Iterative model building, structure refinement and density modification with the PHENIX AutoBuild wizard - PubMed (original) (raw)
Iterative model building, structure refinement and density modification with the PHENIX AutoBuild wizard
Thomas C Terwilliger et al. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2008 Jan.
Abstract
The PHENIX AutoBuild wizard is a highly automated tool for iterative model building, structure refinement and density modification using RESOLVE model building, RESOLVE statistical density modification and phenix.refine structure refinement. Recent advances in the AutoBuild wizard and phenix.refine include automated detection and application of NCS from models as they are built, extensive model-completion algorithms and automated solvent-molecule picking. Model-completion algorithms in the AutoBuild wizard include loop building, crossovers between chains in different models of a structure and side-chain optimization. The AutoBuild wizard has been applied to a set of 48 structures at resolutions ranging from 1.1 to 3.2 A, resulting in a mean R factor of 0.24 and a mean free R factor of 0.29. The R factor of the final model is dependent on the quality of the starting electron density and is relatively independent of resolution.
Figures
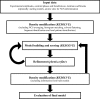
Figure 1
Outline of AutoBuild wizard operation beginning from experimental phase information.
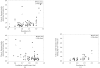
Figure 2
R factors (closed diamonds) and free R factors (open triangles) of final models obtained with the AutoBuild wizard for 48 structures from the PHENIX structure library beginning with experimental phases obtained with the AutoSol wizard. (a) R and free R factors as a function of resolution of the data used in modelling. (b) R and free R factors as a function of the correlation coefficient of the starting density-modified experimental map. (c) R factors as in (a), except that only structures with a correlation coefficient of the starting density-modified experimental map of greater than 0.85 are included.
Figure 3
Completeness of main-chain model (closed diamonds) and assignment of residues to sequence (open triangles) of final models in Fig. 2 ▶. (a) Completeness as a function of resolution of the data used in modelling. (b) Completeness as a function of the correlation coefficient of the starting density-modified experimental map to the model map. (c) Completeness as a function of resolution as in (a), except that only structures with a correlation coefficient of the starting density-modified experimental map of greater than 0.85 are included.
Figure 4
Main-chain (closed diamonds) and side-chain (open triangles) r.m.s.d. of final models in Fig. 2 ▶ compared with refined models previously obtained for the same structures. (a) R.m.s.d. as a function of resolution of the data used in modelling. (b) R.m.s.d. as a function of the correlation coefficient of the starting density-modified experimental map. (c) R.m.s.d. as in (a), except that only structures with a correlation coefficient of the starting density-modified experimental map of greater than 0.85 are included.
Similar articles
- Automated structure solution with the PHENIX suite.
Zwart PH, Afonine PV, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Hung LW, Ioerger TR, McCoy AJ, McKee E, Moriarty NW, Read RJ, Sacchettini JC, Sauter NK, Storoni LC, Terwilliger TC, Adams PD. Zwart PH, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;426:419-35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-058-8_28. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18542881 - Comparison of automated crystallographic model-building pipelines.
Alharbi E, Bond PS, Calinescu R, Cowtan K. Alharbi E, et al. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2019 Dec 1;75(Pt 12):1119-1128. doi: 10.1107/S2059798319014918. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2019. PMID: 31793905 - phenix.mr_rosetta: molecular replacement and model rebuilding with Phenix and Rosetta.
Terwilliger TC, Dimaio F, Read RJ, Baker D, Bunkóczi G, Adams PD, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Afonine PV, Echols N. Terwilliger TC, et al. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2012 Jun;13(2):81-90. doi: 10.1007/s10969-012-9129-3. Epub 2012 Mar 15. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22418934 Free PMC article. - Interactive model building in neutron macromolecular crystallography.
Logan DT. Logan DT. Methods Enzymol. 2020;634:201-224. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2019.11.017. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Methods Enzymol. 2020. PMID: 32093833 Review. - Advances, interactions, and future developments in the CNS, Phenix, and Rosetta structural biology software systems.
Adams PD, Baker D, Brunger AT, Das R, DiMaio F, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC. Adams PD, et al. Annu Rev Biophys. 2013;42:265-87. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-083012-130253. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Annu Rev Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23451892 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Neutralizing and interfering human antibodies define the structural and mechanistic basis for antigenic diversion.
Patel PN, Dickey TH, Hopp CS, Diouf A, Tang WK, Long CA, Miura K, Crompton PD, Tolia NH. Patel PN, et al. Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 6;13(1):5888. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33336-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36202833 Free PMC article. - Initiation of immune tolerance-controlled HIV gp41 neutralizing B cell lineages.
Zhang R, Verkoczy L, Wiehe K, Munir Alam S, Nicely NI, Santra S, Bradley T, Pemble CW 4th, Zhang J, Gao F, Montefiori DC, Bouton-Verville H, Kelsoe G, Larimore K, Greenberg PD, Parks R, Foulger A, Peel JN, Luo K, Lu X, Trama AM, Vandergrift N, Tomaras GD, Kepler TB, Moody MA, Liao HX, Haynes BF. Zhang R, et al. Sci Transl Med. 2016 Apr 27;8(336):336ra62. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf0618. Sci Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27122615 Free PMC article. - Comparative proteomics identifies the cell-associated lethality of M. tuberculosis RelBE-like toxin-antitoxin complexes.
Miallau L, Jain P, Arbing MA, Cascio D, Phan T, Ahn CJ, Chan S, Chernishof I, Maxson M, Chiang J, Jacobs WR Jr, Eisenberg DS. Miallau L, et al. Structure. 2013 Apr 2;21(4):627-37. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.02.008. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Structure. 2013. PMID: 23523424 Free PMC article. - A Crystallographic Examination of Predisposition versus Preorganization in de Novo Designed Metalloproteins.
Ruckthong L, Zastrow ML, Stuckey JA, Pecoraro VL. Ruckthong L, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2016 Sep 14;138(36):11979-88. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b07165. Epub 2016 Sep 2. J Am Chem Soc. 2016. PMID: 27532255 Free PMC article. - Expression, purification and preliminary structural analysis of the head domain of Deinococcus radiodurans RecN.
Pellegrino S, Radzimanowski J, McSweeney S, Timmins J. Pellegrino S, et al. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012 Jan 1;68(Pt 1):81-4. doi: 10.1107/S1744309111048743. Epub 2011 Dec 24. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012. PMID: 22232179 Free PMC article.
References
- Adams, P. D., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., Hung, L.-W., Ioerger, T. R., McCoy, A. J., Moriarty, N. W., Read, R. J., Sacchettini, J. C., Sauter, N. K. & Terwilliger, T. C. (2002). Acta Cryst. D58, 1948–1954. - PubMed
- Afonine, P. V., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W. & Adams, P. D. (2005b). CCP4 Newsl.42, contribution 8.
- Branden, C. I. & Jones, T. A. (1990). Nature (London), 343, 687–689.
- Chaudhuri, B. N., Kleywegt, G. J., Björkman, J., Lehman-McKeeman, L. D., Oliver, J. D. & Jones, T. A. (1999). Acta Cryst. D55, 753–762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P01 GM063210/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM063210-090002/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1P01 GM063210/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources