Interleukin-2 receptor downstream events in regulatory T cells: implications for the choice of immunosuppressive drug therapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2008 Feb 15;7(4):458-62.
doi: 10.4161/cc.7.4.5454. Epub 2007 Dec 18.
Affiliations
- PMID: 18235249
- PMCID: PMC2886808
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.7.4.5454
Review
Interleukin-2 receptor downstream events in regulatory T cells: implications for the choice of immunosuppressive drug therapy
Robert Zeiser et al. Cell Cycle. 2008.
Abstract
Naturally occurring CD4+CD25(high)FOXP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) constitute a powerful mechanism of immune regulation and therefore, have important therapeutic potential for disorders such as autoimmune diseases, allograft rejection and graft-versus-host disease. Disruption of the IL-2R signalling pathway by genetic defects of the interleukin (IL)-2 gene or components of the IL-2 receptor (R) complex results in severe T cell-mediated autoimmunity rather than immunodeficiency, indicating a crucial role for IL-2R signalling for Treg development and function. Signalling downstream of the IL-2R can act through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/mTOR pathway, the Janus kinase (JAK)/Signal transducers and Activators of Transcription (STAT) pathway and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. In this report we focus on the relevance of these pathways as well as the impact of immunosuppressive drugs that may affect or enhance Treg function by targeting IL-2R signalling.
Figures
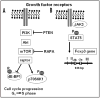
Figure 1
Signalling through growth factor receptors can activate the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and the JAK3/STAT5 pathway. (A) Growth factor receptors first stimulate PI 3 kinase, and through inositol phosphates activate AKT which then phosphorylates mTOR. The phosphorylation of p70S6K and 4EBP by mTOR and the phosphorylation downstream of RPS6 and EIF-4B stimulate translational initiation and contribute to cell growth. The activity of the mTOR pathway is controlled by PTEN a phosphoinositol 3,4,5-triphosphatase that catalyzes the reverse reaction of PI3K. Rapamycin (RAPA) inhibits mTOR kinase activity and has immunosuppressant activity on cells that use the mTOR pathway in the absence of PTEN inhibition. (B) Engagement of Growth factor receptors leads to activation of JAK3 which induces phospharylation and nuclear translocation of STAT5. The Foxp3 promotor has several STAT5B consensus sequences that can be bound and lead to promotor activity. Abbreviations: PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt, protein kinase B; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10; RAPA, rapamycin; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; p, phosphorylation; JAK, Janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; Foxp3, forkhead box P3.
Similar articles
- Transcriptional regulation of Foxp3 gene: multiple signal pathways on the road.
Shen Z, Chen L, Hao F, Wu J. Shen Z, et al. Med Res Rev. 2009 Sep;29(5):742-66. doi: 10.1002/med.20152. Med Res Rev. 2009. PMID: 19267400 Review. - Withasteroid B from D. metel L. regulates immune responses by modulating the JAK/STAT pathway and the IL-17+ RORγt+ /IL-10+ FoxP3+ ratio.
Su Y, Wang Q, Yang B, Wu L, Cheng G, Kuang H. Su Y, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Oct;190(1):40-53. doi: 10.1111/cei.12998. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28617942 Free PMC article. - A function for IL-7R for CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T regulatory cells.
Bayer AL, Lee JY, de la Barrera A, Surh CD, Malek TR. Bayer AL, et al. J Immunol. 2008 Jul 1;181(1):225-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.1.225. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18566388 Free PMC article. - Distinct IL-2 receptor signaling pattern in CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells.
Bensinger SJ, Walsh PT, Zhang J, Carroll M, Parsons R, Rathmell JC, Thompson CB, Burchill MA, Farrar MA, Turka LA. Bensinger SJ, et al. J Immunol. 2004 May 1;172(9):5287-96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.9.5287. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15100267 Free PMC article. - T-cell tolerance and the multi-functional role of IL-2R signaling in T-regulatory cells.
Cheng G, Yu A, Malek TR. Cheng G, et al. Immunol Rev. 2011 May;241(1):63-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01004.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21488890 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Rapid and long-lasting decrease of T-regulatory cells in patients with myelofibrosis treated with ruxolitinib.
Massa M, Rosti V, Campanelli R, Fois G, Barosi G. Massa M, et al. Leukemia. 2014 Feb;28(2):449-51. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.296. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Leukemia. 2014. PMID: 24145312 No abstract available. - A Tale from TGF-β Superfamily for Thymus Ontogeny and Function.
Jurberg AD, Vasconcelos-Fontes L, Cotta-de-Almeida V. Jurberg AD, et al. Front Immunol. 2015 Sep 10;6:442. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00442. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26441956 Free PMC article. Review. - Reprogramming of regulatory T cells in inflammatory tumor microenvironment: can it become immunotherapy turning point?
Liu J, Zhang B, Zhang G, Shang D. Liu J, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 21;15:1345838. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1345838. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38449875 Free PMC article. Review. - Low-dose IL-2 for In vivo expansion of CD4+ and CD8+ regulatory T cells in nonhuman primates.
Aoyama A, Klarin D, Yamada Y, Boskovic S, Nadazdin O, Kawai K, Schoenfeld D, Madsen JC, Cosimi AB, Benichou G, Kawai T. Aoyama A, et al. Am J Transplant. 2012 Sep;12(9):2532-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04133.x. Epub 2012 Jun 8. Am J Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22682297 Free PMC article. - Plasma-Derived Inflammatory Proteins Predict Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Liu KYP, Lu XJD, Zhu YS, Le N, Kim H, Poh CF. Liu KYP, et al. Front Oncol. 2018 Dec 4;8:585. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00585. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30564558 Free PMC article.
References
- Stephens LA, Mottet C, Mason D, Powrie F. Human CD4(+)CD25(+) thymocytes and peripheral T cells have immune suppressive activity in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 2001;31:1247–54. - PubMed
- Nelson BH. IL-2, regulatory T cells, and tolerance. J Immunol. 2004;172:3983–8. - PubMed
- Thornton A, Donovan EE, Piccirillo CA, Shevach EM. Cutting edge: IL-2 is critically required for the in vitro activation of CD4+CD25+ T cell suppressor function. J Immunol. 2004;172:6519–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 CA049605/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL075462/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL075462-050003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA0800065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous