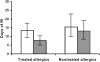Efficacy of Bacillus clausii spores in the prevention of recurrent respiratory infections in children: a pilot study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Efficacy of Bacillus clausii spores in the prevention of recurrent respiratory infections in children: a pilot study
Gian Luigi Marseglia et al. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2007 Mar.
Abstract
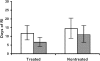
Probiotic milk has been previously demonstrated to reduce the number of respiratory infections (RI) among children attending day care centres. Thus, this pilot study was aimed to assess the efficacy and the safety of 3 month treatment with Bacillus clausii in the prevention of recurrent respiratory infections (RRI) in children. Eighty children with RRI were studied: 40 of them were randomly treated with B. clausii for 3 months, and followed up for further 3 months; 40 were included in the control group during the same period. Children treated with B. clausii had shorter duration of RI in comparison with the control group both during the treatment phase (mean 11.7 days vs 14.37; p=0.037) and the follow-up period (mean 6.6 days vs 10.92; p=0.049). This effect was evident also in allergic children during the follow-up. In conclusion, this pilot study provides the first preliminary evidence that B. clausii may exert a significant and persistent impact on RI in children and is safe and well tolerated.
Figures
Figure 1
Duration of RI (expressed as days in treated and nontreated as children with RRI during the treatment period (white column) and the follow-up (grey column). Abbreviations: RI, respiratory infections; RRI, recurrent respiratory infections.
Figure 2
Duration of RI (expressed as days) in treated and nontreated allergic children with RRI during the treatment period (white column) and the follow-up (grey column). Abbreviations: RI, respiratory infections; RRI, recurrent respiratory infections.
Similar articles
- Cytokines evaluation in nasal lavage of allergic children after Bacillus clausii administration: a pilot study.
Ciprandi G, Tosca MA, Milanese M, Caligo G, Ricca V. Ciprandi G, et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004 Apr;15(2):148-51. doi: 10.1046/j.1399-3038.2003.00102.x. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15059191 - Bacillus clausii UBBC-07 in the symptom management of upper respiratory tract infections in children: a double blind, placebo-controlled randomised study.
Madempudi RS, Neelamraju J, Ahire JJ, Muthukumar M, Rudrappa S, Gopal G, Nagendra K. Madempudi RS, et al. Benef Microbes. 2022 Oct 4;13(4):331-340. doi: 10.3920/BM2021.0187. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Benef Microbes. 2022. PMID: 36004716 Clinical Trial. - Bacillus clausii UBBC-07 reduces severity of diarrhoea in children under 5 years of age: a double blind placebo controlled study.
Sudha MR, Jayanthi N, Pandey DC, Verma AK. Sudha MR, et al. Benef Microbes. 2019 Mar 13;10(2):149-154. doi: 10.3920/BM2018.0094. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Benef Microbes. 2019. PMID: 30638396 Clinical Trial. - Current Progress and Future Perspectives on the Use of Bacillus clausii.
Ghelardi E, Abreu Y Abreu AT, Marzet CB, Álvarez Calatayud G, Perez M 3rd, Moschione Castro AP. Ghelardi E, et al. Microorganisms. 2022 Jun 17;10(6):1246. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10061246. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35744764 Free PMC article. Review. - Bacillus clausii for the Treatment of Acute Diarrhea in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.
Ianiro G, Rizzatti G, Plomer M, Lopetuso L, Scaldaferri F, Franceschi F, Cammarota G, Gasbarrini A. Ianiro G, et al. Nutrients. 2018 Aug 12;10(8):1074. doi: 10.3390/nu10081074. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30103531 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Potential Complementary Effect of Zinc and Alkalihalobacillus clausii on Gut Health and Immunity: A Narrative Review.
Wong-Chew RM, Nguyen TVH, Rogacion JM, Herve M, Pouteau E. Wong-Chew RM, et al. Nutrients. 2024 Mar 19;16(6):887. doi: 10.3390/nu16060887. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38542798 Free PMC article. Review. - Selection of a Probiotic for Its Potential for Developing a Synbiotic Peach and Grape Juice.
Prieto-Santiago V, Aguiló-Aguayo I, Ortiz-Solà J, Anguera M, Abadias M. Prieto-Santiago V, et al. Foods. 2024 Jan 22;13(2):350. doi: 10.3390/foods13020350. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38275717 Free PMC article. - Biological Characterization and Whole-Genome Analysis of Bacillus subtilis MG-1 Isolated from Mink Fecal Samples.
Ren J, Yu D, Li N, Liu S, Xu H, Li J, He F, Zou L, Cao Z, Wen J. Ren J, et al. Microorganisms. 2023 Nov 21;11(12):2821. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11122821. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38137965 Free PMC article. - The Probiotic Bacillus subtilis MB40 Improves Immunity in a Porcine Model of Listeriosis.
Garvey SM, Emami NK, Guice JL, Sriranganathan N, Penet C, Rhoads RP, Spears JL, Dalloul RA, El-Kadi SW. Garvey SM, et al. Microorganisms. 2023 Aug 18;11(8):2110. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11082110. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37630670 Free PMC article. - Immunomodulatory and Antioxidant Properties of a Novel Potential Probiotic Bacillus clausii CSI08.
Khokhlova E, Colom J, Simon A, Mazhar S, García-Lainez G, Llopis S, Gonzalez N, Enrique-López M, Álvarez B, Martorell P, Tortajada M, Deaton J, Rea K. Khokhlova E, et al. Microorganisms. 2023 Jan 18;11(2):240. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020240. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36838205 Free PMC article.
References
- Ciprandi G, Tosca MA, Milanese M, et al. Cytokines evaluation in nasal lavage of allergic children after bacillus clausii administration: a pilot study. Ped Allergy Immunol. 2004;15:148–51. - PubMed
- Ciprandi G, Vizzaccaro A, Cirillo I, et al. Bacillus clausii effects in children with allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 2005a;60:702–3. - PubMed
- Ciprandi G, Vizzaccaro A, Cirillo I, et al. Bacillus clausii exerts immuno-modulatory activity in allergic subjects: a pilot study. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005b;37:129–33. - PubMed
- Ciprandi G, Tosca MA, Fasce L. Allergic children have more numerous and severe respiratory infections than non-allergic children. Ped Allergy Immunol. 2006;17:389–91. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources