Rapid cognitive improvement in Alzheimer's disease following perispinal etanercept administration - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
Rapid cognitive improvement in Alzheimer's disease following perispinal etanercept administration
Edward L Tobinick et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2008.
Abstract
Substantial basic science and clinical evidence suggests that excess tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) is centrally involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. In addition to its pro-inflammatory functions, TNF-alpha has recently been recognized to be a gliotransmitter that regulates synaptic function in neural networks. TNF-alpha has also recently been shown to mediate the disruption in synaptic memory mechanisms, which is caused by beta-amyloid and beta-amyloid oligomers. The efficacy of etanercept, a biologic antagonist of TNF-alpha, delivered by perispinal administration, for treatment of Alzheimer's disease over a period of six months has been previously reported in a pilot study. This report details rapid cognitive improvement, beginning within minutes, using this same anti-TNF treatment modality, in a patient with late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Rapid cognitive improvement following perispinal etanercept may be related to amelioration of the effects of excess TNF-alpha on synaptic mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease and provides a promising area for additional investigation and therapeutic intervention.
Figures
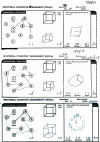
Figure 1
Rapid and sustained improvement in Visuospatial/Executive function following perispinal etanercept documented by the Montreal Cognitive Assessment. The top panel depicts the first three tasks from the Montreal Cognitive Assessment completed by the patient one day prior to perispinal etanercept administration. The middle panel depicts the patient's results two hours after perispinal etanercept administration, showing correct completion of the alternating trail making task documenting improved executive function, and improvement in depiction of a clock face. The bottom panel depicts the patient's results at seven weeks, fourteen days after receiving his previous dose of perispinal etanercept, showing further improvement in his drawing of the clock face, with numerals added, and persistence in improvement in completion of the trail making task. (The instruction for completion of the alternating trail making task are as follows: Please draw a line, going from a number to a letter in ascending order. Begin here [point to (1)] and draw a line from 1 then to A then to 2 and so on. End here [point to (E)]).
Comment in
- Perispinal etanercept: potential as an Alzheimer therapeutic.
Griffin WS. Griffin WS. J Neuroinflammation. 2008 Jan 10;5:3. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2008. PMID: 18186919 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- Rapid improvement in verbal fluency and aphasia following perispinal etanercept in Alzheimer's disease.
Tobinick EL, Gross H. Tobinick EL, et al. BMC Neurol. 2008 Jul 21;8:27. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-8-27. BMC Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18644112 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Perispinal etanercept for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Tobinick E. Tobinick E. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2007 Dec;4(5):550-2. doi: 10.2174/156720507783018217. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2007. PMID: 18220520 Review. - Perispinal etanercept for neuroinflammatory disorders.
Tobinick E. Tobinick E. Drug Discov Today. 2009 Feb;14(3-4):168-77. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2008.10.005. Epub 2008 Dec 6. Drug Discov Today. 2009. PMID: 19027875 Review. - Perispinal etanercept: potential as an Alzheimer therapeutic.
Griffin WS. Griffin WS. J Neuroinflammation. 2008 Jan 10;5:3. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2008. PMID: 18186919 Free PMC article. - Deciphering the physiology underlying the rapid clinical effects of perispinal etanercept in Alzheimer's disease.
Tobinick E. Tobinick E. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012 Jan;9(1):99-109. doi: 10.2174/156720512799015073. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012. PMID: 22191562 Review.
Cited by
- Inhibition of Src kinase activity attenuates amyloid associated microgliosis in a murine model of Alzheimer's disease.
Dhawan G, Combs CK. Dhawan G, et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Jul 2;9:117. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-117. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22673542 Free PMC article. - Excess cerebral TNF causing glutamate excitotoxicity rationalizes treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and neurogenic pain by anti-TNF agents.
Clark IA, Vissel B. Clark IA, et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Sep 5;13(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0708-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27596607 Free PMC article. Review. - Immunity impacts cognitive deficits across neurological disorders.
Shaw BC, Anders VR, Tinkey RA, Habean ML, Brock OD, Frostino BJ, Williams JL. Shaw BC, et al. J Neurochem. 2024 Oct;168(10):3512-3535. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15999. Epub 2023 Oct 29. J Neurochem. 2024. PMID: 37899543 Review. - Melatonin, an Antitumor Necrosis Factor Therapy.
Álvarez-López AI, Cruz-Chamorro I, Lardone PJ, Bejarano I, Aspiazu-Hinostroza K, Ponce-España E, Santos-Sánchez G, Álvarez-Sánchez N, Carrillo-Vico A. Álvarez-López AI, et al. J Pineal Res. 2025 Jan;77(1):e70025. doi: 10.1111/jpi.70025. J Pineal Res. 2025. PMID: 39740227 Free PMC article. Review. - The dual roles of cytokines in Alzheimer's disease: update on interleukins, TNF-α, TGF-β and IFN-γ.
Zheng C, Zhou XW, Wang JZ. Zheng C, et al. Transl Neurodegener. 2016 Apr 5;5:7. doi: 10.1186/s40035-016-0054-4. eCollection 2016. Transl Neurodegener. 2016. PMID: 27054030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, O'Banion MK, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Streit W, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, Van Muiswinkel FL, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss-Coray T. Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2000;21:383–421. doi: 10.1016/S0197-4580(00)00124-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical