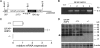Glial cell aquaporin-4 overexpression in transgenic mice accelerates cytotoxic brain swelling - PubMed (original) (raw)
Glial cell aquaporin-4 overexpression in transgenic mice accelerates cytotoxic brain swelling
Baoxue Yang et al. J Biol Chem. 2008.
Abstract
Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) is a water transport protein expressed in glial cell plasma membranes, including glial cell foot processes lining the blood-brain barrier. AQP4 deletion in mice reduces cytotoxic brain edema produced by different pathologies. To determine whether AQP4 is rate-limiting for brain water accumulation and whether altered AQP4 expression, as occurs in various pathologies, could have functional importance, we generated mice that overexpressed AQP4 in brain glial cells by a transgenic approach using the glial fibrillary acid protein promoter. Overexpression of AQP4 protein in brain by approximately 2.3-fold did not affect mouse survival, appearance, or behavior, nor did it affect brain anatomy or intracranial pressure (ICP). However, following acute water intoxication produced by intraperitoneal water injection, AQP4-overexpressing mice had an accelerated progression of cytotoxic brain swelling, with ICP elevation of 20 +/- 2 mmHg at 10 min, often producing brain herniation and death. In contrast, ICP elevation was 14 +/- 2 mmHg at 10 min in control mice and 9.8 +/- 2 mmHg in AQP4 knock-out mice. The deduced increase in brain water content correlated linearly with brain AQP4 protein expression. We conclude that AQP4 expression is rate-limiting for brain water accumulation, and thus, that altered AQP4 expression can be functionally significant.
Figures
FIGURE 1.
Generation and initial characterization of glial cell-targeted, AQP4-overexpressing transgenic mice. A, schematic of GFAP-AQP4 transgene expression vector. Gray box, cytomegalovirus enhancer fragment. Open box, GFAP promoter fragment. Filled box, mouse AQP4 cDNA coding region. Striped box, AQP4 cDNA 3′-untranslated and poly-A sequences. The thin line represents pGEM3Z vector sequences. The arrows indicate the primer sites for genotyping. The numbers indicate the length of fragments. B, genomic PCR of four GFAP-AQP4 founder mice. C, relative AQP4 mRNA expression in brain quantified by real-time PCR, using as template cDNA reversed-transcribed from total brain RNA (S.E., n = 5, *, p < 0.01). D, AQP4 immunoblot of whole brain homogenates, 5 μg of protein/lane (top). The arrow indicates AQP4 protein monomer. β-actin immunoblot was used for normalization.
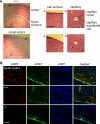
FIGURE 2.
Brain anatomy and AQP4 expression in mice. A, brain histology in hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections from GFAP-AQP4 and wild-type (+/+) mice. Left, low magnification micrograph of cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Scale bar, 1 mm. Right, higher magnification micrographs of indicated regions. Scale bar, 100 μm. B, AQP4 (red, Cy3-labeled) and GFAP (green, fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled) immunofluorescence, with cell nuclei-stained blue (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)). Scale bar, 100 μm.
FIGURE 3.
Accelerated brain water accumulation in AQP4-overexpressing mice in a water intoxication model of cytotoxic brain edema. A, baseline ICP in mice of indicated genotype. Data from individual mice are shown, with averaged data shown with error bars (S.E., differences not significant). B, original ICP curve for GFAP-AQP4 mouse. The arrow indicates the time of intraperitoneal administration of water (IP water, 10% body weight). The inset shows the time course of serum sodium after intraperitoneal administration of water (S.E., n = 4). C, representative ICP curves for two mice of each genotype. D, summary of ICP curve analysis: ΔICP at 10 and 20 min, d(ICP)/d_t_ at 10 min after water intoxication, maximal d(ICP)/d_t_, and time to reach maximal d(ICP)/d_t_ (S.E., 5–8 mice/group, *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01 when compared with +/+ mice).
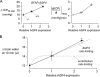
FIGURE 4.
Correlations between ICP parameters and brain AQP4 protein expression. A, ΔICP at 10 min (left) and maximal d(ICP)/d_t_ (right) determined from ICP curve analysis plotted against AQP4 protein expression determined by immunoblot analysis (S.E.). B, deduced increase in brain water at 10 min following intraperitoneal administration of water (Δ brain water, in μl), as a function of brain AQP4 expression. Δ brain water at 10 min is a measure of osmotic water permeability of the blood-brain barrier. Hypothetical curves (dashed) show predictions if AQP4 is rate-limiting for blood-brain barrier water permeability versus if the endothelium is rate-limiting for blood-brain water permeability.
Similar articles
- AQP4-A25Q Point Mutation in Mice Depolymerizes Orthogonal Arrays of Particles and Decreases Polarized Expression of AQP4 Protein in Astrocytic Endfeet at the Blood-Brain Barrier.
Zhu DD, Yang G, Huang YL, Zhang T, Sui AR, Li N, Su WH, Sun HL, Gao JJ, Ntim M, Guan RX, Jin LL, Yu J, Huang ZY, Ma TH, Li S. Zhu DD, et al. J Neurosci. 2022 Oct 26;42(43):8169-8183. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0401-22.2022. Epub 2022 Sep 13. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36100398 Free PMC article. - Aquaporin-4 and brain edema.
Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS. Papadopoulos MC, et al. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007 Jun;22(6):778-84. doi: 10.1007/s00467-006-0411-0. Epub 2007 Mar 9. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17347837 Free PMC article. Review. - Three distinct roles of aquaporin-4 in brain function revealed by knockout mice.
Verkman AS, Binder DK, Bloch O, Auguste K, Papadopoulos MC. Verkman AS, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Aug;1758(8):1085-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.02.018. Epub 2006 Mar 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16564496 Review. - Poldip2 mediates blood-brain barrier disruption and cerebral edema by inducing AQP4 polarity loss in mouse bacterial meningitis model.
Gao M, Lu W, Shu Y, Yang Z, Sun S, Xu J, Gan S, Zhu S, Qiu G, Zhuo F, Xu S, Wang Y, Chen J, Wu X, Huang J. Gao M, et al. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020 Dec;26(12):1288-1302. doi: 10.1111/cns.13446. Epub 2020 Aug 12. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020. PMID: 32790044 Free PMC article. - Deletion of aquaporin-4 changes the perivascular glial protein scaffold without disrupting the brain endothelial barrier.
Eilert-Olsen M, Haj-Yasein NN, Vindedal GF, Enger R, Gundersen GA, Hoddevik EH, Petersen PH, Haug FM, Skare Ø, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Burkhardt JM, Thoren AE, Nagelhus EA. Eilert-Olsen M, et al. Glia. 2012 Mar;60(3):432-40. doi: 10.1002/glia.22277. Epub 2011 Nov 30. Glia. 2012. PMID: 22131281
Cited by
- Effect of methylprednisolone on experimental brain edema in magnetic resonance imaging.
Kozler P, Herynek V, Marešová D, Perez PD, Šefc L, Pokorný J. Kozler P, et al. Physiol Res. 2020 Nov 16;69(5):919-926. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934460. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Physiol Res. 2020. PMID: 32901489 Free PMC article. - Changes in cannabinoid receptors, aquaporin 4 and vimentin expression after traumatic brain injury in adolescent male mice. Association with edema and neurological deficit.
Lopez-Rodriguez AB, Acaz-Fonseca E, Viveros MP, Garcia-Segura LM. Lopez-Rodriguez AB, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Jun 3;10(6):e0128782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128782. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26039099 Free PMC article. - Aquaporins in spinal cord injury: the janus face of aquaporin 4.
Nesic O, Guest JD, Zivadinovic D, Narayana PA, Herrera JJ, Grill RJ, Mokkapati VU, Gelman BB, Lee J. Nesic O, et al. Neuroscience. 2010 Jul 28;168(4):1019-35. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.01.037. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20109536 Free PMC article. Review. - The Dual Role of AQP4 in Cytotoxic and Vasogenic Edema Following Spinal Cord Contusion and Its Possible Association With Energy Metabolism via COX5A.
Huang Y, Li SN, Zhou XY, Zhang LX, Chen GX, Wang TH, Xia QJ, Liang N, Zhang X. Huang Y, et al. Front Neurosci. 2019 Jun 14;13:584. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00584. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31258460 Free PMC article. - Acetazolamide Treatment Prevents Redistribution of Astrocyte Aquaporin 4 after Murine Traumatic Brain Injury.
Glober NK, Sprague S, Ahmad S, Mayfield KG, Fletcher LM, Digicaylioglu MH, Sayre NL. Glober NK, et al. Neurosci J. 2019 May 2;2019:2831501. doi: 10.1155/2019/2831501. eCollection 2019. Neurosci J. 2019. PMID: 31187032 Free PMC article.
References
- Ghabriel, M. N., Thomas, A., and Vink, R. (2006) Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 96 402-406 - PubMed
- Neal, C. J., Lee, E. Y., Gyorgy, A., Ecklund, J. M., Agoston, D. V., and Ling, G. S. (2007) J. Neurotrauma 24 1609-1617 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK 35124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EB 00415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- HL 59198/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- EY 13574/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 73856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK 72517/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases