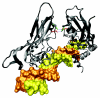Protein interactions in human genetic diseases - PubMed (original) (raw)
Protein interactions in human genetic diseases
Benjamin Schuster-Böckler et al. Genome Biol. 2008.
Abstract
We present a novel method that combines protein structure information with protein interaction data to identify residues that form part of an interaction interface. Our prediction method can retrieve interaction hotspots with an accuracy of 60% (at a 20% false positive rate). The method was applied to all mutations in the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) database, predicting 1,428 mutations to be related to an interaction defect. Combining predicted and hand-curated sets, we discuss how mutations affect protein interactions in general.
Figures
Figure 1
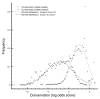
Conservation difference between wild-type and mutated residues. Histogram of conservation of wild-type and mutated residues. Triangles denote the residue-conservation frequency of all residues in disease protein regions that map to an _i_Pfam domain. Circles show the conservation of the pathogenic alleles (see Materials and methods). Trendlines are added to delineate normal distributions.
Figure 2
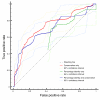
ROC curves calculated on a set of alanine scanning experiments. The red line represents the performance of our algorithm when changing only the conservation threshold, applying no percentage identity cutoff. The green line shows the performance using only percentage identity as a threshold. The blue line reflects performance using conservation as threshold, but applying a 30% sequence identity filter. Confidence intervals where calculated using the Statistics::ROC Perl module [59].
Figure 3
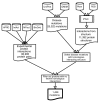
Data integration steps for interacting residue prediction. Schematic outline of data integration for the prediction of interacting residues. Mutations from OMIM and UniProt for which a residue in a homologous structure is involved in an interaction are selected. This set is restricted further by searching for homologous proteins with known interactions, taken from a range of protein interaction databases. We require that the the homologous interacting proteins contain the same pair of Pfam domains that was observed in the structural template. This results in a set of 1,428 interaction related mutations.
Figure 4
Structure of Rattus norvegicus Ras-related protein Rab-3A [PDB:1ZBD]. The small G protein Rab3A with bound GTP interacting with the effector domain of rabphilin-3A. The residue corresponding to the mutated Trp73 from human RAB27A is highlighted in red, while the two residues in contact with it are coloured green.
Figure 5
Structure of X. laevis Brachyury protein [PDB:1XBR]. The crystal structure of a T-domain from X. laevis bound to DNA. The residues highlighted in red are the mutated Ser128, with green residues representing the contact residues in the partner protein. Blue dashed lines show residue contacts.
Figure 6
Structure of the Myc/Max transcription factor complex binding DNA [PDB:1NKP]. Both Myc-c and Max form a basic helix-loop-helix motif. They dimerize mainly through their extended helix II regions. The residue that corresponds to Ile156 in H-Twist is Ile550, shown in red. The residue sits at a key position of the interface, forming bonds with seven residues in Max, shown in green.
Similar articles
- Searching Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) for information for genetic loci involved in human disease.
Baxevanis AD. Baxevanis AD. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2003 Feb;Chapter 9:Unit9.13. doi: 10.1002/0471142905.hg0913s35. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2003. PMID: 18428346 - Searching Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) for information on genetic loci involved in human disease.
Borate B, Baxevanis AD. Borate B, et al. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2009 Sep;Chapter 1:Unit 1.2. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0102s27. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19728286 - Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), a knowledgebase of human genes and genetic disorders.
Hamosh A, Scott AF, Amberger J, Bocchini C, Valle D, McKusick VA. Hamosh A, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):52-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.52. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11752252 Free PMC article. - Mutations at protein-protein interfaces: Small changes over big surfaces have large impacts on human health.
Jubb HC, Pandurangan AP, Turner MA, Ochoa-Montaño B, Blundell TL, Ascher DB. Jubb HC, et al. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2017 Sep;128:3-13. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27913149 Review. - Residue mutations and their impact on protein structure and function: detecting beneficial and pathogenic changes.
Studer RA, Dessailly BH, Orengo CA. Studer RA, et al. Biochem J. 2013 Feb 1;449(3):581-94. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121221. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23301657 Review.
Cited by
- Retinoschisis and Norrie disease: a missing link.
Rajendran R, Sudha D, Chidambaram S, Nagarajan H, Vetrivel U, Arunachalam JP. Rajendran R, et al. BMC Res Notes. 2021 May 26;14(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s13104-021-05617-5. BMC Res Notes. 2021. PMID: 34039417 Free PMC article. - Systems medicine: the future of medical genomics and healthcare.
Auffray C, Chen Z, Hood L. Auffray C, et al. Genome Med. 2009 Jan 20;1(1):2. doi: 10.1186/gm2. Genome Med. 2009. PMID: 19348689 Free PMC article. - A systems biology investigation of neurodegenerative dementia reveals a pivotal role of autophagy.
Caberlotto L, Nguyen TP. Caberlotto L, et al. BMC Syst Biol. 2014 Jun 7;8:65. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-8-65. BMC Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 24908109 Free PMC article. - A dynamical view of protein-protein complexes: Studies by molecular dynamics simulations.
Martin J, Frezza E. Martin J, et al. Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Oct 6;9:970109. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.970109. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36275619 Free PMC article. - The properties of human disease mutations at protein interfaces.
Livesey BJ, Marsh JA. Livesey BJ, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Feb 4;18(2):e1009858. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009858. eCollection 2022 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 35120134 Free PMC article.
References
- Gandhi TK, Zhong J, Mathivanan S, Karthick L, Chandrika KN, Mohan SS, Sharma S, Pinkert S, Nagaraju S, Periaswamy B, Mishra G, Nandakumar K, Shen B, Deshpande N, Nayak R, Sarker M, Boeke JD, Parmigiani G, Schultz J, Bader JS, Pandey A. Analysis of the human protein interactome and comparison with yeast, worm and fly interaction datasets. Nat Genet. 2006;38:285–293. doi: 10.1038/ng1747. - DOI - PubMed
- Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C, Patel AJ, Szabó G, Rual JF, Fisk CJ, Li N, Smolyar A, Hill DE, Barabási AL, Vidal M, Zoghbi HY. A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration. Cell. 2006;125:801–814. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.032. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical