Phylogenetic position of the langur genera Semnopithecus and Trachypithecus among Asian colobines, and genus affiliations of their species groups - PubMed (original) (raw)
Phylogenetic position of the langur genera Semnopithecus and Trachypithecus among Asian colobines, and genus affiliations of their species groups
Martin Osterholz et al. BMC Evol Biol. 2008.
Abstract
Background: The evolutionary history of the Asian colobines is less understood. Although monophyly of the odd-nosed monkeys was recently confirmed, the relationships among the langur genera Presbytis, Semnopithecus and Trachypithecus and their position among Asian colobines remained unclear. Moreover, in Trachypithecus various species groups are recognized, but their affiliations are still disputed. To address these issues, mitochondrial and Y chromosomal sequence data were phylogenetically related and combined with presence/absence analyses of retroposon integrations.
Results: The analysed 5 kb fragment of the mitochondrial genome allows no resolution of the phylogenetic relationships among langur genera, but five retroposon integrations were detected which link Trachypithecus and Semnopithecus. According to Y chromosomal data and a 573 bp fragment of the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene, a common origin of the species groups T. [cristatus], T. [obscurus] and T. [francoisi] and their reciprocal monophyly is supported, which is also underpinned by an orthologous retroposon insertion. T. [vetulus] clusters within Semnopithecus, which is confirmed by two retroposon integrations. Moreover, this species group is paraphyletic, with T. vetulus forming a clade with the Sri Lankan, and T. johnii with the South Indian form of S. entellus. Incongruence between gene trees was detected for T. [pileatus], in that Y chromosomal data link it with T. [cristatus], T. [obscurus] and T. [francoisi], whereas mitochondrial data affiliates it with the Semnopithecus clade.
Conclusion: Neither relationships among the three langur genera nor their position within Asian colobines can be settled with 5 kb mitochondrial sequence data, but retroposon integrations confirm at least a common origin of Semnopithecus and Trachypithecus. According to Y chromosomal and 573 bp mitochondrial sequence data, T. [cristatus], T. [obscurus] and T. [francoisi] represent true members of the genus Trachypithecus, whereas T. [vetulus] clusters within Semnopithecus. Due to paraphyly of T. [vetulus] and polyphyly of Semnopithecus, a split of the genus into three species groups (S. entellus - North India, S. entellus - South India + T. johnii, S. entellus - Sri Lanka + T. vetulus) seems to be appropriate. T. [pileatus] posses an intermediate position between both genera, indicating that the species group might be the result of ancestral hybridization.
Figures
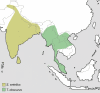
Figure 1
Distribution of the genus Semnopithecus and Trachypithecus [_obscurus_]. Genus affiliations and species groups after Groves [4].
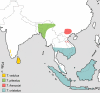
Figure 2
Distribution of the Trachypithecus species groups T. [_vetulus_], T. [_pileatus_], T. [_francoisi_] and T. [_cristatus_]. Genus affiliations and species groups after Groves [4].
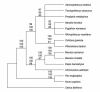
Figure 3
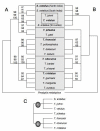
Phylogenetic relationships among colobines and related genera based on mitochondrial data. Numbers on nodes indicate support values >80% (first: ML, second: NJ, third: MP).
Figure 4
Phylogenetic relationships among Asian colobine genera based on retroposon integrations. Dark dots represent new generated data, whereas light dots refer to already published data [37]. Numbers in dots indicate single integration events.
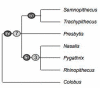
Figure 5
Phylogenetic relationships among Semnopithecus and Trachypithecus species groups based on a) mitochondrial data, b) Y chromosomal data, and c) retroposon integrations. Numbers on nodes indicate support values (first: ML, second: NJ, third: MP), and boxed species belong to a species group, with species in bold giving the name of the group.
Similar articles
- Full-length Numt analysis provides evidence for hybridization between the Asian colobine genera Trachypithecus and Semnopithecus.
Wang B, Zhou X, Shi F, Liu Z, Roos C, Garber PA, Li M, Pan H. Wang B, et al. Am J Primatol. 2015 Aug;77(8):901-10. doi: 10.1002/ajp.22419. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Am J Primatol. 2015. PMID: 25903086 - Phylogenetic incongruence between nuclear and mitochondrial markers in the Asian colobines and the evolution of the langurs and leaf monkeys.
Ting N, Tosi AJ, Li Y, Zhang YP, Disotell TR. Ting N, et al. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2008 Feb;46(2):466-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2007.11.008. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2008. PMID: 18180172 - Molecular phylogeny and biogeography of langurs and leaf monkeys of South Asia (Primates: Colobinae).
Karanth KP, Singh L, Collura RV, Stewart CB. Karanth KP, et al. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2008 Feb;46(2):683-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2007.11.026. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2008. PMID: 18191589 - Nuclear versus mitochondrial DNA: evidence for hybridization in colobine monkeys.
Roos C, Zinner D, Kubatko LS, Schwarz C, Yang M, Meyer D, Nash SD, Xing J, Batzer MA, Brameier M, Leendertz FH, Ziegler T, Perwitasari-Farajallah D, Nadler T, Walter L, Osterholz M. Roos C, et al. BMC Evol Biol. 2011 Mar 24;11:77. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-77. BMC Evol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21435245 Free PMC article. - Feeding strategies of primates in temperate and alpine forests: comparison of Asian macaques and colobines.
Tsuji Y, Hanya G, Grueter CC. Tsuji Y, et al. Primates. 2013 Jul;54(3):201-15. doi: 10.1007/s10329-013-0359-1. Epub 2013 May 25. Primates. 2013. PMID: 23708996 Review.
Cited by
- A Pervasive History of Gene Flow in Madagascar's True Lemurs (Genus Eulemur).
Everson KM, Donohue ME, Weisrock DW. Everson KM, et al. Genes (Basel). 2023 May 23;14(6):1130. doi: 10.3390/genes14061130. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372308 Free PMC article. - Historical Demography and Species Distribution Models Shed Light on Speciation in Primates of Northeast India.
Trivedi M, Arekar K, Manu S, Kuderna LFK, Rogers J, Farh KK, Bonet TM, Umapathy G. Trivedi M, et al. Ecol Evol. 2025 Feb 25;15(2):e70968. doi: 10.1002/ece3.70968. eCollection 2025 Feb. Ecol Evol. 2025. PMID: 40008062 Free PMC article. - Macroevolutionary dynamics and historical biogeography of primate diversification inferred from a species supermatrix.
Springer MS, Meredith RW, Gatesy J, Emerling CA, Park J, Rabosky DL, Stadler T, Steiner C, Ryder OA, Janečka JE, Fisher CA, Murphy WJ. Springer MS, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49521. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049521. Epub 2012 Nov 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23166696 Free PMC article. - Taxonomic Revision and Evolutionary Phylogeography of Dusky Langur (Trachypithecus obscurus) in Peninsular Malaysia.
Aifat NR, Abdul-Latiff MAB, Roos C, Munir Md-Zain B. Aifat NR, et al. Zool Stud. 2020 Nov 30;59:e64. doi: 10.6620/ZS.2020.59-64. eCollection 2020. Zool Stud. 2020. PMID: 34140981 Free PMC article. - Is the new primate genus rungwecebus a baboon?
Zinner D, Arnold ML, Roos C. Zinner D, et al. PLoS One. 2009;4(3):e4859. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004859. Epub 2009 Mar 19. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19295908 Free PMC article.
References
- Napier JR, Napier PH. Old World monkeys. New York: Academic Press; 1970.
- Szalay FS, Delson E. Evolutionary history of the primates. New York: Academic Press; 1979.
- Davies AG, Oates JF. Colobine monkeys: their ecology, behaviour, and evolution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1994.
- Groves CP. Primate Taxonomy. Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press; 2001.
- Rosenblum LL, Supriatna J, Hasan MN, Melnick DJ. High mitochondrial DNA diversity with little structure within and among leaf monkey populations (Trachypithecus cristatus and Trachypithecus auratus) Int J Primatol. 1997;18:1005–1028. doi: 10.1023/A:1026304415648. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources