Myosin phosphatase target subunit: Many roles in cell function - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Myosin phosphatase target subunit: Many roles in cell function
Fumio Matsumura et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008.
Abstract
Phosphorylation of myosin II is important in many aspects of cell function and involves a myosin kinase, e.g. myosin light chain kinase, and a myosin phosphatase (MP). MP is regulated by the myosin phosphatase target subunit (MYPT1). The domain structure, properties, and genetic analyses of MYPT1 and its isoforms are outlined. MYPT1 binds the catalytic subunit of type 1 phosphatase, delta isoform, and also acts as an interactive platform for many other proteins. A key reaction for MP is with phosphorylated myosin II and the first process shown to be regulated by MP was contractile activity of smooth muscle. In cell division and cell migration myosin II phosphorylation also plays a critical role and these are discussed. However, based on the wide range of partners for MYPT1 it is likely that MP is implicated with substrates other than myosin II. Open questions are whether the diverse functions of MP reflect different cellular locations and/or specific roles for the MYPT1 isoforms.
Figures
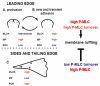
Fig. 1
Model for the roles of MP and MLCK at the leading edge during protrusion (A) or retraction and adhesion (B) and along the side and trailing edge (C). For details see text.
Similar articles
- Myosin phosphatase targeting subunit 1 affects cell migration by regulating myosin phosphorylation and actin assembly.
Xia D, Stull JT, Kamm KE. Xia D, et al. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Apr 1;304(2):506-17. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.11.025. Epub 2004 Dec 30. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15748895 - Myosin phosphatase: structure, regulation and function.
Ito M, Nakano T, Erdodi F, Hartshorne DJ. Ito M, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004 Apr;259(1-2):197-209. doi: 10.1023/b:mcbi.0000021373.14288.00. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15124925 Review. - Regulation of Smooth Muscle Myosin Light Chain Phosphatase by Multisite Phosphorylation of the Myosin Targeting Subunit, MYPT1.
MacDonald JA, Walsh MP. MacDonald JA, et al. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2018;18(1):4-13. doi: 10.2174/1871529X18666180326120638. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 29577868 Review. - Phosphorylation of the myosin phosphatase target subunit by integrin-linked kinase.
Murányi A, MacDonald JA, Deng JT, Wilson DP, Haystead TA, Walsh MP, Erdodi F, Kiss E, Wu Y, Hartshorne DJ. Murányi A, et al. Biochem J. 2002 Aug 15;366(Pt 1):211-6. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020401. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12030846 Free PMC article. - Okadaic acid induces phosphorylation and translocation of myosin phosphatase target subunit 1 influencing myosin phosphorylation, stress fiber assembly and cell migration in HepG2 cells.
Lontay B, Kiss A, Gergely P, Hartshorne DJ, Erdodi F. Lontay B, et al. Cell Signal. 2005 Oct;17(10):1265-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.01.008. Epub 2005 Mar 3. Cell Signal. 2005. PMID: 16038801
Cited by
- Constitutive phosphorylation of cardiac myosin regulatory light chain in vivo.
Chang AN, Battiprolu PK, Cowley PM, Chen G, Gerard RD, Pinto JR, Hill JA, Baker AJ, Kamm KE, Stull JT. Chang AN, et al. J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 24;290(17):10703-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.642165. Epub 2015 Mar 2. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25733667 Free PMC article. - The dominant protein phosphatase PP1c isoform in smooth muscle cells, PP1cβ, is essential for smooth muscle contraction.
Chang AN, Gao N, Liu Z, Huang J, Nairn AC, Kamm KE, Stull JT. Chang AN, et al. J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 26;293(43):16677-16686. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003083. Epub 2018 Sep 5. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30185619 Free PMC article. - Endothelial cell rearrangements during vascular patterning require PI3-kinase-mediated inhibition of actomyosin contractility.
Angulo-Urarte A, Casado P, Castillo SD, Kobialka P, Kotini MP, Figueiredo AM, Castel P, Rajeeve V, Milà-Guasch M, Millan J, Wiesner C, Serra H, Muixi L, Casanovas O, Viñals F, Affolter M, Gerhardt H, Huveneers S, Belting HG, Cutillas PR, Graupera M. Angulo-Urarte A, et al. Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 16;9(1):4826. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07172-3. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30446640 Free PMC article. - SARS-CoV-2 replication in airway epithelia requires motile cilia and microvillar reprogramming.
Wu CT, Lidsky PV, Xiao Y, Cheng R, Lee IT, Nakayama T, Jiang S, He W, Demeter J, Knight MG, Turn RE, Rojas-Hernandez LS, Ye C, Chiem K, Shon J, Martinez-Sobrido L, Bertozzi CR, Nolan GP, Nayak JV, Milla C, Andino R, Jackson PK. Wu CT, et al. Cell. 2023 Jan 5;186(1):112-130.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.11.030. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Cell. 2023. PMID: 36580912 Free PMC article. - Dual efficacy of Fasudil at improvement of survival and reinnervation of flap through RhoA/ROCK/PI3K/Akt pathway.
Wang H, Fang F, Chen S, Jing X, Zhuang Y, Xie Y. Wang H, et al. Int Wound J. 2022 Dec;19(8):2000-2011. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13800. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Int Wound J. 2022. PMID: 35315211 Free PMC article.
References
- Hartshorne DJ, Ito M, Erdodi F. Role of protein phosphatase type 1 in contractile functions: myosin phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:37211–37214. - PubMed
- Dirksen WP, Vladic F, Fisher SA. A myosin phosphatase targeting subunit isoform transition defines a smooth muscle developmental phenotypic switch. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2000;278:C589–C600. - PubMed
- Payne MC, Zhang H-Y, Prosdocimo T, Joyce KM, Koga Y, Ikebe M, Fisher SA. Myosin phosphatase isoform switching in vascular smooth muscle development. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2006;40:274–282. - PubMed
- Wu Y, Muranyi A, Erdodi F, Hartshorne DJ. Localization of myosin phosphatase target subunit and its mutants. J. Mus. Res. Cell Motil. 2005;26:123–134. - PubMed
- Toth A, Kiss E, Herberg FW, Hartshorne DJ, Erdodi F. Study of the subunit interactions in myosin phosphatase by surface plasmon resonance. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000;267:1687–1697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA042742-23/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL023615-29/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA042742/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA042742/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL023615/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 23615/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 42742/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources