A "class action" against the microenvironment: do cancer cells cooperate in metastasis? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
A "class action" against the microenvironment: do cancer cells cooperate in metastasis?
François-Clément Bidard et al. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008 Mar.
Abstract
The authors review how cancer cells may cooperate in metastasis by means of microenvironmental changes. The main mechanisms underlying this cooperation are clustered migration of cancer cells, extracellular matrix degradation, paracrine loops of released signaling factors and/or induction of adhesion molecules on stromal cells. Another critical factor could be temporal cooperation: successive waves of cancer cells may induce progressive conditioning of the microenvironment. The "class action" of cancer cells against the microenvironment involves successive steps of the metastatic process: invasion of the primary tumor microenvironment, collective migration through the extracellular matrix, blood vessel disruption, vascular or lymphatic tumor emboli, establishment of a premetastatic niche by secreted factors and endothelial precursor recruitment, induction of cell adhesion molecule expression in endothelial cells, extravasation, micrometastasis dormancy and establishment of a new growth in distant sites. As a result, after completion of the metastatic process, the series of microenvironmental changes from the primary tumor to the metastatic site may promote colonization of metastases by nonmetastatic cancer cells of the primary tumor.
Figures
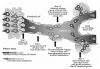
Figure 1. Premetastatic niche conditioning
Possible cooperations between successive waves of homogeneous or heterogeneous circulating cancer cells.
Similar articles
- The matrix environmental and cell mechanical properties regulate cell migration and contribute to the invasive phenotype of cancer cells.
Mierke CT. Mierke CT. Rep Prog Phys. 2019 Jun;82(6):064602. doi: 10.1088/1361-6633/ab1628. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Rep Prog Phys. 2019. PMID: 30947151 Review. - The Extracellular Matrix Modulates the Metastatic Journey.
Kai F, Drain AP, Weaver VM. Kai F, et al. Dev Cell. 2019 May 6;49(3):332-346. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.03.026. Dev Cell. 2019. PMID: 31063753 Free PMC article. Review. - Hypoxia-mediated metastasis.
Chang J, Erler J. Chang J, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;772:55-81. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5915-6_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24272354 Review. - Site-specific metastasis: A cooperation between cancer cells and the metastatic microenvironment.
Izraely S, Witz IP. Izraely S, et al. Int J Cancer. 2021 Mar 15;148(6):1308-1322. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33247. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Int J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 32761606 Free PMC article. Review. - Paget's "Seed and Soil" Theory of Cancer Metastasis: An Idea Whose Time has Come.
Akhtar M, Haider A, Rashid S, Al-Nabet ADMH. Akhtar M, et al. Adv Anat Pathol. 2019 Jan;26(1):69-74. doi: 10.1097/PAP.0000000000000219. Adv Anat Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30339548 Review.
Cited by
- CD44v6 dependence of premetastatic niche preparation by exosomes.
Jung T, Castellana D, Klingbeil P, Cuesta Hernández I, Vitacolonna M, Orlicky DJ, Roffler SR, Brodt P, Zöller M. Jung T, et al. Neoplasia. 2009 Oct;11(10):1093-105. doi: 10.1593/neo.09822. Neoplasia. 2009. PMID: 19794968 Free PMC article. - Nestin delineates pancreatic cancer stem cells in metastatic foci of NOD/Shi-scid IL2Rγ(null) (NOG) mice.
Matsuda Y, Yoshimura H, Ueda J, Naito Z, Korc M, Ishiwata T. Matsuda Y, et al. Am J Pathol. 2014 Mar;184(3):674-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.11.014. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Am J Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24412093 Free PMC article. - Propagating waves of directionality and coordination orchestrate collective cell migration.
Zaritsky A, Kaplan D, Hecht I, Natan S, Wolf L, Gov NS, Ben-Jacob E, Tsarfaty I. Zaritsky A, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Jul 24;10(7):e1003747. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003747. eCollection 2014 Jul. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 25058592 Free PMC article. - Role of the tissue microenvironment as a therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Rani B, Cao Y, Malfettone A, Tomuleasa C, Fabregat I, Giannelli G. Rani B, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr 21;20(15):4128-40. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4128. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24764651 Free PMC article. Review. - Evolutionary shift dynamics on a cycle.
Allen B, Nowak MA. Allen B, et al. J Theor Biol. 2012 Oct 21;311:28-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2012.07.006. Epub 2012 Jul 16. J Theor Biol. 2012. PMID: 22814475 Free PMC article.
References
- Hoon DS, Kitago M, Kim J, Mori T, Piris A, Szyfelbein K, Mihm MC, Nathanson SD, Padera TP, Chambers AF, Vantyghem SA, MacDonald IC, Shivers SC, Alsarraj M, Reintgen DS, Passlick B, Sienel W, Pantel K. Molecular mechanisms of metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006;25:203–220. - PubMed
- Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:563–572. - PubMed
- Steeg PS. Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 2006;12:895–904. - PubMed
- Fidler IJ. Critical determinants of metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2002;12:89–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials