Quality scores and SNP detection in sequencing-by-synthesis systems - PubMed (original) (raw)
Quality scores and SNP detection in sequencing-by-synthesis systems
William Brockman et al. Genome Res. 2008 May.
Abstract
Promising new sequencing technologies, based on sequencing-by-synthesis (SBS), are starting to deliver large amounts of DNA sequence at very low cost. Polymorphism detection is a key application. We describe general methods for improved quality scores and accurate automated polymorphism detection, and apply them to data from the Roche (454) Genome Sequencer 20. We assess our methods using known-truth data sets, which is critical to the validity of the assessments. We developed informative, base-by-base error predictors for this sequencer and used a variant of the phred binning algorithm to combine them into a single empirically derived quality score. These quality scores are more useful than those produced by the system software: They both better predict actual error rates and identify many more high-quality bases. We developed a SNP detection method, with variants for low coverage, high coverage, and PCR amplicon applications, and evaluated it on known-truth data sets. We demonstrate good specificity in single reads, and excellent specificity (no false positives in 215 kb of genome) in high-coverage data.
Figures
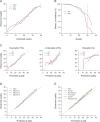
Figure 1.
New quality scores for 454 reads. Old: quality scores from 454 software v.1.0.52. New: quality scores developed for this work. Data for panels A, B, and C come from 13 different runs on DNA from five different species. (A) Predicted vs. observed quality for old and new quality scores. New quality scores are much closer to the ideal, 1:1 line. (B) Proportion of bases greater than a given actual quality. The new quality scores accurately identify many more bases at quality ≥30 (63% vs. 23%). (C) Error prediction by error type. New quality scores accurately predict different types of errors: predicted vs. actual quality when errors are separated into overcalls, undercalls, and miscalls. (D) New quality scores are stable across machines. Predicted vs. actual quality for three runs of the same human BAC library on three different machines. (E) New quality scores are stable across genomes. Predicted vs. actual quality for five genomes varying in GC content and proportion of bases in homopolymers.
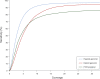
Figure 2.
Sensitivity of SNP calling as a function of coverage. Coverage is counted by bases accepted for SNP calling. At all coverages, the fraction of the reference that could be correctly called in haploid DNA (a BAC) exceeds the sensitivity for heterozygous SNPs that can be called in diploid DNA (a mixture of two different, overlapping BACs). Sensitivity is generally lower for heterozygous SNPs in PCR amplicons, due to pooling variation. No false positives were found at any coverage level in genomic data: ∼545 kb haploid, ∼220 kb diploid. For PCR amplicons approximately one false positive was found in ∼27 kb.
Similar articles
- PhredEM: a phred-score-informed genotype-calling approach for next-generation sequencing studies.
Liao P, Satten GA, Hu YJ. Liao P, et al. Genet Epidemiol. 2017 Jul;41(5):375-387. doi: 10.1002/gepi.22048. Epub 2017 May 31. Genet Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 28560825 Free PMC article. - An investigation of causes of false positive single nucleotide polymorphisms using simulated reads from a small eukaryote genome.
Ribeiro A, Golicz A, Hackett CA, Milne I, Stephen G, Marshall D, Flavell AJ, Bayer M. Ribeiro A, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Nov 11;16:382. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0801-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26558718 Free PMC article. - HySA: a Hybrid Structural variant Assembly approach using next-generation and single-molecule sequencing technologies.
Fan X, Chaisson M, Nakhleh L, Chen K. Fan X, et al. Genome Res. 2017 May;27(5):793-800. doi: 10.1101/gr.214767.116. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Genome Res. 2017. PMID: 28104618 Free PMC article. - Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities.
Ewing B, Green P. Ewing B, et al. Genome Res. 1998 Mar;8(3):186-94. Genome Res. 1998. PMID: 9521922 - Basecalling with LifeTrace.
Walther D, Bartha G, Morris M. Walther D, et al. Genome Res. 2001 May;11(5):875-88. doi: 10.1101/gr.177901. Genome Res. 2001. PMID: 11337481 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Evolutionary change driven by metal exposure as revealed by coding SNP genome scan in wild yellow perch (Perca flavescens).
Bélanger-Deschênes S, Couture P, Campbell PG, Bernatchez L. Bélanger-Deschênes S, et al. Ecotoxicology. 2013 Jul;22(5):938-57. doi: 10.1007/s10646-013-1083-8. Epub 2013 May 31. Ecotoxicology. 2013. PMID: 23722603 - Small-scale high-throughput sequencing-based identification of new therapeutic tools in cystic fibrosis.
Bonini J, Varilh J, Raynal C, Thèze C, Beyne E, Audrezet MP, Ferec C, Bienvenu T, Girodon E, Tuffery-Giraud S, Des Georges M, Claustres M, Taulan-Cadars M. Bonini J, et al. Genet Med. 2015 Oct;17(10):796-806. doi: 10.1038/gim.2014.194. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Genet Med. 2015. PMID: 25569440 - Windshield splatter analysis with the Galaxy metagenomic pipeline.
Kosakovsky Pond S, Wadhawan S, Chiaromonte F, Ananda G, Chung WY, Taylor J, Nekrutenko A; Galaxy Team. Kosakovsky Pond S, et al. Genome Res. 2009 Nov;19(11):2144-53. doi: 10.1101/gr.094508.109. Epub 2009 Oct 9. Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19819906 Free PMC article. - Massively parallel sequencing: the next big thing in genetic medicine.
Tucker T, Marra M, Friedman JM. Tucker T, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2009 Aug;85(2):142-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.06.022. Am J Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19679224 Free PMC article. Review. - Novel software package for cross-platform transcriptome analysis (CPTRA).
Zhou X, Su Z, Sammons RD, Peng Y, Tranel PJ, Stewart CN Jr, Yuan JS. Zhou X, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Oct 8;10 Suppl 11(Suppl 11):S16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-S11-S16. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19811681 Free PMC article.
References
- Altshuler D., Pollara V., Cowles C., Van Etten W., Baldwin J., Linton L., Lander E., Pollara V., Cowles C., Van Etten W., Baldwin J., Linton L., Lander E., Cowles C., Van Etten W., Baldwin J., Linton L., Lander E., Van Etten W., Baldwin J., Linton L., Lander E., Baldwin J., Linton L., Lander E., Linton L., Lander E., Lander E. An SNP map of the human genome generated by reduced representation shotgun sequencing. Nature. 2000;407:513–516. - PubMed
- Applied Biosystems, Inc. 2004.
- Ewing B., Green P., Green P. Basecalling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res. 1998;8:186–194. - PubMed
- Ewing B., Hillier L., Wendl M., Green P., Hillier L., Wendl M., Green P., Wendl M., Green P., Green P. Basecalling of automated sequencer traces using phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res. 1998;8:175–185. - PubMed
- International HapMap Consortium The International HapMap Project. Nature. 2003;426:789–796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources