Role of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor at glutamatergic synapses - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2008 Mar;153 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S310-24.
doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707509. Epub 2007 Dec 3.
Affiliations
- PMID: 18059328
- PMCID: PMC2268077
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707509
Review
Role of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor at glutamatergic synapses
A L Carvalho et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Mar.
Abstract
The neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) plays an important role in the activity-dependent regulation of synaptic structure and function, particularly of the glutamatergic synapses. BDNF may be released in the mature form, which activates preferentially TrkB receptors, or as proBDNF, which is coupled to the stimulation of the p75(NTR). In the mature form BDNF induces rapid effects on glutamate release, and may induce short- and long-term effects on the postsynaptic response to the neurotransmitter. BDNF may affect glutamate receptor activity by inducing the phosphorylation of the receptor subunits, which may also affect the interaction with intracellular proteins and, consequently, their recycling and localization to defined postsynaptic sites. Stimulation of the local protein synthesis and transcription activity account for the delayed effects of BDNF on glutamatergic synaptic strength. Several evidences show impaired synaptic plasticity of glutamatergic synapses in diseases where compromised BDNF function has been observed, such as Huntington's disease, depression, anxiety, and the BDNF polymorphism Val66Met, suggesting that upregulating BDNF-activated pathways may be therapeutically relevant. This review focuses on recent advances in the understanding of the regulation of the glutamatergic synapse by BDNF, and its implications in synaptic plasticity.
Figures
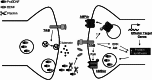
Figure 1
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) modulates glutamatergic synapses through pre- and postsynaptic targets. ProBDNF is secreted in an activity-regulated way, processed by extracellular proteases, such as plasmin, and acts on pre- and postsynaptic TrkB receptors. Presynaptically, BDNF regulates glutamate release, whereas the postsynaptic actions of BDNF include changes in glutamate receptor phosphorylation and synthesis, changes in gene expression and local alterations in protein synthesis. These effects of BDNF influence synaptic plasticity, and spine density and morphology.
Similar articles
- Altered balance of glutamatergic/GABAergic synaptic input and associated changes in dendrite morphology after BDNF expression in BDNF-deficient hippocampal neurons.
Singh B, Henneberger C, Betances D, Arevalo MA, Rodríguez-Tébar A, Meier JC, Grantyn R. Singh B, et al. J Neurosci. 2006 Jul 5;26(27):7189-200. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5474-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16822976 Free PMC article. - BDNF signaling in the formation, maturation and plasticity of glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses.
Gottmann K, Mittmann T, Lessmann V. Gottmann K, et al. Exp Brain Res. 2009 Dec;199(3-4):203-34. doi: 10.1007/s00221-009-1994-z. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Exp Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19777221 Review. - Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the functional elimination of synaptic contacts at polyinnervated neuromuscular synapses during development.
Garcia N, Santafe MM, Tomàs M, Lanuza MA, Besalduch N, Tomàs J. Garcia N, et al. J Neurosci Res. 2010 May 15;88(7):1406-19. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22320. J Neurosci Res. 2010. PMID: 20029969 - Neurotrophin-dependent modulation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the mammalian CNS.
Lessmann V. Lessmann V. Gen Pharmacol. 1998 Nov;31(5):667-74. doi: 10.1016/s0306-3623(98)00190-6. Gen Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9809461 Review. - BDNF and synaptic plasticity, cognitive function, and dysfunction.
Lu B, Nagappan G, Lu Y. Lu B, et al. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;220:223-50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-45106-5_9. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24668475 Review.
Cited by
- Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Gene Val66Met Polymorphism Is a Risk Factor for Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in a Turkish Sample.
Ozturk O, Basay BK, Buber A, Basay O, Alacam H, Bacanlı A, Yılmaz ŞG, Erdal ME, Herken H, Ercan ES. Ozturk O, et al. Psychiatry Investig. 2016 Sep;13(5):518-525. doi: 10.4306/pi.2016.13.5.518. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Psychiatry Investig. 2016. PMID: 27757130 Free PMC article. - Prefrontal cortical trkB, glucocorticoids, and their interactions in stress and developmental contexts.
Barfield ET, Gourley SL. Barfield ET, et al. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018 Dec;95:535-558. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.10.015. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018. PMID: 30477984 Free PMC article. Review. - Acute stress induces an aberrant increase of presynaptic release of glutamate and cellular activation in the hippocampus of BDNFVal/Met mice.
Musazzi L, Tornese P, Sala N, Lee FS, Popoli M, Ieraci A. Musazzi L, et al. J Cell Physiol. 2022 Oct;237(10):3834-3844. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30833. Epub 2022 Jul 31. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35908196 Free PMC article. - Neurotrophins induce nitric oxide generation in human pulmonary artery endothelial cells.
Meuchel LW, Thompson MA, Cassivi SD, Pabelick CM, Prakash YS. Meuchel LW, et al. Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Sep 1;91(4):668-76. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr107. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21498417 Free PMC article. - Ampakine pretreatment enables a single brief hypoxic episode to evoke phrenic motor facilitation.
Wollman LB, Streeter KA, Fuller DD. Wollman LB, et al. J Neurophysiol. 2020 Mar 1;123(3):993-1003. doi: 10.1152/jn.00708.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 15. J Neurophysiol. 2020. PMID: 31940229 Free PMC article.
References
- Aakalu G, Smith WB, Nguyen N, Jiang C, Schuman EM. Dynamic visualization of local protein synthesis in hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 2001;30:489–502. - PubMed
- Abidin I, Kohler T, Weiler E, Zoidl G, Eysel UT, Lessmann V, et al. Reduced presynaptic efficiency of excitatory synaptic transmission impairs LTP in the visual cortex of BDNF-heterozygous mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;24:3519–3531. - PubMed
- Almeida RD, Manadas BJ, Melo CV, Gomes JR, Mendes CS, Graos MM, et al. Neuroprotection by BDNF against glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death is mediated by ERK and PI3-kinase pathways. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12:1329–1343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials