Role of the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Role of the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease
Mike G Laukoetter et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2008.
Abstract
A critical function of the intestinal mucosa is to form a barrier that separates luminal contents from the interstitium. The single layer of intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) serves as a dynamic interface between the host and its environment. Cell polarity and structural properties of the epithelium is complex and is important in the development of epithelial barrier function. Epithelial cells associate with each other via a series of intercellular junctions. The apical most intercellular junctional complex referred to as the Apical Junction Complex (AJC) is important in not only cell-cell recognition, but also in the regulation of paracellular movement of fluid and solutes. Defects in the intestinal epithelial barrier function have been observed in a number of intestinal disorders such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It is now becoming evident that an aberrant epithelial barrier function plays a central role in the pathophysiology of IBD. Thus, a better understanding of the intestinal epithelial barrier structure and function in healthy and disease states such as IBD will foster new ideas for the development of therapies for such chronic disorders.
Figures
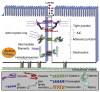
Figure 1
Intestinal epithelial intercellular junctions.
Similar articles
- Inflammatory bowel disease and the apical junctional complex.
Bruewer M, Samarin S, Nusrat A. Bruewer M, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Aug;1072:242-52. doi: 10.1196/annals.1326.017. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17057204 Review. - Numb modulates the paracellular permeability of intestinal epithelial cells through regulating apical junctional complex assembly and myosin light chain phosphorylation.
Yang Y, Chen L, Tian Y, Ye J, Liu Y, Song L, Pan Q, He Y, Chen W, Peng Z, Wang R. Yang Y, et al. Exp Cell Res. 2013 Dec 10;319(20):3214-25. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Exp Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23872314 - Intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in disease and possible therapeutical interventions.
Catalioto RM, Maggi CA, Giuliani S. Catalioto RM, et al. Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(3):398-426. doi: 10.2174/092986711794839179. Curr Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21143118 Review. - Regulation of the intestinal epithelial barrier by the apical junctional complex.
Laukoetter MG, Bruewer M, Nusrat A. Laukoetter MG, et al. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2006 Mar;22(2):85-9. doi: 10.1097/01.mog.0000203864.48255.4f. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16462161 Review. - Inflammation and the Intestinal Barrier: Leukocyte-Epithelial Cell Interactions, Cell Junction Remodeling, and Mucosal Repair.
Luissint AC, Parkos CA, Nusrat A. Luissint AC, et al. Gastroenterology. 2016 Oct;151(4):616-32. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.07.008. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 27436072 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Lactobacillus gasseri ATCC33323 affects the intestinal mucosal barrier to ameliorate DSS-induced colitis through the NR1I3-mediated regulation of E-cadherin.
Qian G, Zang H, Tang J, Zhang H, Yu J, Jia H, Zhang X, Zhou J. Qian G, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2024 Sep 9;20(9):e1012541. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012541. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39250508 Free PMC article. - Adalimumab Decorated Nanoparticles Enhance Antibody Stability and Therapeutic Outcome in Epithelial Colitis Targeting.
Ries M, Moulari B, Shetab Boushehri MA, Ali ME, Molnar D, Béduneau A, Pellequer Y, Lamprecht A. Ries M, et al. Pharmaceutics. 2022 Feb 2;14(2):352. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020352. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214083 Free PMC article. - Mind over Microplastics: Exploring Microplastic-Induced Gut Disruption and Gut-Brain-Axis Consequences.
Sofield CE, Anderton RS, Gorecki AM. Sofield CE, et al. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 30;46(5):4186-4202. doi: 10.3390/cimb46050256. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38785524 Free PMC article. Review. - Breaking down the barriers: the gut microbiome, intestinal permeability and stress-related psychiatric disorders.
Kelly JR, Kennedy PJ, Cryan JF, Dinan TG, Clarke G, Hyland NP. Kelly JR, et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Oct 14;9:392. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00392. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26528128 Free PMC article. Review. - Shaping the future of gastrointestinal cancers through metabolic interactions with host gut microbiota.
Xie W, Sharma A, Kaushik H, Sharma L, Nistha, Anwer MK, Sachdeva M, Elossaily GM, Zhang Y, Pillappan R, Kaur M, Behl T, Shen B, Singla RK. Xie W, et al. Heliyon. 2024 Jul 27;10(15):e35336. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35336. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170494 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Watson AJ, Chu S, Sieck L, Gerasimenko O, Bullen T, Campbell F, McKenna M, Rose T, Montrose MH. Epithelial barrier function in vivo is sustained despite gaps in epithelial layers. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:902–912. - PubMed
- Clayburgh DR, Shen L, Turner JR. A porous defense: the leaky epithelial barrier in intestinal disease. Lab Invest. 2004;84:282–291. - PubMed
- Turner JR, Rill BK, Carlson SL, Carnes D, Kerner R, Mrsny RJ, Madara JL. Physiological regulation of epithelial tight junctions is associated with myosin light-chain phosphorylation. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:C1378–C1385. - PubMed
- Fasano A, Nataro JP. Intestinal epithelial tight junctions as targets for enteric bacteria-derived toxins. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004;56:795–807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R29 DK055679/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK 55679/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055679/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK 59888/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK059888/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources