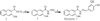Use of dynasore, the small molecule inhibitor of dynamin, in the regulation of endocytosis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Use of dynasore, the small molecule inhibitor of dynamin, in the regulation of endocytosis
Tom Kirchhausen et al. Methods Enzymol. 2008.
Abstract
The large GTPase dynamin is essential for clathrin-dependent coated-vesicle formation. Dynasore is a cell-permeable small molecule that inhibits the GTPase activity of dynamin1, dynamin2 and Drp1, the mitochondrial dynamin. Dynasore was discovered in a screen of approximately 16,000 compounds for inhibitors of the dynamin2 GTPase. Dynasore is a noncompetitive inhibitor of dynamin GTPase activity and blocks dynamin-dependent endocytosis in cells, including neurons. It is fast acting (seconds) and its inhibitory effect in cells can be reversed by washout. Here we present a detailed synthesis protocol for dynasore, and describe a series of experiments used to analyze the inhibitory effects of dynasore on dynamin in vitro and to study the effects of dynasore on endocytosis in cells.
Figures
Figure 6.1
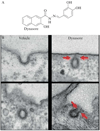
(A) Chemical structure of dynasore. (B) Effect of dynasore on clathrin-coated structures. The figure shows representative images of clathrin-coated structures of cells treated with DMSO (vehicle) or with 80 µM dynasore. The upper and lower left panels illustrate the appearance of endocytic coated pits and coated vesicles; the upper and lower right panels show the appearance of “U” and “O” shape-coated pits associated with the plasma membrane in cells treated with dynasore. The gray arrows highlight the extent of the constriction states observed upon treatment with dynasore. (From Macia, E., Ehrlich, M., Massol, R., Boucrot, E., Brunner, C., and Kirchhausen, T. (2006). Dynasore, a cell-permeable inhibitor of dynamin. Dev. Cell 10, 839–850.)
Figure 6.2
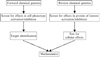
Strategy for the chemical genetics discovery approach. The reverse chemical genetics approach was used to discover dynasore. Dynasore is cell permeable and interferes with all functions known to be associated with dynamin. (From Macia, E., Ehrlich, M., Massol, R., Boucrot, E., Brunner, C., and Kirchhausen, T. (2006). Dynasore, a cell-permeable inhibitor of dynamin. Dev. Cell 10, 839–850; and Newton, A. J., Kirchhausen, T., Murthy, V.N. (2006). Inhibition of dynamin completely blocks compensatory synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 17955–17960.)
Figure 6.3
Schemefor the synthesis of dynasore. (a) H4N2, CH3OH, 65°, 43% yield. (b) 3,4-dihydroxy-benzaldehyde, CH3CO2H, CH3CH2OH, 78°, 85% yield.
Figure 6.4
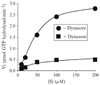
Determination of kinetics parameters for the effects of dynasore on the GTPase activity of dynamin. Effect of 40 µM dynasore on the rate of GTPase hydrolysis of 0.2 mM Dyn2ΔPRD determined at ambient temperature. The control experiment was done in the presence of 1% DMSO (vehicle) Initial rates of GTP hydrolysis were determined for different concentrations of GTP (S).
Similar articles
- Dynasore, a cell-permeable inhibitor of dynamin.
Macia E, Ehrlich M, Massol R, Boucrot E, Brunner C, Kirchhausen T. Macia E, et al. Dev Cell. 2006 Jun;10(6):839-50. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.04.002. Dev Cell. 2006. PMID: 16740485 - Building a better dynasore: the dyngo compounds potently inhibit dynamin and endocytosis.
McCluskey A, Daniel JA, Hadzic G, Chau N, Clayton EL, Mariana A, Whiting A, Gorgani NN, Lloyd J, Quan A, Moshkanbaryans L, Krishnan S, Perera S, Chircop M, von Kleist L, McGeachie AB, Howes MT, Parton RG, Campbell M, Sakoff JA, Wang X, Sun JY, Robertson MJ, Deane FM, Nguyen TH, Meunier FA, Cousin MA, Robinson PJ. McCluskey A, et al. Traffic. 2013 Dec;14(12):1272-89. doi: 10.1111/tra.12119. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Traffic. 2013. PMID: 24025110 Free PMC article. - Synthesis of potent chemical inhibitors of dynamin GTPase.
Lee S, Jung KY, Park J, Cho JH, Kim YC, Chang S. Lee S, et al. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Aug 15;20(16):4858-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.06.092. Epub 2010 Jun 22. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010. PMID: 20621477 - Dynasore - not just a dynamin inhibitor.
Preta G, Cronin JG, Sheldon IM. Preta G, et al. Cell Commun Signal. 2015 Apr 10;13:24. doi: 10.1186/s12964-015-0102-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2015. PMID: 25889964 Free PMC article. Review. - Targeting membrane trafficking in infection prophylaxis: dynamin inhibitors.
Harper CB, Popoff MR, McCluskey A, Robinson PJ, Meunier FA. Harper CB, et al. Trends Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;23(2):90-101. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2012.10.007. Epub 2012 Nov 17. Trends Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23164733 Review.
Cited by
- Nonpathogenic Lactobacillus rhamnosus activates the inflammasome and antiviral responses in human macrophages.
Miettinen M, Pietilä TE, Kekkonen RA, Kankainen M, Latvala S, Pirhonen J, Österlund P, Korpela R, Julkunen I. Miettinen M, et al. Gut Microbes. 2012 Nov-Dec;3(6):510-22. doi: 10.4161/gmic.21736. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Gut Microbes. 2012. PMID: 22895087 Free PMC article. - Channel properties of Nax expressed in neurons.
Matsumoto M, Hiyama TY, Kuboyama K, Suzuki R, Fujikawa A, Noda M. Matsumoto M, et al. PLoS One. 2015 May 11;10(5):e0126109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126109. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25961826 Free PMC article. - Endocytosis of Connexin 36 is Mediated by Interaction with Caveolin-1.
Kotova A, Timonina K, Zoidl GR. Kotova A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 29;21(15):5401. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155401. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751343 Free PMC article. - The dynamin chemical inhibitor dynasore impairs cholesterol trafficking and sterol-sensitive genes transcription in human HeLa cells and macrophages.
Girard E, Paul JL, Fournier N, Beaune P, Johannes L, Lamaze C, Védie B. Girard E, et al. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029042. Epub 2011 Dec 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22205993 Free PMC article. - Entry of nanoparticles into cells and tissues: status and challenges.
Sandvig K, Iversen TG, Skotland T. Sandvig K, et al. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2024 Aug 12;15:1017-1029. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.15.83. eCollection 2024. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39161463 Free PMC article.
References
- Barylko B, Binns D, Lin KM, Atkinson MAL, Jameson DM, Yin HL, Albanesi JP. Synergistic activation of dynamin gtpase by grb2 and phosphoinositides. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:3791–3797. - PubMed
- Cao H, Thompson HM, Krueger EW, McNiven MA. Disruption of Golgi structure and function in mammalian cells expressing a mutant dynamin. J. Cell Sci. 2000;113:1993–2002. - PubMed
- Cogan EB, Birrell GB, Griffith OH. A robotics-based automated assay for inorganic and organic phosphates. Anal. Biochem. 1999;271:29–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM036548/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM062566/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM075252/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM03548/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM075252/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM62566/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous