The regulation of cell motility and chemotaxis by phospholipid signaling - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The regulation of cell motility and chemotaxis by phospholipid signaling
Verena Kölsch et al. J Cell Sci. 2008.
Abstract
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), PTEN and localized phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate [PtdIns(3,4,5)P3] play key roles in chemotaxis, regulating cell motility by controlling the actin cytoskeleton in Dictyostelium and mammalian cells. PtdIns(3,4,5)P3, produced by PI3K, acts via diverse downstream signaling components, including the GTPase Rac, Arf-GTPases and the kinase Akt (PKB). It has become increasingly apparent, however, that chemotaxis results from an interplay between the PI3K-PTEN pathway and other parallel pathways in Dictyostelium and mammalian cells. In Dictyostelium, the phospholipase PLA2 acts in concert with PI3K to regulate chemotaxis, whereas phospholipase C (PLC) plays a supporting role in modulating PI3K activity. In adenocarcinoma cells, PLC and the actin regulator cofilin seem to provide the direction-sensing machinery, whereas PI3K might regulate motility.
Figures
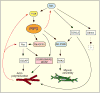
Fig. 1
PtdIns(3,4,5)_P_3 (PIP3) controls cell motility. Basic cell motility is regulated by a Ras–PI3K–PtdIns(3,4,5)_P_3–F-actin circuit. During chemotaxis, this circuit becomes restricted to the leading edge, allowing directed movement. Several downstream effectors of PtdIns(3,4,5)_P_3, such as RacGEFs and Akt, activate F-actin polymerization and myosin assembly (see text for details). Positive-feedback loops (red arrows) allow signal amplification, enhanced actin polymerization at the leading edge and the production of pseudopodia. In addition, Ras effectors, such as TORC2 (target of rapamycin complex 2), regulate the actin cytoskeleton and myosin assembly independently of PI3K and PtdIns(3,4,5)_P_3 (Lee et al., 2005). TORC2 functions, in part, by phosphorylating Akt in the C-terminal hydrophobic domain (Bhaskar and Hay, 2007). In Dictyostelium, Akt is thus regulated by two Ras-mediated pathways, PI3K and TORC2 (Lee et al., 2005).
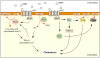
Fig. 2
PLA2 and PI3K/PTEN regulate chemotaxis in Dictyostelium. In Dictyostelium, chemotaxis is regulated by at least two intertwined and partly redundant pathways involving PI3K and PLA2. Both pathways are regulated by extracellular cAMP. The PI3K pathway is regulated, via PtdIns(4,5)_P_2 (PIP2)/PTEN, by PLC. The PLA2 pathway depends on cytosolic Ca2+, which is regulated by IP3 (thus partly by PLC), fatty acids and Ca2+ uptake. In steep gradients, either pathway is dispensable; in shallow gradients, both pathways are necessary to allow efficient chemotaxis (see text for details). Red arrows indicate enzymatic reactions. PL, phospholipids; Lyso-PL, lyso-phospholipids; Gαβγ, heterotrimeric G protein; cAR1, cAMP receptor; PIP3, PtdIns(3,4,5)_P_3.
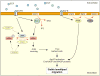
Fig. 3
PLC and cofilin are the gradient-sensing machinery in adenocarcinoma cells. In response to EGF stimulation, PLC becomes activated. By hydrolyzing PtdIns(4,5)_P_2 (PIP2), it activates cofilin. By severing actin filaments, cofilin increases the number of free barbed ends, producing the platform for the Arp2/3 complex and Ena/VASP proteins. This allows initial protrusion and determines the direction of movement. Activation of PI3K via EGF and its signaling to Arp2/3 promotes the formation of a stable lamellipod and efficient migration (see text for details). The phosphatase SSH and 14-3-3 proteins might be involved in regulating the phosphorylation state of cofilin. Red arrows indicate enzymatic reactions. EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; PIP3, PtdIns(3,4,5)_P_3; SSH, Slingshot.
Similar articles
- Phospholipase C regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate-mediated chemotaxis.
Kortholt A, King JS, Keizer-Gunnink I, Harwood AJ, Van Haastert PJ. Kortholt A, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Dec;18(12):4772-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-05-0407. Epub 2007 Sep 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17898079 Free PMC article. - Leading the way: Directional sensing through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and other signaling pathways.
Merlot S, Firtel RA. Merlot S, et al. J Cell Sci. 2003 Sep 1;116(Pt 17):3471-8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00703. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12893811 Review. - Essential role of PI3-kinase and phospholipase A2 in Dictyostelium discoideum chemotaxis.
van Haastert PJ, Keizer-Gunnink I, Kortholt A. van Haastert PJ, et al. J Cell Biol. 2007 Jun 4;177(5):809-16. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200701134. Epub 2007 May 29. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17535967 Free PMC article. - PLA2 and PI3K/PTEN pathways act in parallel to mediate chemotaxis.
Chen L, Iijima M, Tang M, Landree MA, Huang YE, Xiong Y, Iglesias PA, Devreotes PN. Chen L, et al. Dev Cell. 2007 Apr;12(4):603-14. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.03.005. Dev Cell. 2007. PMID: 17419997 Free PMC article. - Nuclear phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Akt, and PTen: emerging key regulators of anti-apoptotic signaling and carcinogenesis.
Martelli AM, Cocco L, Capitani S, Miscia S, Papa S, Manzoli FA. Martelli AM, et al. Eur J Histochem. 2007;51 Suppl 1:125-31. Eur J Histochem. 2007. PMID: 17703603 Review.
Cited by
- Genetic Markers of Spina Bifida in an Indian Cohort.
Goel P, Sharma M, Kaushik H, Kumar S, Singh H, Jain V, Dhua AK, Yadav DK, Kumar N, Agarwala S. Goel P, et al. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2024 Sep-Oct;29(5):529-535. doi: 10.4103/jiaps.jiaps_64_24. Epub 2024 Sep 9. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2024. PMID: 39479418 Free PMC article. - PIK Your Poison: The Effects of Combining PI3K and CDK Inhibitors against Metastatic Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Vitro.
Perry JR, Genenger B, Thind AS, Ashford B, Ranson M. Perry JR, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 15;16(2):370. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020370. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254859 Free PMC article. - Activation of the WAVE complex by coincident signals controls actin assembly.
Lebensohn AM, Kirschner MW. Lebensohn AM, et al. Mol Cell. 2009 Nov 13;36(3):512-24. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.10.024. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19917258 Free PMC article. - Fibroblast growth factor acts upon the transcription of phospholipase C genes in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Lo Vasco VR, Leopizzi M, Puggioni C, Della Rocca C, Businaro R. Lo Vasco VR, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014 Mar;388(1-2):51-9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1898-x. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24242047 - A PIP5 kinase essential for efficient chemotactic signaling.
Fets L, Nichols JM, Kay RR. Fets L, et al. Curr Biol. 2014 Feb 17;24(4):415-21. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.12.052. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Curr Biol. 2014. PMID: 24485835 Free PMC article.
References
- Aizawa H, Sutoh K, Tsubuki S, Kawashima S, Ishii A, Yahara I. Identification, characterization, and intracellular distribution of cofilin in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:10923–10932. - PubMed
- Aizawa H, Fukui Y, Yahara I. Live dynamics of Dictyostelium cofilin suggests a role in remodeling actin latticework into bundles. J Cell Sci. 1997;110:2333–2344. - PubMed
- Anai M, Shojima N, Katagiri H, Ogihara T, Sakoda H, Onishi Y, Ono H, Fujishiro M, Fukushima Y, Horike N, et al. A novel protein kinase B (PKB)/Akt-binding protein enhances PKB kinase activity and regulates DNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:18525–18535. - PubMed
- Andrew N, Insall RH. Chemotaxis in shallow gradients is mediated independently of PtdIns 3-kinase by biased choices between random protrusions. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:193–200. - PubMed
- Azuma Y, Kosaka K, Kashimata M. Phospholipase D-dependent and -independent p38MAPK activation pathways are required for superoxide production and chemotactic induction, respectively, in rat neutrophils stimulated by fMLP. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;568:260–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM037830-22/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM037830/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM024279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM024279-30/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM084227/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous