Role of gp130-mediated signalling pathways in the heart and its impact on potential therapeutic aspects - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2008 Mar;153 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S414-27.
doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.1. Epub 2008 Feb 4.
Affiliations
- PMID: 18246092
- PMCID: PMC2268054
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.1
Review
Role of gp130-mediated signalling pathways in the heart and its impact on potential therapeutic aspects
P Fischer et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Mar.
Abstract
IL-6-type cytokines bind to plasma membrane receptor complexes containing the common signal transducing receptor chain gp130 that is ubiquitously expressed in most tissues including the heart. The two major signalling cascades activated by the gp130 receptor, SHP2/ERK and STAT pathways, have been demonstrated to play important roles in cardiac development, hypertrophy, protection and remodelling in response to physiological and pathophysiological stimuli. Experimental data, both in vivo and in vitro, imply beneficial effects of gp130 signalling on cardiomyocytes in terms of growth and survival. In contrast, it has been reported that elevated serum levels of IL-6 cytokines and gp130 proteins are strong prognostic markers for morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure or after myocardial infarction. Moreover, it has been shown that the local gp130 receptor system is altered in failing human hearts. In the present review, we summarize the basic principles of gp130 signalling, which requires simultaneous activation of STAT and ERK pathways under the tight control of positive and negative intracellular signalling modulators to provide a balanced biological outcome. Furthermore, we highlight the key role of the gp130 receptor and its major downstream effectors in the heart in terms of development and regeneration and in response to various physiological and pathophysiological stress situations. Finally, we comment on tissue-specific diversity and challenges in targeted pharmacological interference with components of the gp130 receptor system.
Figures
Figure 1
Role of glycoprotein 130 (gp130) downstream signalling in the heart. Scheme of gp130 receptor activation showing interleukin-6 (IL-6) type cytokines binding to their transmembrane receptor α-subunits, which induces homodimerization of the gp130 receptor β-subunits or heterodimerization of gp130 with either one of the structurally and functionally similar leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF) receptor and oncostatin M (OSM) receptor β-subunits. Following dimerization of the gp130 receptor complex, Janus kinase-1/2 (JAK1/2) constitutively connected to the intracytoplasmatic membrane proximal regions of the receptor subunits are catalytically activated and themselves transphosphorylate tyrosine residues in the gp130 receptor intracellular domain. Subsequently, two major intracellular signalling cascades are triggered, the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)-1/3 pathway and the SH2 domain-containing cytoplasmic protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP2)/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. Via the formation of complexes with growth factor receptor binding protein-2 (Grb2)-associated binding protein-1/2 (Gab1/2) and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K), SHP2 activation furthermore initiates the Akt pathway and additionally enhances MEK/ERK signalling. Activation of gp130-mediated signalling plays essential roles in stem cells and cardiomyogenesis. In the adult heart, it is involved in numerous physiological and pathophysiological processes. MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/ERK kinase.
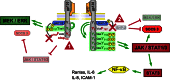
Figure 2
Mutations in the glycoprotein 130 (gp130) receptor lead to an imbalance in downstream signalling pathways. Detailed schematic view of the gp130 receptor structure shows tyrosine 757 (Y757) necessary for SH2 domain-containing cytoplasmic protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP2) phosphorylation and suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS)-3 binding. A point mutation (Y757 → F757, tyrosine → phenylalanine) abolishes binding of SHP2 and SOCS3 (arrowhead 1) and leads to uncontrolled Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) activation with exaggerated STAT3 activation. As a consequence, proinflammatory pathways, that is nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation, are promoted. The left side displays a truncated gp130 intracellular domain incapable of binding and activating the STAT1/3 pathway (arrowhead 2) from its membrane-distal phosphotyrosine residues. This mutant form is characterized by the substitution of Y765 by F765 and is truncated at the C-terminal side of amino acid 768. Deficient STAT1/3 signalling in this model is accompanied by enhanced signalling via the SHP2/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule-1. MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/ERK kinase.
Similar articles
- Survival pathways in hypertrophy and heart failure: the gp130-STAT axis.
Fischer P, Hilfiker-Kleiner D. Fischer P, et al. Basic Res Cardiol. 2007 Sep;102(5):393-411. doi: 10.1007/s00395-007-0674-z. Basic Res Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17918316 Review. - Survival pathways in hypertrophy and heart failure: the gp130-STAT3 axis.
Fischer P, Hilfiker-Kleiner D. Fischer P, et al. Basic Res Cardiol. 2007 Jul;102(4):279-97. doi: 10.1007/s00395-007-0658-z. Epub 2007 May 29. Basic Res Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17530315 Corrected and republished. Review. - gp130 Controls Cardiomyocyte Proliferation and Heart Regeneration.
Li Y, Feng J, Song S, Li H, Yang H, Zhou B, Li Y, Yue Z, Lian H, Liu L, Hu S, Nie Y. Li Y, et al. Circulation. 2020 Sep 8;142(10):967-982. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044484. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Circulation. 2020. PMID: 32600062 - Cardiotrophin-1 and the role of gp130-dependent signaling pathways in cardiac growth and development.
Wollert KC, Chien KR. Wollert KC, et al. J Mol Med (Berl). 1997 Jul;75(7):492-501. doi: 10.1007/s001090050134. J Mol Med (Berl). 1997. PMID: 9253712 Review. - Activation of gp130 transduces hypertrophic signals via STAT3 in cardiac myocytes.
Kunisada K, Tone E, Fujio Y, Matsui H, Yamauchi-Takihara K, Kishimoto T. Kunisada K, et al. Circulation. 1998 Jul 28;98(4):346-52. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.98.4.346. Circulation. 1998. PMID: 9711940
Cited by
- CRLF1 bridges AKT and mTORC2 through SIN1 to inhibit pyroptosis and enhance chemo-resistance in ovarian cancer.
Xiang C, Chen L, Zhu S, Chen Y, Huang H, Yang C, Chi Y, Wang Y, Lei Y, Cai X. Xiang C, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2024 Sep 10;15(9):662. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07035-4. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39256356 Free PMC article. - ART1 knockdown decreases the IL-6-induced proliferation of colorectal cancer cells.
Lin T, Zhang S, Tang Y, Xiao M, Li M, Gong H, Xie H, Wang Y. Lin T, et al. BMC Cancer. 2024 Mar 19;24(1):354. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12120-0. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38504172 Free PMC article. - CD9 exacerbates pathological cardiac hypertrophy through regulating GP130/STAT3 signaling pathway.
Li Y, Fan S, Kong L, Hao Z, Zhou Y, Shangguan J, Gao L, Wang M, Kang Y, Li X, Huang K, Zhang C, Liu Z. Li Y, et al. iScience. 2023 Sep 28;26(11):108070. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108070. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37860696 Free PMC article. - Cardiovascular manifestations of inflammatory bowel diseases and the underlying pathogenic mechanisms.
Xiao Y, Powell DW, Liu X, Li Q. Xiao Y, et al. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2023 Aug 1;325(2):R193-R211. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00300.2022. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37335014 Free PMC article. Review. - Heart-targeting exosomes from human cardiosphere-derived cells improve the therapeutic effect on cardiac hypertrophy.
Mao L, Li YD, Chen RL, Li G, Zhou XX, Song F, Wu C, Hu Y, Hong YX, Dang X, Li GR, Wang Y. Mao L, et al. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Oct 4;20(1):435. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01630-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 36195937 Free PMC article.
References
- Ancey C, Menet E, Corbi P, Fredj S, Garcia M, Rucker-Martin C, et al. Human cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced in vitro by gp130 stimulation. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;59:78–85. - PubMed
- Berry MF, Pirolli TJ, Jayasankar V, Morine KJ, Moise MA, Fisher O, et al. Targeted overexpression of leukemia inhibitory factor to preserve myocardium in a rat model of postinfarction heart failure. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;128:866–875. - PubMed
- Birks EJ, Latif N, Owen V, Bowles C, Felkin LE, Mullen AJ, et al. Quantitative myocardial cytokine expression and activation of the apoptotic pathway in patients who require left ventricular assist devices. Circulation. 2001;104 12 Suppl 1:I233–I240. - PubMed
- Burdon T, Smith A, Savatier P. Signalling, cell cycle and pluripotency in embryonic stem cells. Trends Cell Biol. 2002;12:432–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous