Foveolar choroidal circulation and choroidal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration - PubMed (original) (raw)
Foveolar choroidal circulation and choroidal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration
Tatyana I Metelitsina et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Jan.
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate in a longitudinal study whether foveolar choroidal blood flow changes are associated with the development of choroidal neovascularization (CNV) in AMD.
Methods: Relative foveolar choroidal blood velocity (ChBVel), volume (ChBVol), and flow (ChBFlow) were assessed in 135 patients with AMD, at baseline and then annually with laser Doppler flowmetry. All study eyes had visual acuity of 20/40 or better and no CNV at the time of enrollment. Comparison of foveolar choroidal circulatory measurements at baseline and their change before the development of CNV was made between eyes that had CNV and those that did not.
Results: CNV developed in 28 eyes during the study. Baseline average foveolar ChBVol and ChBFlow in these eyes were 24% (P < 0.0001) and 20% (P = 0.0007) lower than that observed in the 165 eyes in which CNV did not develop. In the eyes with CNV, foveolar ChBVol and ChBFlow decreased by 9.6% and 11.5% before the formation of CNV, whereas in the eyes that did not, they increased by 6.7% (P = 0.006) and 2.8% (P = 0.004), respectively. Eyes with lower baseline foveolar ChBFlow were more likely (risk ratio = 3.47, 95% CI: 1.24-8.70) to show visual loss of three or more lines than were eyes with a higher baseline ChBFlow (P = 0.005).
Conclusions: The development of CNV and visual loss are associated with lower choroidal circulatory parameters at baseline. In addition, the results suggest that decreases in the foveolar choroidal circulation precede the development of CNV in AMD and may play some role in its development.
Figures
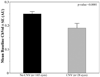
FIGURE 1
Comparison of baseline foveolar ChBVol between eyes with or without newly developing CNV. Results were shown in arbitrary units (AU). Error bar, SE. Student’s _t_-test showed a statistically significant difference between the two groups (P < 0.0001).
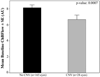
FIGURE 2
Comparison of baseline foveolar ChBFlow between eyes with and without newly developing CNV. Results are shown in arbitrary units (AU). Error bars, SE. Student’s _t_-test showed a statistically significant difference between the two groups (P = 0.0007).
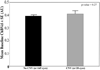
FIGURE 3
Comparison of baseline foveolar ChBVel between eyes with and without newly developing CNV. Results are shown in arbitrary units (AU). Error bars, SE. Student’s _t_-test showed a statistically significant difference between the two groups (P = 0.27).
FIGURE 4
Comparison of percentage of change in foveolar ChBFlow during two annual visits before CNV appeared in AMD eyes and yearly percentage of change in ChBFlow in eyes in which CNV it did not develop. Student’s _t_-test shows a statistically significant difference between the two groups (P = 0.004). Each box plot includes the upper extreme (whisker, excluding outliers indicated as circles outside the box), upper quartile (top portion of box), median (horizontal line in box), lower quartile (bottom portion of box), and lower extreme (whisker).
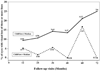
FIGURE 5
All eyes in the study were divided into two groups according to the baseline foveolar ChBFlow. One group included all eyes with ChBFlow below or equal to the median (n = 92 eyes) and the other group included all patients with ChBFlow above the median (n = 91 eyes). The graph shows for each follow-up visit a comparison of the percentage of eyes with loss of visual acuity of three or more lines between the eyes with baseline ChBFlow below (solid line) and above (dotted line) the median. The numerator represents the number of eyes with visual acuity loss of three or more lines, and the denominator represents the number of eyes that completed the specific follow-up visit. Patients with ChBFlow below or equal to the median were three times more likely to have three or more lines of visual acuity loss within the study follow-up.
Similar articles
- Reduced foveolar choroidal blood flow in eyes with increasing AMD severity.
Grunwald JE, Metelitsina TI, Dupont JC, Ying GS, Maguire MG. Grunwald JE, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Mar;46(3):1033-8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-1050. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15728562 - Association of risk factors for choroidal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration with decreased foveolar choroidal circulation.
Xu W, Grunwald JE, Metelitsina TI, DuPont JC, Ying GS, Martin ER, Dunaief JL, Brucker AJ. Xu W, et al. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010 Jul;150(1):40-47.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2010.01.041. Epub 2010 May 20. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 20493466 Free PMC article. - Foveolar choroidal blood flow in age-related macular degeneration.
Grunwald JE, Hariprasad SM, DuPont J, Maguire MG, Fine SL, Brucker AJ, Maguire AM, Ho AC. Grunwald JE, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998 Feb;39(2):385-90. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998. PMID: 9477998 - Effect of systemic hypertension on foveolar choroidal blood flow in age related macular degeneration.
Metelitsina TI, Grunwald JE, DuPont JC, Ying GS. Metelitsina TI, et al. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006 Mar;90(3):342-6. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2005.082974. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006. PMID: 16488959 Free PMC article. - Choroidal blood flow and progression of age-related macular degeneration in the fellow eye in patients with unilateral choroidal neovascularization.
Boltz A, Luksch A, Wimpissinger B, Maar N, Weigert G, Frantal S, Brannath W, Garhöfer G, Ergun E, Stur M, Schmetterer L. Boltz A, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Aug;51(8):4220-5. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4968. Epub 2010 May 19. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20484590
Cited by
- Alterations of choroidal blood flow regulation in young healthy subjects with complement factor H polymorphism.
Told R, Palkovits S, Haslacher H, Frantal S, Schmidl D, Boltz A, Lasta M, Kaya S, Werkmeister RM, Garhöfer G, Schmetterer L. Told R, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 15;8(4):e60424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060424. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23596508 Free PMC article. - Endoplasmic reticulum stress in age-related macular degeneration: trigger for neovascularization.
Salminen A, Kauppinen A, Hyttinen JM, Toropainen E, Kaarniranta K. Salminen A, et al. Mol Med. 2010 Nov-Dec;16(11-12):535-42. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00070. Epub 2010 Jul 27. Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20683548 Free PMC article. Review. - Quantitative analysis of choriocapillaris in non-human primates using swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography (SS-OCTA).
Tan B, Chua J, Barathi VA, Baskaran M, Chan A, Lin E, Ang M, Klose G, Schmetterer L. Tan B, et al. Biomed Opt Express. 2018 Dec 21;10(1):356-371. doi: 10.1364/BOE.10.000356. eCollection 2019 Jan 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2018. PMID: 30775105 Free PMC article. - The association between drusen extent and foveolar choroidal blood flow in age-related macular degeneration.
Berenberg TL, Metelitsina TI, Madow B, Dai Y, Ying GS, Dupont JC, Grunwald L, Brucker AJ, Grunwald JE. Berenberg TL, et al. Retina. 2012 Jan;32(1):25-31. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e3182150483. Retina. 2012. PMID: 21878837 Free PMC article.
References
- Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 1992;359:843–845. - PubMed
- Grunwald JE, Hariprasad SM, DuPont J, et al. Foveolar choroidal blood flow in age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998;39:385–390. - PubMed
- Grunwald JE, Metelitsina TI, Dupont JC, Ying GS, Maguire MG. Reduced foveolar choroidal blood flow in eyes with increasing AMD severity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46:1033–1038. - PubMed
- Riva CE, Cranstoun SD, Grunwald JE, Petrig BL. Choroidal blood flow in the foveal region of the human ocular fundus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994;35:4273–4281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical