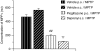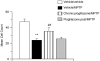The PPARgamma agonist pioglitazone is effective in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease through inhibition of monoamine oxidase B - PubMed (original) (raw)
The PPARgamma agonist pioglitazone is effective in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease through inhibition of monoamine oxidase B
L P Quinn et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2008 May.
Abstract
Background and purpose: The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma) agonist pioglitazone has previously been shown to attenuate dopaminergic cell loss in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) mouse model of Parkinson's disease, an effect attributed to its anti-inflammatory properties. In the present investigation, we provide evidence that pioglitazone is effective in the MPTP mouse model, not via an anti-inflammatory action, but through inhibition of MAO-B, the enzyme required to biotransform MPTP to its active neurotoxic metabolite 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+).
Experimental approach: Mice were treated with pioglitazone (20 mg kg(-1) b.i.d. (twice a day), p.o., for 7 days), prior and post or post-MPTP (30 mg kg(-1) s.c.) treatment. Mice were then assessed for motor impairments on a beam-walking apparatus and for reductions in TH immunoreactivity in the substantia nigra and depletions in striatal dopamine. The effects of pioglitazone on striatal MPP+ levels and MAO-B activity were also assessed.
Key results: Mice treated with MPTP showed deficits in motor performance, marked depletions in striatal dopamine levels and a concomitant reduction in TH immunoreactivity in the substantia nigra. Pretreatment with pioglitazone completely prevented these effects of MPTP. However, pretreatment with pioglitazone also significantly inhibited the MPTP-induced production of striatal MPP+ and the activity of MAO-B in the striatum.
Conclusions and implications: The neuroprotection observed with pioglitazone pretreatment in the MPTP mouse model was due to the blockade of the conversion of MPTP to its active toxic metabolite MPP+, via inhibition of MAO-B.
Figures
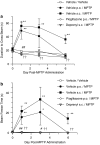
Figure 1
(a) MPTP-induced increase in time to traverse the beam and inhibition with the MAO-B inhibitor _R_-(−)-deprenyl and the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone (b) MPTP-induced increase in freeze time and inhibition with the MAO-B inhibitor _R_-(−)-deprenyl and the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone. All data are mean±s.e.mean, n_=6–10 per group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01: significantly different from vehicle/vehicle-treated mice, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01: significantly different from vehicle p.o./MPTP-treated mice, ††_P< 0.01: significantly different from vehicle s.c./MPTP-treated mice by two-way ANOVA with repeated measures followed by planned comparisons. MPTP, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ.
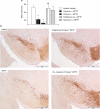
Figure 2
(a) MPTP-induced decrease in TH-positive cell counts and inhibition with the MAO-B inhibitor _R_-(−)-deprenyl and the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone, day 7 post-MPTP administration. All data are mean±s.e.mean, n_=6–10 per group. **P<0.01: significantly different from vehicle/vehicle-treated mice, ##P<0.01: significantly different from vehicle p.o./MPTP-treated mice, ††_P< 0.01: significantly different from vehicle s.c./MPTP-treated mice by ANOVA and Dunnett's test. (b) Photomicrographs of MPTP-induced TH-positive cell decrease in the substantia nigra and inhibition with the MAO-B inhibitor _R_-(−)-deprenyl and the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone, day 7 post-MPTP administration. MPTP, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ.
Figure 3
MPTP-induced increase in MPP+ and inhibition with the MAO-B inhibitor _R_-(−)-deprenyl and the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone, 3 h post-MPTP administration. All data are mean±s.e.mean, n_=7–10 per group. ##P<0.01: significantly different from vehicle p.o./MPTP-treated mice, ††_P<0.01: significantly different from vehicle s.c./MPTP-treated mice by ANOVA and LSD test. MPP+, 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; MPTP, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine.
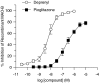
Figure 4
Inhibition of recombinant MAO-B activity by pioglitazone and _R_-(−)-deprenyl.
Figure 5
Inhibition of striatal MAO-B in MPTP-treated mice, pretreated with either _R_-(−)-deprenyl or pioglitazone. All data are mean±s.e.mean, _n_=4 per group. **P<0.01: significantly different from vehicle p.o./MPTP-treated mice, ##P<0.01: significantly different from vehicle s.c./MPTP-treated mice by ANOVA followed by planned comparisons on the predicted means. MPTP, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine.
Figure 6
MPTP-induced decrease in TH-positive cell counts and inhibition with the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone on chronic pretreatment, day 7 post-MPTP administration. All data are mean±s.e.mean, _n_=8–12 per treatment group. **P<0.01: significantly different from vehicle/vehicle-treated mice, ##P<0.01: significantly different from vehicle/MPTP-treated mice, by ANOVA and Dunnett's test. MPTP, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ.
Similar articles
- Monoamine oxidase-inhibition and MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in the non-human primate: comparison of rasagiline (TVP 1012) with selegiline.
Kupsch A, Sautter J, Götz ME, Breithaupt W, Schwarz J, Youdim MB, Riederer P, Gerlach M, Oertel WH. Kupsch A, et al. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2001;108(8-9):985-1009. doi: 10.1007/s007020170018. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2001. PMID: 11716151 - Protective action of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist pioglitazone in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease.
Breidert T, Callebert J, Heneka MT, Landreth G, Launay JM, Hirsch EC. Breidert T, et al. J Neurochem. 2002 Aug;82(3):615-24. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.00990.x. J Neurochem. 2002. PMID: 12153485 - Inhibition of transcription factor SP1 produces neuroprotective effects through decreasing MAO B activity in MPTP/MPP+ Parkinson's disease models.
Yao L, Dai X, Sun Y, Wang Y, Yang Q, Chen X, Liu Y, Zhang L, Xie W, Liu J. Yao L, et al. J Neurosci Res. 2018 Oct;96(10):1663-1676. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24266. Epub 2018 Jul 13. J Neurosci Res. 2018. PMID: 30004136 - Selegiline can mediate neuronal rescue rather than neuronal protection.
Tatton WG. Tatton WG. Mov Disord. 1993;8 Suppl 1:S20-30. doi: 10.1002/mds.870080506. Mov Disord. 1993. PMID: 8302304 Review. - The actions of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in animals as a model of Parkinson's disease.
Jenner P, Marsden CD. Jenner P, et al. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1986;20:11-39. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1986. PMID: 3091760 Review.
Cited by
- Comparative effects of parathion and chlorpyrifos on endocannabinoid and endocannabinoid-like lipid metabolites in rat striatum.
Liu J, Parsons L, Pope C. Liu J, et al. Neurotoxicology. 2015 Sep;50:20-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Neurotoxicology. 2015. PMID: 26215119 Free PMC article. - PPARβ/δ Agonist Provides Neuroprotection by Suppression of IRE1α-Caspase-12-Mediated Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway in the Rotenone Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease.
Tong Q, Wu L, Gao Q, Ou Z, Zhu D, Zhang Y. Tong Q, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Aug;53(6):3822-3831. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9309-9. Epub 2015 Jul 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26160761 - Double Attack to Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Disorders: MAO-B and Nrf2 as Elected Targets.
Basagni F, Di Paolo ML, Cozza G, Dalla Via L, Fagiani F, Lanni C, Rosini M, Minarini A. Basagni F, et al. Molecules. 2023 Nov 4;28(21):7424. doi: 10.3390/molecules28217424. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37959843 Free PMC article. - Effects and Mechanisms of Five Psoralea Prenylflavonoids on Aging-Related Diseases.
Zhou YT, Zhu L, Yuan Y, Ling S, Xu JW. Zhou YT, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jun 17;2020:2128513. doi: 10.1155/2020/2128513. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32655760 Free PMC article. Review. - Dual role of PPAR-γ in induction and expression of behavioral sensitization to cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN55,212-2.
Enayatfard L, Rostami F, Nasoohi S, Oryan S, Ahmadiani A, Dargahi L. Enayatfard L, et al. Neuromolecular Med. 2013 Sep;15(3):523-35. doi: 10.1007/s12017-013-8238-x. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Neuromolecular Med. 2013. PMID: 23794089
References
- Breidert T, Callebert J, Heneka MT, Landreth G, Launay JM, Hirsch EC. Protective action of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ agonist pioglitazone in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 2002;82:615–624. - PubMed
- Dehmer T, Heneka MT, Sastre M, Dichgans J, Schultz JB. Protection by pioglitazone in the MPTP model of Parkinson's disease correlates with IκBα induction and block of NFκB and iNOS activation. J Neurochem. 2004;88:494–501. - PubMed
- Feinstein DL, Galea E, Gavrilyuk V, Brosnan CF, Whitacre CC, Dumitrescu-Ozimek L, et al. Peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-gamma agonists prevent experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Ann Neurol. 2002;51:694–702. - PubMed
- Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Academic Press: San Diego; 1997.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical