Acquisition of conditioned taste aversion is impaired in the amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Acquisition of conditioned taste aversion is impaired in the amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
P J Pistell et al. Neuroscience. 2008.
Abstract
Research into the underlying mechanisms of cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease (AD) has relied traditionally on tasks such as the water maze which evaluate spatial learning and memory. Since non-spatial forms of memory are also disrupted by AD, it is critical to establish other paradigms capable of investigating these deficits. Utilizing a non-spatial learning task, acquisition of conditioned taste aversion (CTA) was evaluated in a mouse model of AD. This line of transgenic mice encode a mutated allele of the human amyloid precursor protein (APP) and presenilin 1 (PS1) genes and exhibit extensive amyloid plaque deposition in the brain by 6-7 mo of age. Compared with wild-type mice, 10-17 month old APP/PS1 mice failed to acquire CTA to saccharin. Mice that only possessed one of the two mutations were able to acquire CTA to the saccharin. In 2-5 month old APP/PS1 mice acquisition of CTA was disrupted despite the lack of extensive plaque deposition. However, further analysis indicated a potential gender difference in both the CTA deficit and onset of plaque deposition with females showing greater conditioned aversion.
Figures
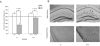
Figure 1
A) Mean saccharin preference (+/- 1 s.e.m.) after LiCl or saline administration in older APP/PS1 and wildtype mice. B) Images of the hippocampus, amygdala and cortex from representative brains of 10-17 month old APP/PS1 and wildtype mice, stained with Congo red and counterstained with cresyl violet. The images were taken at 5X and then cropped with image editing software. The brains were examined visually and no quantitative analysis was conducted.
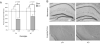
Figure 2
A) Mean saccharin preference (+/- 1 s.e.m.) after LiCl or saline administration in mice with either the mutation in APP (+/-) or PS1 (-/+). B) Images of the hippocampus, amygdala and cortex from representative brains of 9-17 month old APP (+/-) and PS1 (-/+), stained with Congo red and counterstained with cresyl violet. The images were taken at 5X and then cropped with image editing software.
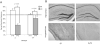
Figure 3
A) Mean saccharin preference (+/- 1 s.e.m.) after LiCl administration in 2-5 month old APP/PS1 and wildtype mice. B) Images of the hippocampus, amygdala and cortex from representative brains of 2-5 month old APP/PS1 and wildtype mice, stained with Congo red and counterstained with cresyl violet. The images were taken at 5X and then cropped with image editing software. The brains were examined visually and no quantitative analysis was conducted.
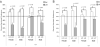
Figure 4
A) Mean saccharin preference (+/- 1 s.e.m.) in 2-5 month old APP/PS1 and wildtype mice from experiment 3 broken into groups by gender and genotype. B) Mean saccharin preference (+/- 1 s.e.m.) in 10-17 month old APP/PS1 and wildtype mice from experiment 1 broken down into groups by gender and genotype.
Figure 5
Images of the hippocampus, amygdala and cortex from representative brains of 2-5 month old male and female APP/PS1 mice, stained with Congo red and counterstained with cresyl violet, showing the sporadic Aβ deposition present in some of the brains. The images were taken at 5X and then cropped with image editing software. The brains were examined visually and no quantitative analysis was conducted. Because the plaques were more difficult to visualize in black & white, for the younger mice, arrows indicate the presence and location of plaques.
Similar articles
- Effects of accelerated senescence on learning and memory, locomotion and anxiety-like behavior in APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Lok K, Zhao H, Zhang C, He N, Shen H, Wang Z, Zhao W, Yin M. Lok K, et al. J Neurol Sci. 2013 Dec 15;335(1-2):145-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.09.018. Epub 2013 Sep 21. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24095271 - CC chemokine receptor 2 deficiency aggravates cognitive impairments and amyloid pathology in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Naert G, Rivest S. Naert G, et al. J Neurosci. 2011 Apr 20;31(16):6208-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0299-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21508244 Free PMC article. - Neurologic and motor dysfunctions in APP transgenic mice.
Lalonde R, Fukuchi K, Strazielle C. Lalonde R, et al. Rev Neurosci. 2012;23(4):363-79. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2012-0041. Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23089603 Free PMC article. Review. - When neurogenesis encounters aging and disease.
Lazarov O, Mattson MP, Peterson DA, Pimplikar SW, van Praag H. Lazarov O, et al. Trends Neurosci. 2010 Dec;33(12):569-79. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2010.09.003. Epub 2010 Oct 18. Trends Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20961627 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Expression Profiling of Cytokine, Cholinergic Markers, and Amyloid-β Deposition in the APPSWE/PS1dE9 Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease Pathology.
Reale M, D'Angelo C, Costantini E, Di Nicola M, Yarla NS, Kamal MA, Salvador N, Perry G. Reale M, et al. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;62(1):467-476. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170999. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 29439355 Free PMC article. - Impairments in remote memory stabilization precede hippocampal synaptic and cognitive failures in 5XFAD Alzheimer mouse model.
Kimura R, Ohno M. Kimura R, et al. Neurobiol Dis. 2009 Feb;33(2):229-35. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.10.006. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Neurobiol Dis. 2009. PMID: 19026746 Free PMC article. - Electroacupuncture attenuates reference memory impairment associated with astrocytic NDRG2 suppression in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.
Wang F, Zhong H, Li X, Peng Y, Kinden R, Liang W, Li X, Shi M, Liu L, Wang Q, Xiong L. Wang F, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Oct;50(2):305-13. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8609-1. Epub 2014 Jan 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24390566 - Sexual Dimorphism in the 3xTg-AD Mouse Model and Its Impact on Pre-Clinical Research.
Dennison JL, Ricciardi NR, Lohse I, Volmar CH, Wahlestedt C. Dennison JL, et al. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;80(1):41-52. doi: 10.3233/JAD-201014. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 33459720 Free PMC article. Review. - Sex and Gender Differences in Alzheimer's Disease: Genetic, Hormonal, and Inflammation Impacts.
Kolahchi Z, Henkel N, Eladawi MA, Villarreal EC, Kandimalla P, Lundh A, McCullumsmith RE, Cuevas E. Kolahchi Z, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 3;25(15):8485. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158485. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39126053 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Ashe KH. Synaptic structure and function in transgenic APP mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;924:39–41. - PubMed
- Ashe KH. Learning and memory in transgenic mice modeling Alzheimer’s disease. Learn Mem. 2001;8:301–308. - PubMed
- Ashe KH. Mechanisms of memory loss in Abeta and tau mouse models. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005;33:591–594. - PubMed
- Best P, Orr J. Effects of hippocampal lesions on passive avoidance and taste aversion learning. Physiol Behav. 1973;10:193–196. - PubMed
- Borchelt DR, Ratovitski T, van Lare J, Lee MK, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Price DL, Sisodia SS. Accelerated amyloid deposition in the brains of transgenic mice coexpressing mutant presenilin 1 and amyloid precursor proteins. Neuron. 1997;19:939–945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20 RR021945/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1P30 DK072476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1P20RR02-1945/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072476-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR021945-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases