Histone H2A monoubiquitination represses transcription by inhibiting RNA polymerase II transcriptional elongation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Histone H2A monoubiquitination represses transcription by inhibiting RNA polymerase II transcriptional elongation
Wenlai Zhou et al. Mol Cell. 2008.
Abstract
Solving the biological roles of covalent histone modifications, including monoubiquitination of histone H2A, and the molecular mechanisms by which these modifications regulate specific transcriptional programs remains a central question for all eukaryotes. Here we report that the N-CoR/HDAC1/3 complex specifically recruits a specific histone H2A ubiquitin ligase, 2A-HUB/hRUL138, to a subset of regulated gene promoters. 2A-HUB catalyzes monoubiquitination of H2A at lysine 119, functioning as a combinatoric component of the repression machinery required for specific gene regulation programs. Thus, 2A-HUB mediates a selective repression of a specific set of chemokine genes in macrophages, critically modulating migratory responses to TLR activation. H2A monoubiquitination acts to prevent FACT recruitment at the transcriptional promoter region, blocking RNA polymerase II release at the early stage of elongation. We suggest that distinct H2A ubiquitinases, each recruited based on interactions with different corepressor complexes, contribute to distinct transcriptional repression programs.
Figures
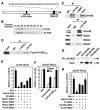
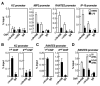
Figure 1. 2A-HUB Functions as a Transcriptional Repressor
(A) Schematic representation of the domain organization of 2A-HUB protein. (B) 2A-HUB cofractions with N-CoR. The fractions (34–42) were analyzed by Western blot analysis to detect N-CoR and 2A-HUB. (C) Endogenous co-immunoprecipitation of 2A-HUB with N-CoR and HDACs. Nuclear extracts of C2C12 cells were immunoprecipitated using control IgG, anti-N-CoR, anti-SMRT, or anti-2A-HUB antibodies and co-immunoprecipitated proteins were detected by Western blot analysis using indicated antibodies. (D) 2A-HUBmut interacts with N-CoR and HDAC1. Cell lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with Flag-2A-HUBmut was incubated with IgG or anti-HDAC1 or anti-N-CoR antibody, and immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by anti-Flag antibodies. 5% of the input was loaded. (E) Reporter assays using a Gal4-dependant luciferase reporter in HEK293T cells. Cells were first transfected with control siRNA or siRNAs against HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3 and N-CoR, and then transfected with _3XUAS-TK_-luciferase reporter in combination with vector expressing Gal4, Gal4-2A-HUB. (F) Reporter assays using a Gal4-dependant luciferase reporter in HEK293T cells. Cells were transfected with 3XUAS-TK/luciferase reporter in combination with vector expressing Gal4 or Gal4-2A-HUB or Gal4-2A-HUBmut and then treated with DMSO or TSA. (G) Endogenous 2A-HUB coimmunoprecipitated with HA-UbcH5b in vivo. Cell lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with a HA-UbcH5a, HA-UbcH5b or HA-UbcH5c expression plasmid was incubated with anti-2A-HUB antibody and immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by anti-HA antibodies. 5% of the input was loaded. (H) Reporter assays using a Gal4-dependant luciferase reporter in HEK293T cells. Cells were first transfected with control siRNA or siRNAs against UbcH5b or N-CoR as indicated, and then transfected with _3XUAS-TK_-luciferase reporter in combination with vector expressing Gal4, Gal4-2A-HUB. In (E), (F) and (H), the activity observed from Gal4 was arbitrarily set as 10. Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.
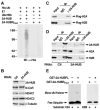
Figure 2. 2A-HUB Monoubiquitinates Histone H2A in Vitro
(A) In vitro ubiquitination assay for 2A-HUB. In vitro ubiquitination reactions were performed in the presence of recombinant E1, recombinant E2 (UbcH5b), recombinant His-ubiquitin and in vitro-translated 35S labeled 2A-HUB or 2A-HUBRmut. Reaction products were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and subject to Western blot analysis with anti-His antibodies to visualize ubiquitin conjugates. (B) Western blot analysis of 2A-HUB, N-CoR, HDAC1, HDAC3 protein levels after knockdown of 2A-HUB. Equal loading was confirmed using anti-β-tubulin antibodies. (C) Endogenous 2A-HUB coimmunoprecipitated with Flag-H2A or Flag-H2B in vivo. Soluble chromatin extracted from HEK293T cells transfected with a Flag-H2A or Flag-H2B expression plasmid was incubated with anti-2A-HUB antibody and immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by anti-Flag antibodies. 5% of the input was loaded. (D) Endogenous 2A-HUB associates with endogenous H2A and H2B in vivo. Soluble chromatin extracts from either HEK293T transfected with control siRNA or 2A-HUB siRNA was incubated with IgG or anti-2A-HUB antibody, and immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by anti-H2A or anti-H2B antibodies. 5% of the input was loaded. (E) In vitro ubiquitination assay for H2A or H2B. In vitro ubiquitination reactions were performed in the presence of recombinant E1, recombinant E2(UbcH5b), recombinant His-ubiquitin, histone H2A or H2B and purified recombinant GST-fused wt 2A-HUB or recombinant GST-fused 2A-HUBRmut as indicated. Reaction products were probed with antibodies against His to visualize ubiquitin conjugates.
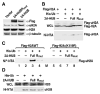
Figure 3. 2A-HUB Monoubiquitinates Histone H2A in Vivo
(A) Western blot analysis endogenous uH2A and H2A. Soluble chromatin extracts from HEK293T transfected with Flag-2A-HUB or Flag-2A-HUBRmut were probed with anti-Flag, anti-uH2A, anti-Histone H2A and anti-β-tubulin antibodies. (B) In vivo ubiquitination of Histone H2A by 2A-HUB. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated combinations of expression plasmids. The top panel shows the whole cell lysates (WCL) were probed with anti-Flag antibodies. The lower panel shows Ni-NTA agarose precipitates of the lysates of transfected cells, which were probed with anti-Flag antibodies. (C) In vivo ubiquitination assays using wt Flag-H2A- or Flag-H2A(K119R)-expressing plasmid. HEK293T were transfected with the indicated combinations of expression plasmids. The Ni-NTA agarose precipitates of the lysates of transfected cells were probed with anti-Flag antibodies. (D) In vivo ubiquitination of Histone H2B by 2A-HUB. The experiment was carried out as described in Figure 3B.
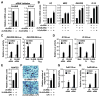
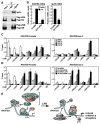
Figure 4. 2A-HUB and N-CoR Regulate a Subset of Chemokine Gene Expression
(A) Real-time RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis was performed to document efficiency of 2A-HUB 1# siRNA, N-CoR siRNAs to diminish endogenous 2A-HUB and N-CoR. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of several endogenous 2A-HUB/N-CoR target genes upon 2A-HUB 1# siRNA or N-CoR siRNA transfection. In (A) and (B), values (normalized to corresponding values of internal control gene Hprt) are the average of three replicates ± SEM. (C&D) Reporter assays using a _RANTES_-200-Luc reporter (C), _IP-10_-Luc reporter (D), in RAW264.7 cells. Cells were transfected with the reporters, siRNA or different expression plasmids as indicated. 24 hours after transfection, cells were treated with DMSO or LPS for 12 hours. (E) RT-qPCR analysis of RANTES genes expression upon control siRNA or 2A-HUB 1# siRNA transfection. 48 hours after transfection, cells were treated with LPS for 8 hours. Values (normalized to corresponding values of internal control gene Hprt) are the average of three replicates ± SEM. (F) Migration of RAW 264.7 cells was increased in response to the supernatant from LPS-treated 2A-HUB knockdown macrophages (see Supplemental Experimental Procedure). Values are means ± SEM from three independent experiments. *P<0.05 (versus control, Student t test). (G&H) Reporter assays using a 3x_AP-1_-Luc reporter (G), 3x_NF-κB_-Luc reporter (H), in RAW264.7 cells. Cells were transfected with the reporters, control siRNA and 2A-HUB siRNA as indicated. 24 hours after transfection, cells were treated with TPA or TNF-α for 12 hours. In (C), (D), (G) and (H), values are the relative values to normalized activity from basal, reporter-only transfected cells (bar 1, set as 1) and are expressed as average of three independent experiments ± SEM.
Figure 5. The Recruitment of 2A-HUB and uH2A on the Target Gene Promoters
(A)ChIP analyses were performed after cells were stimulated with LPS for 30 minutes. Soluble chromatin was immunoprecipitated by the antibodies indicated, the bound DNA was analyzed by quantitative PCR using a primer pair flanking the regulatory sequence of the promoter of KC, MIP2, RANTES or IP-10. The ChIP was performed as described in Methods. (B) Two-step ChIP assays were performed, showing that 2A-HUB is not recruited to the N-coR+ KC promoter. (C) Two-step ChIP assays were performed, showing that 2A-HUB is recruited to the N-coR+ RANTES promoter. (D)ChIP analyses of the occupancy of 2A-HUB on the RANTES promoter after depletion of N-CoR by siRNA in RAW 264.7 cells. Values (ratios of ChIP to corresponding inputs) in (A)–(D) are means ± SEM of at least two independent experiments.
Figure 6. H2A Ubiquitination by 2A-HUB Prevents FACT Recruitment
(A) Coimmunoprecipitation of Spt16 and H2A/H2B. Top panel, immunoprecipitation of endogenous Spt16. Middle panel, co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous Spt16 with unmodified Flag-H2A, but not Flag-uH2A, in HEK293 cells stably expressing Flag-H2A. Bottom panel, co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous Spt16 with both unmodified Flag-H2B and Flag-uH2B in HEK293 cells stably expressing Flag-H2B. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of endogenous RANTES gene expression upon LPS treatment after depletion Spt16 by siRNA. Values (normalized to corresponding values of internal control gene Hprt) are the average of three replicates ± SEM. (C) ChIP in RAW246.7 cells treated with LPS (time courses as indicated) using a panel of antibodies as shown. PCR primers amplifying the promoter region and a downstream region corresponding to exon 3 of the RANTES gene were used. (D) ChIP was performed in RAW264.7 cells, first treated with control or 2A-HUB siRNA and then induced by LPS for 30 minutes. A panel of antibodies was used as shown. Values (ratios of ChIP to corresponding inputs) in (C) and (D) are the mean ± SEM of at least two independent experiments. (E) Model: H2A monoubiquitination mediated by 2A-HUB inhibits the early step of RNA Pol II transcriptional elongation by blocking the recruitment of FACT and maintains gene in a repressed status. Upon gene activation by LPS, removing ubiquitin from H2A by H_2A d_e_ub_iquitinase (2A-DUB) increases FACT recruitment and facilitates RNA polymerase II transcriptional elongation.
Similar articles
- Histone H2B monoubiquitination functions cooperatively with FACT to regulate elongation by RNA polymerase II.
Pavri R, Zhu B, Li G, Trojer P, Mandal S, Shilatifard A, Reinberg D. Pavri R, et al. Cell. 2006 May 19;125(4):703-17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.029. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16713563 - Writing Histone Monoubiquitination in Human Malignancy-The Role of RING Finger E3 Ubiquitin Ligases.
Marsh DJ, Dickson KA. Marsh DJ, et al. Genes (Basel). 2019 Jan 18;10(1):67. doi: 10.3390/genes10010067. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30669413 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of histone H2A ubiquitination in Polycomb silencing.
Wang H, Wang L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Vidal M, Tempst P, Jones RS, Zhang Y. Wang H, et al. Nature. 2004 Oct 14;431(7010):873-8. doi: 10.1038/nature02985. Epub 2004 Sep 22. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15386022 - SAP30, a component of the mSin3 corepressor complex involved in N-CoR-mediated repression by specific transcription factors.
Laherty CD, Billin AN, Lavinsky RM, Yochum GS, Bush AC, Sun JM, Mullen TM, Davie JR, Rose DW, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG, Ayer DE, Eisenman RN. Laherty CD, et al. Mol Cell. 1998 Jul;2(1):33-42. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80111-2. Mol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9702189 - Histone H2A ubiquitination in transcriptional regulation and DNA damage repair.
Zhou W, Wang X, Rosenfeld MG. Zhou W, et al. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Jan;41(1):12-5. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.09.016. Epub 2008 Sep 26. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18929679 Review.
Cited by
- Epigenetics: the link between nature and nurture.
Tammen SA, Friso S, Choi SW. Tammen SA, et al. Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Jul-Aug;34(4):753-64. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.07.018. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 22906839 Free PMC article. Review. - EZH2: a pivotal regulator in controlling cell differentiation.
Chen YH, Hung MC, Li LY. Chen YH, et al. Am J Transl Res. 2012;4(4):364-75. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Am J Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 23145205 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide activities of Polycomb complexes control pervasive transcription.
Lee HG, Kahn TG, Simcox A, Schwartz YB, Pirrotta V. Lee HG, et al. Genome Res. 2015 Aug;25(8):1170-81. doi: 10.1101/gr.188920.114. Epub 2015 May 18. Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 25986499 Free PMC article. - SAGA function in tissue-specific gene expression.
Weake VM, Workman JL. Weake VM, et al. Trends Cell Biol. 2012 Apr;22(4):177-84. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2011.11.005. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Trends Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22196215 Free PMC article. - Epigenetic gene regulation by histone demethylases: emerging role in oncogenesis and inflammation.
Kang MK, Mehrazarin S, Park NH, Wang CY. Kang MK, et al. Oral Dis. 2017 Sep;23(6):709-720. doi: 10.1111/odi.12569. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Oral Dis. 2017. PMID: 27514027 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Amendt BA, Sutherland LB, Semina EV, Russo AF. The molecular basis of Rieger syndrome. Analysis of Pitx2 homeodomain protein activities. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1998;273:20066–20072. - PubMed
- Bondarenko VA, Steele LM, Ujvari A, Gaykalova DA, Kulaeva OI, Polikanov YS, Luse DS, Studitsky VM. Nucleosomes can form a polar barrier to transcript elongation by RNA polymerase II. Molecular cell. 2006;24:469–479. - PubMed
- Borden KL. RING domains: master builders of molecular scaffolds? J Mol Biol. 2000;295:1103–1112. - PubMed
- Breiling A, Turner BM, Bianchi ME, Orlando V. General transcription factors bind promoters repressed by Polycomb group proteins. Nature. 2001;412:651–655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 DK039949-24S1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK039949-18/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK039949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK039949-17/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034934-17/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065445-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065445-05S1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097134/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK018477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK039949-25/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097134-06A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK039949-17S1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009523/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868-01A1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034934/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034934-18/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034934-16/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK018477-31A1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK039949-26/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868-01A1S1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065445/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK039949-24/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065445-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK018477-32/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034934-19/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK039949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous