways leads to diseases such as cancer. Recent studies have identified FIP200 as a crucial signaling component to coordinately regulate different cellular events by its interaction with multiple signaling pathways. This review will focus on the cellular functions of FIP200 and its interacting proteins, as well as the emerging roles of FIP200 in embryogenesis and cancer development. Further understanding of FIP200 function might provide novel therapeutic targets for human diseases such as cancer.
Figures
Figure 1. Structural domains and binding proteins of FIP200
FIP200 consists of a putative nuclear localization signal (NLS) at N-terminus, a large coiled-coil (CC) domain and a leucine zipper (LZ) motif located at C-terminus. The proteins known to interact with specific regions of FIP200 are also shown.
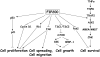
Figure 2. FIP200 signaling pathway
FIP200 functions to regulate diverse cellular processes, including cell proliferation, cell spreading, cell migration, cell growth and cell survival. FIP200 suppresses cell proliferation by regulation of p53-p21, Cyclin D1, Rb1 and FAK pathways; FIP200 negatively regulates cell spreading and migration by its inhibition of FAK function; FIP200 promotes mTOR activation and cell growth through its interaction with TSC1-TSC2 complex; FIP200 positively regulates cell survival by its inhibition of Pyk2 activity and regulation of TNFα-JNK signaling cascade (see text for details).
Similar articles
- Role of FIP200 in cardiac and liver development and its regulation of TNFalpha and TSC-mTOR signaling pathways.
Gan B, Peng X, Nagy T, Alcaraz A, Gu H, Guan JL. Gan B, et al. J Cell Biol. 2006 Oct 9;175(1):121-33. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200604129. Epub 2006 Oct 2. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17015619 Free PMC article. - Autophagy gene FIP200 in neural progenitors non-cell autonomously controls differentiation by regulating microglia.
Wang C, Yeo S, Haas MA, Guan JL. Wang C, et al. J Cell Biol. 2017 Aug 7;216(8):2581-2596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201609093. Epub 2017 Jun 20. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28634261 Free PMC article. - Inactivation of FIP200 leads to inflammatory skin disorder, but not tumorigenesis, in conditional knock-out mouse models.
Wei H, Gan B, Wu X, Guan JL. Wei H, et al. J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 27;284(9):6004-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806375200. Epub 2008 Dec 23. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19106106 Free PMC article. - The role of focal-adhesion kinase in cancer - a new therapeutic opportunity.
McLean GW, Carragher NO, Avizienyte E, Evans J, Brunton VG, Frame MC. McLean GW, et al. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005 Jul;5(7):505-15. doi: 10.1038/nrc1647. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16069815 Review. - Muscle fatigue: MK2 signaling and myofibroblast differentiation.
Hagood JS, Olman MA. Hagood JS, et al. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007 Nov;37(5):503-6. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0005ED. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17940320 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Does Huntingtin play a role in selective macroautophagy?
Steffan JS. Steffan JS. Cell Cycle. 2010 Sep 1;9(17):3401-13. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.17.12718. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20703094 Free PMC article. - Exploring the evolutionary relationship of insulin receptor substrate family using computational biology.
Chakraborty C, Agoramoorthy G, Hsu MJ. Chakraborty C, et al. PLoS One. 2011 Feb 25;6(2):e16580. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016580. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21364910 Free PMC article. - The ULK1 complex: sensing nutrient signals for autophagy activation.
Wong PM, Puente C, Ganley IG, Jiang X. Wong PM, et al. Autophagy. 2013 Feb 1;9(2):124-37. doi: 10.4161/auto.23323. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Autophagy. 2013. PMID: 23295650 Free PMC article. Review. - The incredible ULKs.
Alers S, Löffler AS, Wesselborg S, Stork B. Alers S, et al. Cell Commun Signal. 2012 Mar 13;10(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-10-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2012. PMID: 22413737 Free PMC article. - Autophagy signal transduction by ATG proteins: from hierarchies to networks.
Wesselborg S, Stork B. Wesselborg S, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Dec;72(24):4721-57. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2034-8. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26390974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Conlon I, Raff M. Cell. 1999;96(2):235–244. - PubMed
- Lauffenburger DA, Horwitz AF. Cell. 1996;84(3):359–369. - PubMed
- Chano T, Ikegawa S, Kontani K, Okabe H, Baldini N, Saeki Y. Oncogene. 2002;21(8):1295–1298. - PubMed
- Nagase T, Seki N, Ishikawa K, Ohira M, Kawarabayasi Y, Ohara O, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Miyajima N, Nomura N. DNA Res. 1996;3(5):321–329. 341–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources