Oxidative stress and inflammation are associated with adiposity in moderate to severe CKD - PubMed (original) (raw)
Oxidative stress and inflammation are associated with adiposity in moderate to severe CKD
Luis F Ramos et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008 Mar.
Abstract
Adiposity contributes to inflammation and oxidative stress in the general population, but this association has not been examined in the chronic kidney disease (CKD) population. We investigated the relationship between body mass index, body fat percentage, and markers of inflammation (C-reactive protein) and oxidative stress (F(2)-isoprostanes and protein thiols) in 184 patients with stages III to IV CKD and 43 healthy controls. We found that, on average, patients with CKD had 62% higher F(2)-isoprostanes, 7% lower protein thiols (a measure of endogenous anti-oxidant capacity, inversely related to protein oxidation), and 150% higher C-reactive protein levels than healthy controls (all unadjusted P < 0.001). In separate multivariable linear regression models, body mass index and body fat percentage each positively correlated with levels of F(2)-isoprostanes and C-reactive protein and negatively correlated with levels of protein thiols among patients with CKD after adjusting for age, sex, race, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, smoking history, estimated glomerular filtration rate, total cholesterol, serum albumin, and study site. We conclude that increased adiposity may amplify the oxidative stress and inflammation that accompany moderate to severe CKD. Interventions focused on weight loss may decrease the inflammatory and oxidative burden in CKD, which may ultimately attenuate cardiovascular risk in this population.
Figures
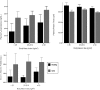
Figure 1.
Relationship between BMI and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in 184 patients with CKD and 43 control subjects. The effect of BMI on F2-isoprostanes (P = 0.21 for interaction) and protein thiols (P = 0.75 for interaction) was similar in CKD and control groups. There may be a potential effect modification by disease status on the effect of BMI and CRP (P = 0.10 for interaction).
Similar articles
- Effects of combination tocopherols and alpha lipoic acid therapy on oxidative stress and inflammatory biomarkers in chronic kidney disease.
Ramos LF, Kane J, McMonagle E, Le P, Wu P, Shintani A, Ikizler TA, Himmelfarb J. Ramos LF, et al. J Ren Nutr. 2011 May;21(3):211-8. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2010.08.003. Epub 2010 Dec 24. J Ren Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21185738 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Annual variation in body fat is associated with systemic inflammation in chronic kidney disease patients Stages 3 and 4: a longitudinal study.
Carvalho LK, Barreto Silva MI, da Silva Vale B, Bregman R, Martucci RB, Carrero JJ, Avesani CM. Carvalho LK, et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012 Apr;27(4):1423-8. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr450. Epub 2011 Aug 8. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012. PMID: 21825305 - Platelet activation in obese women: role of inflammation and oxidant stress.
Davì G, Guagnano MT, Ciabattoni G, Basili S, Falco A, Marinopiccoli M, Nutini M, Sensi S, Patrono C. Davì G, et al. JAMA. 2002 Oct 23-30;288(16):2008-14. doi: 10.1001/jama.288.16.2008. JAMA. 2002. PMID: 12387653 - Oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular disease in chronic renal failure.
Cottone S, Lorito MC, Riccobene R, Nardi E, Mulè G, Buscemi S, Geraci C, Guarneri M, Arsena R, Cerasola G. Cottone S, et al. J Nephrol. 2008 Mar-Apr;21(2):175-9. J Nephrol. 2008. PMID: 18446711 Review. - Blood Thiol Redox State in Chronic Kidney Disease.
Garavaglia ML, Giustarini D, Colombo G, Reggiani F, Finazzi S, Calatroni M, Landoni L, Portinaro NM, Milzani A, Badalamenti S, Rossi R, Dalle-Donne I. Garavaglia ML, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 5;23(5):2853. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052853. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269995 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The Pivotal Role of a Novel Biomarker of Reactive Oxygen Species in Chronic Kidney Disease.
Hirata Y, Yamamoto E, Tokitsu T, Fujisue K, Kurokawa H, Sugamura K, Sakamoto K, Tsujita K, Tanaka T, Kaikita K, Hokimoto S, Sugiyama S, Ogawa H. Hirata Y, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Jun;94(25):e1040. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001040. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 26107676 Free PMC article. - New insights into the role of oxidative stress in scleroderma fibrosis.
Gabrielli A, Svegliati S, Moroncini G, Amico D. Gabrielli A, et al. Open Rheumatol J. 2012;6:87-95. doi: 10.2174/1874312901206010087. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Open Rheumatol J. 2012. PMID: 22802906 Free PMC article. - AKI on CKD: heightened injury, suppressed repair, and the underlying mechanisms.
He L, Wei Q, Liu J, Yi M, Liu Y, Liu H, Sun L, Peng Y, Liu F, Venkatachalam MA, Dong Z. He L, et al. Kidney Int. 2017 Nov;92(5):1071-1083. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.06.030. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Kidney Int. 2017. PMID: 28890325 Free PMC article. Review. - The association of retinopathy and low GFR in type 2 diabetes.
Mottl AK, Kwon KS, Garg S, Mayer-Davis EJ, Klein R, Kshirsagar AV. Mottl AK, et al. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012 Dec;98(3):487-93. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2012.09.041. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012. PMID: 23068959 Free PMC article. - Dietary Intake of Proteins and Calories Is Inversely Associated With The Oxidation State of Plasma Thiols in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients.
Fanti P, Giustarini D, Rossi R, Cunningham SE, Folli F, Khazim K, Cornell J, Matteucci E, Bansal S. Fanti P, et al. J Ren Nutr. 2015 Nov;25(6):494-503. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Ren Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26235932 Free PMC article.
References
- Jones CA, McQuillan GM, Kusek JW, Eberhardt MS, Herman WH, Coresh J, Salive M, Jones CP, Agodoa LY: Serum creatinine levels in the US population: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis 32: 992–999, 1998 - PubMed
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY: Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351: 1296–1305, 2004 - PubMed
- Cheung AK, Sarnak MJ, Yan G, Dwyer JT, Heyka RJ, Rocco MV, Teehan BP, Levey AS: Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risks in chronic hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 58: 353–362, 2000 - PubMed
- Yeun JY, Levine RA, Mantadilok V, Kaysen GA: C-Reactive protein predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 35: 469–476, 2000 - PubMed
- Locatelli F, Canaud B, Eckardt KU, Stenvinkel P, Wanner C, Zoccali C: Oxidative stress in end-stage renal disease: An emerging threat to patient outcome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18: 1272–1280, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 ES000267/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK45604/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070938/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK062849/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK045604/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK62849/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials