Genome-wide association study identifies genes for biomarkers of cardiovascular disease: serum urate and dyslipidemia - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.11.001.
Stephen J Newhouse, Peter Braund, Feng Zhang, Martin Tobin, Mario Falchi, Kourosh Ahmadi, Richard J Dobson, Ana Carolina B Marçano, Cother Hajat, Paul Burton, Panagiotis Deloukas, Morris Brown, John M Connell, Anna Dominiczak, G Mark Lathrop, John Webster, Martin Farrall, Tim Spector, Nilesh J Samani, Mark J Caulfield, Patricia B Munroe
Affiliations
- PMID: 18179892
- PMCID: PMC2253977
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.11.001
Meta-Analysis
Genome-wide association study identifies genes for biomarkers of cardiovascular disease: serum urate and dyslipidemia
Chris Wallace et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2008 Jan.
Abstract
Many common diseases are accompanied by disturbances in biochemical traits. Identifying the genetic determinants could provide novel insights into disease mechanisms and reveal avenues for developing new therapies. Here, we report a genome-wide association analysis for commonly measured serum and urine biochemical traits. As part of the WTCCC, 500,000 SNPs genome wide were genotyped in 1955 hypertensive individuals characterized for 25 serum and urine biochemical traits. For each trait, we assessed association with individual SNPs, adjusting for age, sex, and BMI. Lipid measurements were further examined in a meta-analysis of genome-wide data from a type 2 diabetes scan. The most promising associations were examined in two epidemiological cohorts. We discovered association between serum urate and SLC2A9, a glucose transporter (p = 2 x 10(-15)) and confirmed this in two independent cohorts, GRAPHIC study (p = 9 x 10(-15)) and TwinsUK (p = 8 x 10(-19)). The odds ratio for hyperuricaemia (defined as urate >0.4 mMol/l) is 1.89 (95% CI = 1.36-2.61) per copy of common allele. We also replicated many genes previously associated with serum lipids and found previously recognized association between LDL levels and SNPs close to genes encoding PSRC1 and CELSR2 (p = 1 x 10(-7)). The common allele was associated with a 6% increase in nonfasting serum LDL. This region showed increased association in the meta-analysis (p = 4 x 10(-14)). This finding provides a potential biological mechanism for the recent association of this same allele of the same SNP with increased risk of coronary disease.
Figures
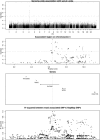
Figure 1
Genome-Wide Association with Serum Urate The dotted line represents the threshold for genome-wide significance.
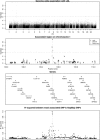
Figure 2
Genome-Wide Association with Serum LDL The dotted line represents the threshold for genome-wide significance.
Similar articles
- Association of three genetic loci with uric acid concentration and risk of gout: a genome-wide association study.
Dehghan A, Köttgen A, Yang Q, Hwang SJ, Kao WL, Rivadeneira F, Boerwinkle E, Levy D, Hofman A, Astor BC, Benjamin EJ, van Duijn CM, Witteman JC, Coresh J, Fox CS. Dehghan A, et al. Lancet. 2008 Dec 6;372(9654):1953-61. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61343-4. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Lancet. 2008. PMID: 18834626 Free PMC article. - Genetically determined serum urate levels and cardiovascular and other diseases in UK Biobank cohort: A phenome-wide mendelian randomization study.
Li X, Meng X, He Y, Spiliopoulou A, Timofeeva M, Wei WQ, Gifford A, Yang T, Varley T, Tzoulaki I, Joshi P, Denny JC, Mckeigue P, Campbell H, Theodoratou E. Li X, et al. PLoS Med. 2019 Oct 18;16(10):e1002937. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002937. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Med. 2019. PMID: 31626644 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide scan identifies a quantitative trait locus at 4p15.3 for serum urate.
Cummings N, Dyer TD, Kotea N, Kowlessur S, Chitson P, Zimmet P, Blangero J, Jowett JB. Cummings N, et al. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010 Nov;18(11):1243-7. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2010.97. Epub 2010 Jun 30. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20588307 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide association study for serum urate concentrations and gout among African Americans identifies genomic risk loci and a novel URAT1 loss-of-function allele.
Tin A, Woodward OM, Kao WH, Liu CT, Lu X, Nalls MA, Shriner D, Semmo M, Akylbekova EL, Wyatt SB, Hwang SJ, Yang Q, Zonderman AB, Adeyemo AA, Palmer C, Meng Y, Reilly M, Shlipak MG, Siscovick D, Evans MK, Rotimi CN, Flessner MF, Köttgen M, Cupples LA, Fox CS, Köttgen A; CARe and CHARGE Consortia. Tin A, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Oct 15;20(20):4056-68. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr307. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21768215 Free PMC article. - Copy number polymorphisms near SLC2A9 are associated with serum uric acid concentrations.
Scharpf RB, Mireles L, Yang Q, Köttgen A, Ruczinski I, Susztak K, Halper-Stromberg E, Tin A, Cristiano S, Chakravarti A, Boerwinkle E, Fox CS, Coresh J, Linda Kao WH. Scharpf RB, et al. BMC Genet. 2014 Jul 9;15:81. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-15-81. BMC Genet. 2014. PMID: 25007794 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Genome-wide linkage and positional association analyses identify associations of novel AFF3 and NTM genes with triglycerides: the GenSalt study.
Li C, Bazzano LA, Rao DC, Hixson JE, He J, Gu D, Gu CC, Shimmin LC, Jaquish CE, Schwander K, Liu DP, Huang J, Lu F, Cao J, Chong S, Lu X, Kelly TN. Li C, et al. J Genet Genomics. 2015 Mar 20;42(3):107-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2015.02.003. Epub 2015 Feb 17. J Genet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25819087 Free PMC article. - CDH13 promoter SNPs with pleiotropic effect on cardiometabolic parameters represent methylation QTLs.
Putku M, Kals M, Inno R, Kasela S, Org E, Kožich V, Milani L, Laan M. Putku M, et al. Hum Genet. 2015 Mar;134(3):291-303. doi: 10.1007/s00439-014-1521-6. Epub 2014 Dec 28. Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 25543204 Free PMC article. - Investigation of gene-by-sex interactions for lipid traits in diverse populations from the population architecture using genomics and epidemiology study.
Taylor KC, Carty CL, Dumitrescu L, Bůžková P, Cole SA, Hindorff L, Schumacher FR, Wilkens LR, Shohet RV, Quibrera PM, Johnson KC, Henderson BE, Haessler J, Franceschini N, Eaton CB, Duggan DJ, Cochran B, Cheng I, Carlson CS, Brown-Gentry K, Anderson G, Ambite JL, Haiman C, Le Marchand L, Kooperberg C, Crawford DC, Buyske S, North KE, Fornage M; PAGE Study. Taylor KC, et al. BMC Genet. 2013 May 1;14:33. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-14-33. BMC Genet. 2013. PMID: 23634756 Free PMC article. - Regulation of uric acid excretion by the kidney.
Lipkowitz MS. Lipkowitz MS. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012 Apr;14(2):179-88. doi: 10.1007/s11926-012-0240-z. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22359229 Review. - The association of common SNPs and haplotypes in CETP gene with HDL cholesterol levels in Latvian population.
Radovica I, Fridmanis D, Vaivade I, Nikitina-Zake L, Klovins J. Radovica I, et al. PLoS One. 2013 May 13;8(5):e64191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064191. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23675527 Free PMC article.
References
- Mitchell B.D., Kammerer C.M., Blangero J., Mahaney M.C., Rainwater D.L., Dyke B., Hixson J.E., Henkel R.D., Sharp R.M., Comuzzie A.G. Genetic and environmental contributions to cardiovascular risk factors in Mexican Americans. The San Antonio Family Heart Study. Circulation. 1996;94:2159–2170. - PubMed
- Pekkanen J., Linn S., Heiss G., Suchindran C.M., Leon A., Rifkind B.M., Tyroler H.A. Ten-year mortality from cardiovascular disease in relation to cholesterol level among men with and without preexisting cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990;322:1700–1707. - PubMed
- Saxena R., Voight B.F., Lyssenko V., Burtt N.P., de Bakker P.I., Chen H., Roix J.J., Kathiresan S., Hirschhorn J.N., Daly M.J. Genome-wide association analysis identifies loci for type 2 diabetes and triglyceride levels. Science. 2007;316:1331–1336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G106/1216/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400874/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0501942/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 076113/B/04/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials