Critical role of lipid raft redox signaling platforms in endostatin-induced coronary endothelial dysfunction - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Critical role of lipid raft redox signaling platforms in endostatin-induced coronary endothelial dysfunction
Si Jin et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008 Mar.
Abstract
Objective: Endostatin (EST) was found to initiate a redox signaling cascade associated with activation of NADPH oxidase in endothelial cells (ECs). The present study tested whether EST stimulates clustering of ceramide-enriched lipid rafts (LRs), which assembles and activates NADPH oxidase to form redox signaling platforms.
Methods and results: Using confocal microscopy, we first demonstrated a colocalization of LR clusters with NADPH oxidase subunits, gp91(phox) and p47(phox) in the ECs membrane on EST stimulation. Immunoblot analysis of floated detergent-resistant membrane fractions found that in LR fractions NADPH oxidase subunits gp91(phox) and p47(phox) are enriched and that the activity of this enzyme increased dramatically, as measured by electron spin resonance (ESR) spectrometry. This EST-increased LR platform formation was shown to be attenuated by inhibition or RNA interference of acid sphingomyelinase (A-SMase). Functionally, EST pretreatment significantly impaired bradykinin or A23187-induced vasodilation in isolated small coronary arteries, which could be partially reversed by LR disruptors.
Conclusions: The early injury effect of EST on the vascular endothelium is associated with the formation of redox signaling platforms via lipid raft clustering.
Figures
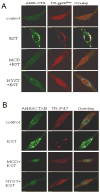
Figure 1. Representative confocal images of LR clusters (Alexa488-CTX) and gp91_phox_(A), P_47phox_(B) labeling (Texas red-conjugated)
The overlay images exhibited yellow spots or patches (right), which represented co-localization of gp91_phox_ or P47_phox_ and LR component, ganglioside GM1.2. The figure presents representative images from experiments done using 6 batches of ECs cultures.
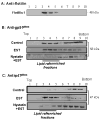
Figure 2. Distribution and localization of gp91phox and p47phox in floated membrane fractions from ECs
A: using LR marker protein flotillin-1, B: using anti-gp91phox, and C: using anti-p47_phox_ (all were representative gels from 4 separated experiments).
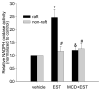
Figure 3. Effects of LRs disruption on EST-induced increase of NADPH oxidase activity in LR-enriched fractions and non-LR fractions
*P < 0.05 vs. vehicle; & p<0.05 vs. EST; # P<0.05 vs. vehicle; n=6.
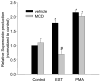
Figure 4. Effects of LRs disruption on EST-induced O2.− production in CAECs
Summarized data depicting changes in O2.− production in CAECs with different treatments. * indicates P<0.05 vs. control; # indicates P<0.05 vs. EST group; n = 5.
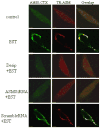
Figure 5. Confocal microscopic analysis of A-SMase in LR clusters in ECs stimulated with EST
Texas-red conjugated anti-A-SMase in the left and LRs markers (Al488-CTX in the middle) were used to stain cells. Desip = desipramine; A-SMase siRNA was A-SMase siRNA transfection. The images are representatives from 6 separated experiments.
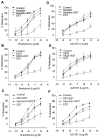
Figure 6. Effects of LR disruptors on EST-induced impairment of the vasodilator responses
A: Nyst, responses to BK; D: Nyst, responses to A23187. B: MCD, responses to BK; E: MCD, responses to A23187. C: DPI, apocynin, responses to BK; F: DPI, apocynin, responses to A23187. n=7 or 6, *P<0.05 vs. control.
Similar articles
- Lipid raft redox signaling platforms in vascular dysfunction: features and mechanisms.
Jin S, Zhou F. Jin S, et al. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2009 May;11(3):220-6. doi: 10.1007/s11883-009-0034-6. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2009. PMID: 19361354 Review. - Acid sphingomyelinase and its redox amplification in formation of lipid raft redox signaling platforms in endothelial cells.
Zhang AY, Yi F, Jin S, Xia M, Chen QZ, Gulbins E, Li PL. Zhang AY, et al. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007 Jul;9(7):817-28. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1509. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007. PMID: 17508908 - Lipid raft clustering and redox signaling platform formation in coronary arterial endothelial cells.
Zhang AY, Yi F, Zhang G, Gulbins E, Li PL. Zhang AY, et al. Hypertension. 2006 Jan;47(1):74-80. doi: 10.1161/10.1161/01.HYP.0000196727.53300.62. Epub 2005 Dec 12. Hypertension. 2006. PMID: 16344372 - Formation of lipid raft redox signalling platforms in glomerular endothelial cells: an early event of homocysteine-induced glomerular injury.
Yi F, Jin S, Zhang F, Xia M, Bao JX, Hu J, Poklis JL, Li PL. Yi F, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Sep;13(9B):3303-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00743.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 20196779 Free PMC article. - Lipid raft redox signaling platforms in endothelial dysfunction.
Li PL, Zhang Y, Yi F. Li PL, et al. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007 Sep;9(9):1457-70. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1667. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007. PMID: 17661535 Review.
Cited by
- Attenuation by statins of membrane raft-redox signaling in coronary arterial endothelium.
Wei YM, Li X, Xiong J, Abais JM, Xia M, Boini KM, Zhang Y, Li PL. Wei YM, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 May;345(2):170-9. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.201442. Epub 2013 Feb 22. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013. PMID: 23435541 Free PMC article. - Sildenafil Protects Endothelial Cells From Radiation-Induced Oxidative Stress.
Wortel RC, Mizrachi A, Li H, Markovsky E, Enyedi B, Jacobi J, Brodsky O, Cao J, Lippert AR, Incrocci L, Mulhall JP, Haimovitz-Friedman A. Wortel RC, et al. J Sex Med. 2019 Nov;16(11):1721-1733. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2019.08.015. Epub 2019 Oct 1. J Sex Med. 2019. PMID: 31585804 Free PMC article. - Lipid raft redox signaling platforms in vascular dysfunction: features and mechanisms.
Jin S, Zhou F. Jin S, et al. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2009 May;11(3):220-6. doi: 10.1007/s11883-009-0034-6. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2009. PMID: 19361354 Review. - Unraveling the Crosstalk between Lipids and NADPH Oxidases in Diabetic Kidney Disease.
Njeim R, Alkhansa S, Fornoni A. Njeim R, et al. Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 28;15(5):1360. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051360. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242602 Free PMC article. Review. - Collagen type XVIII alpha 1 chain (COL18A1) variants affect the risk of anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: A prospective study.
Cheng Y, Jiao L, Li W, Wang J, Lin Z, Lai H, Ying B. Cheng Y, et al. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Feb;35(2):e23630. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23630. Epub 2020 Dec 9. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 33296124 Free PMC article.
References
- OReilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR, Folkman J. Endostatin: An endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell. 1997;88:277–285. - PubMed
- Folkman J. Antiangiogenesis in cancer therapy - endostatin and its mechanisms of action. Experimental Cell Research. 2006;312:594–607. - PubMed
- Zhang AY, Teggatz EG, Zou AP, Campbell WB, Li PL. Endostatin uncouples NO and Ca2+ response to bradykinin through enhanced O-2(-center dot) production in the intact coronary endothelium. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2005;288:H686–H694. - PubMed
- Bollinger CR, Teichgraber V, Gulbins E. Ceramide-enriched membrane domains. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Molecular Cell Research. 2005;1746:284–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK54927/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054927-10/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL057244-12/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-75316/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075316/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL057244-11/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075316-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075316-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL057244/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054927-11/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R29 HL057244/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054927/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL-57244/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous