IL-6 involvement in epithelial cancers - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comment
IL-6 involvement in epithelial cancers
Zachary T Schafer et al. J Clin Invest. 2007 Dec.
Abstract
In this issue of the JCI, two reports provide intriguing new information on the role of the inflammatory cytokine IL-6 in breast and lung cancer. The study by Sansone et al. implicates IL-6 in the instigation of malignant properties in breast cancer stem cells (see the related article beginning on page 3988). The study by Gao et al. identifies mutant variants of EGFR as inducers of IL-6 in lung adenocarcinomas (see the related article beginning on page 3846). These studies add to our understanding of potential roles for IL-6 in cancer and further motivate investigations of IL-6-targeted chemotherapeutics.
Figures
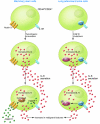
Figure 1. Models for role of IL-6 in breast and lung carcinomas.
In this issue of the JCI, Sansone et al. (6) show that the tumorigenic conversion of mammary stem cells (CD44hiCD24lo) results in an increase in IL-6 expression and secretion. IL-6 secretion results in a positive feedback loop causing further IL-6 upregulation and secretion. Once secreted, IL-6 can bind the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R), causing the upregulation of the Notch-3 ligand Jagged-1, which triggers the upregulation of CA-IX. While not depicted here, it should be noted that Jagged-1 is a transmembrane ligand. The result of these changes is the promotion of malignant features in these mammary stem cells. Also in this issue, Gao et al. (7) show that EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma cells cause an increase in IL-6 expression and secretion. This, in turn, promotes malignant features in these cells through the IL-6 receptor activation–mediated phosphorylation of STAT3.
Comment on
- Mutations in the EGFR kinase domain mediate STAT3 activation via IL-6 production in human lung adenocarcinomas.
Gao SP, Mark KG, Leslie K, Pao W, Motoi N, Gerald WL, Travis WD, Bornmann W, Veach D, Clarkson B, Bromberg JF. Gao SP, et al. J Clin Invest. 2007 Dec;117(12):3846-56. doi: 10.1172/JCI31871. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 18060032 Free PMC article. - IL-6 triggers malignant features in mammospheres from human ductal breast carcinoma and normal mammary gland.
Sansone P, Storci G, Tavolari S, Guarnieri T, Giovannini C, Taffurelli M, Ceccarelli C, Santini D, Paterini P, Marcu KB, Chieco P, Bonafè M. Sansone P, et al. J Clin Invest. 2007 Dec;117(12):3988-4002. doi: 10.1172/JCI32533. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 18060036 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- IL-6 triggers malignant features in mammospheres from human ductal breast carcinoma and normal mammary gland.
Sansone P, Storci G, Tavolari S, Guarnieri T, Giovannini C, Taffurelli M, Ceccarelli C, Santini D, Paterini P, Marcu KB, Chieco P, Bonafè M. Sansone P, et al. J Clin Invest. 2007 Dec;117(12):3988-4002. doi: 10.1172/JCI32533. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 18060036 Free PMC article. - Mutations in the EGFR kinase domain mediate STAT3 activation via IL-6 production in human lung adenocarcinomas.
Gao SP, Mark KG, Leslie K, Pao W, Motoi N, Gerald WL, Travis WD, Bornmann W, Veach D, Clarkson B, Bromberg JF. Gao SP, et al. J Clin Invest. 2007 Dec;117(12):3846-56. doi: 10.1172/JCI31871. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 18060032 Free PMC article. - A study on Notch signaling in human breast cancer.
Zang S, Ji Ch, Qu X, Dong X, Ma D, Ye J, Ma R, Dai J, Guo D. Zang S, et al. Neoplasma. 2007;54(4):304-10. Neoplasma. 2007. PMID: 17822320 - Blockade of Jagged/Notch pathway abrogates transforming growth factor β2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human retinal pigment epithelium cells.
Chen X, Xiao W, Liu X, Zeng M, Luo L, Wu M, Ye S, Liu Y. Chen X, et al. Curr Mol Med. 2014 May;14(4):523-34. doi: 10.2174/1566524014666140331230411. Curr Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24694299 Review. - Mammary Development and Breast Cancer: a Notch Perspective.
Chen W, Wei W, Yu L, Ye Z, Huang F, Zhang L, Hu S, Cai C. Chen W, et al. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2021 Sep;26(3):309-320. doi: 10.1007/s10911-021-09496-1. Epub 2021 Aug 10. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2021. PMID: 34374886 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Epithelial stem cells, wound healing and cancer.
Arwert EN, Hoste E, Watt FM. Arwert EN, et al. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 Feb 24;12(3):170-80. doi: 10.1038/nrc3217. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22362215 Review. - Cancer-driven changes link T cell frequency to muscle strength in people with cancer: a pilot study.
Narsale A, Moya R, Ma J, Anderson LJ, Wu D, Garcia JM, Davies JD. Narsale A, et al. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019 Aug;10(4):827-843. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12424. Epub 2019 Apr 12. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019. PMID: 30977974 Free PMC article. - Integrated epigenetics of human breast cancer: synoptic investigation of targeted genes, microRNAs and proteins upon demethylation treatment.
Radpour R, Barekati Z, Kohler C, Schumacher MM, Grussenmeyer T, Jenoe P, Hartmann N, Moes S, Letzkus M, Bitzer J, Lefkovits I, Staedtler F, Zhong XY. Radpour R, et al. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027355. Epub 2011 Nov 4. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22076154 Free PMC article. - Molecular pathogenesis of cholangiocarcinoma.
Rizvi S, Gores GJ. Rizvi S, et al. Dig Dis. 2014;32(5):564-9. doi: 10.1159/000360502. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Dig Dis. 2014. PMID: 25034289 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6: from basic science to medicine — 40 years in immunology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005;23:1–21. - PubMed
- Hodge D.R., Hurt E.M., Farrar W.L. The role of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur. J. Cancer. 2005;41:2502–2512. - PubMed
- Chiu J.J., Sgagias M.K., Cowan K.H. Interleukin 6 acts as a paracrine growth factor in human mammary carcinoma cell lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 1996;2:215–221. - PubMed
- Conze D., et al. Autocrine production of interleukin 6 causes multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61:8851–8858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous