DDAVP is effective in preventing and reversing inadvertent overcorrection of hyponatremia - PubMed (original) (raw)
DDAVP is effective in preventing and reversing inadvertent overcorrection of hyponatremia
Anjana Perianayagam et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008 Mar.
Abstract
Background and objectives: Adherence to therapeutic guidelines for the treatment of hyponatremia becomes difficult when water diuresis emerges during therapy. The objective of this study was to assess the effectiveness and safety of desmopressin acetate as a therapeutic agent to avoid overcorrection of hyponatremia and to lower the plasma sodium concentration again after inadvertent overcorrection.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Retrospective chart review was conducted of all patients who were given desmopressin acetate during the treatment of hyponatremia during 6 yr in a 528-bed community teaching hospital.
Results: Six patients (group 1) were given desmopressin acetate after the 24-h limit of 12 mmol/L had already been reached or exceeded; correction was prevented from exceeding the 48-h limit of 18 mmol/L in five of the six. Fourteen patients (group 2) were given desmopressin acetate in anticipation of overcorrection after the plasma sodium concentration had increased by 1 to 12 mmol/L. In all 14 patients who were treated with desmopressin acetate as a preventive measure, correction was prevented from exceeding either the 24- or 48-h limits. After desmopressin acetate was administered, the plasma sodium concentration of 14 of the 20 patients fell by 2 to 9 mmol/L. In all six group 1 patients and in five of the group 2 patients, the plasma sodium concentration was actively lowered again by the concurrent administration of desmopressin acetate and 5% dextrose in water; no serious adverse consequences from this maneuver were observed.
Conclusion: Desmopressin acetate is effective in preventing and reversing inadvertent overcorrection of hyponatremia.
Figures
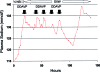
Figure 1.
Patient 2, who presented with delirium as a result of a plasma sodium concentration (PNa) of 115 mmol/L and alcohol withdrawal, was given multiple doses of desmopressin acetate (DDAVP; filled arrows) in the intensive care unit after a spontaneous water diuresis had increased her PNa by 20 mmol/L over 21 h despite infusion of 0.45% saline (1/2 NS) at 150 ml/h. The final dose of DDAVP was given just before transfer from the intensive care unit, and it was followed by excessive re-lowering of the PNa because of the unintentional continuation of 5% dextrose in water (D5W). After the PNa had fallen from 133 to 122 mmol/L over 24 h (with no worsening of the patient's neurologic condition), a final water diuresis emerged, increasing the PNa to 138 over 17 h despite continued infusion of D5W at 150 ml/h without DDAVP.
Similar articles
- Outcomes in Severe Hyponatremia Treated With and Without Desmopressin.
MacMillan TE, Cavalcanti RB. MacMillan TE, et al. Am J Med. 2018 Mar;131(3):317.e1-317.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.09.048. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Am J Med. 2018. PMID: 29061503 - Use of desmopressin acetate in severe hyponatremia in the intensive care unit.
Rafat C, Schortgen F, Gaudry S, Bertrand F, Miguel-Montanes R, Labbé V, Ricard JD, Hajage D, Dreyfuss D. Rafat C, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Feb;9(2):229-37. doi: 10.2215/CJN.00950113. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24262506 Free PMC article. - Evaluation of Desmopressin in Critically Ill Patients with Hyponatremia Requiring 3% Hypertonic Saline.
Tran LK, Marino KK, DeGrado JR, Szumita PM, Dube KM. Tran LK, et al. Am J Med Sci. 2021 Jun;361(6):711-717. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2021.03.012. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Am J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33812910 - Desmopressin to Prevent Rapid Sodium Correction in Severe Hyponatremia: A Systematic Review.
MacMillan TE, Tang T, Cavalcanti RB. MacMillan TE, et al. Am J Med. 2015 Dec;128(12):1362.e15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.04.040. Epub 2015 May 30. Am J Med. 2015. PMID: 26031887 Review. - Treatment of hyponatremia.
Sterns RH, Hix JK, Silver S. Sterns RH, et al. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010 Sep;19(5):493-8. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32833bfa64. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010. PMID: 20539224 Review.
Cited by
- Safety and efficacy of proactive versus reactive administration of desmopressin in severe symptomatic hyponatremia: a randomized controlled trial.
Pakchotanon K, Kanjanasuphak N, Chuasuwan A, Gojaseni P, Chittinandana A. Pakchotanon K, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 29;14(1):7487. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57657-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38553491 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - [Consensus recommendations on the diagnosis and treatment of hyponatremia from the Austrian Society for Nephrology 2024].
Schwarz C, Lindner G, Windpessl M, Knechtelsdorfer M, Saemann MD. Schwarz C, et al. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2024 Feb;136(Suppl 1):1-33. doi: 10.1007/s00508-024-02325-5. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2024. PMID: 38421476 Free PMC article. German. - Treatment Guidelines for Hyponatremia: Stay the Course.
Sterns RH, Rondon-Berrios H, Adrogué HJ, Berl T, Burst V, Cohen DM, Christ-Crain M, Cuesta M, Decaux G, Emmett M, Garrahy A, Gankam-Kengne F, Hix JK, Hoorn EJ, Kamel KS, Madias NE, Peri A, Refardt J, Rosner MH, Sherlock M, Silver SM, Soupart A, Thompson CJ, Verbalis JG; PRONATREOUS Investigators. Sterns RH, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024 Jan 1;19(1):129-135. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000244. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 37379081 Review. - Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuresis: From Pathophysiology to Management.
Warren AM, Grossmann M, Christ-Crain M, Russell N. Warren AM, et al. Endocr Rev. 2023 Sep 15;44(5):819-861. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnad010. Endocr Rev. 2023. PMID: 36974717 Free PMC article. Review. - Hyponatremia Demystified: Integrating Physiology to Shape Clinical Practice.
Workeneh BT, Meena P, Christ-Crain M, Rondon-Berrios H. Workeneh BT, et al. Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2023 Mar;30(2):85-101. doi: 10.1053/j.akdh.2022.11.004. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2023. PMID: 36868737 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Sterns RH, Riggs JE, Schochet SS Jr: Osmotic demyelination syndrome following correction of hyponatremia. N Engl J Med 314: 1535–1542, 1986 - PubMed
- Sterns RH: Severe symptomatic hyponatremia: Treatment and outcome. A study of 64 cases. Ann Intern Med 107: 656–664, 1987 - PubMed
- Sterns RH, Cappuccio JD, Silver SM, Cohen EP: Neurologic sequelae after treatment of severe hyponatremia: A multicenter perspective. J Am Soc Nephrol 4: 1522–1530, 1994 - PubMed
- Karp BI, Laureno R: Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: A neurologic disorder following rapid correction of hyponatremia. Medicine (Baltimore) 72: 359–373, 1993 - PubMed
- Ellis SJ: Severe hyponatraemia: Complications and treatment. QJM 88: 905–909, 1995 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources