Cooperative retraction of bundled type IV pili enables nanonewton force generation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Cooperative retraction of bundled type IV pili enables nanonewton force generation
Nicolas Biais et al. PLoS Biol. 2008.
Abstract
The causative agent of gonorrhea, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, bears retractable filamentous appendages called type IV pili (Tfp). Tfp are used by many pathogenic and nonpathogenic bacteria to carry out a number of vital functions, including DNA uptake, twitching motility (crawling over surfaces), and attachment to host cells. In N. gonorrhoeae, Tfp binding to epithelial cells and the mechanical forces associated with this binding stimulate signaling cascades and gene expression that enhance infection. Retraction of a single Tfp filament generates forces of 50-100 piconewtons, but nothing is known, thus far, on the retraction force ability of multiple Tfp filaments, even though each bacterium expresses multiple Tfp and multiple bacteria interact during infection. We designed a micropillar assay system to measure Tfp retraction forces. This system consists of an array of force sensors made of elastic pillars that allow quantification of retraction forces from adherent N. gonorrhoeae bacteria. Electron microscopy and fluorescence microscopy were used in combination with this novel assay to assess the structures of Tfp. We show that Tfp can form bundles, which contain up to 8-10 Tfp filaments, that act as coordinated retractable units with forces up to 10 times greater than single filament retraction forces. Furthermore, single filament retraction forces are transient, whereas bundled filaments produce retraction forces that can be sustained. Alterations of noncovalent protein-protein interactions between Tfp can inhibit both bundle formation and high-amplitude retraction forces. Retraction forces build over time through the recruitment and bundling of multiple Tfp that pull cooperatively to generate forces in the nanonewton range. We propose that Tfp retraction can be synchronized through bundling, that Tfp bundle retraction can generate forces in the nanonewton range in vivo, and that such high forces could affect infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
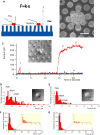
Figure 1. N. gonorrhoeae Tfp Can Exert Forces in the nN Range
(A) Schematic of the force measurement assay used in this study. (B) SEM micrograph of a microcolony with Tfp pulling on pillars (here the pillars are molded in polydimethylsiloxane, a widely used, silicon-based polymer, to enable SEM). Scale bar = 2 μm. (C) Time course of the force exerted on a pillar. (1, trace β): short-lived, low-force pulling event. (2, trace β): long-lived, high-force event. Trace α shows a neighboring pillar that did not move. (D and E), Histograms of the forces recorded in static studies for WT MS11 in DMEM (D) or in DMEM + BSA (E). Inserts are differential interference contrast images of representative microlonies in the samples. Scale bar=5 μm. (F and G), Histograms of the forces recorded in dynamic studies of WT MS11 in DMEM (F) or DMEM + BSA (G). Inserts represent close-ups of the tail of each force distribution curve (forces between 200 pN and 1000 pN).
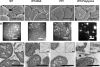
Figure 2. Tfp from WT MS11 and MS11PilT in Different States of Bundling
WT: MS11 not exposed to BSA; WT + BSA: MS11 incubated with BSA; PilT: MS11PilT not exposed to BSA; WT + polylysine: MS11 incubated with polylysine. (A) SEM micrographs. Scale bar = 500 nm. (B) Fluorescent images of microcolonies immunostained with monoclonal anti-Tfp antibody (anti-SM1). Scale bar = 2 μm. (C) Thin-section EM image of Tfp and Tfp bundles. Insert in each panel represents a higher magnification image of representative Tfp in the sample. Note the bundles in the WT and WT+polylysine samples that are not present in the WT+BSA and pilT samples. Scale bar = 500nm. Scale bar = 50 nm in the inserts.
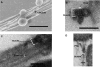
Figure 3. Structure of Tfp Bundles
(A) SEM picture of a collection of bundles in a polylysine-treated sample. Scale bar = 500 nm. (B) Thin-section microscopy image of the cross-section of a collection of bundles in a polylysine-treated sample (here composed of two bundles). Scale bar = 50 nm. (C) Thin-section microscopy image of the long axis of a collection of bundles in a polylysine-treated sample (here composed of three bundles). Scale bar = 50 nm. (D) Thin-section microscopy image of a bundle attached to a bacterium in a sample incubated with DMEM only. Scale bar = 50 nm.
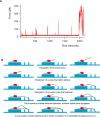
Figure 4. Model for Tfp Bundling and Retraction
(A) Progressive rise of force applied by a bacterium on one pillar over time (more than 30 min total time). (B) Cartoon showing the successive association (bundling) of Tfp filaments with each other and their retraction. Timeline begins with top left panel and is read from left to right, top to bottom.
Similar articles
- Influence of type IV pilus retraction on the architecture of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae-infected cell cortex.
Higashi DL, Zhang GH, Biais N, Myers LR, Weyand NJ, Elliott DA, So M. Higashi DL, et al. Microbiology (Reading). 2009 Dec;155(Pt 12):4084-4092. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.032656-0. Epub 2009 Sep 17. Microbiology (Reading). 2009. PMID: 19762436 Free PMC article. - Pilus retraction powers bacterial twitching motility.
Merz AJ, So M, Sheetz MP. Merz AJ, et al. Nature. 2000 Sep 7;407(6800):98-102. doi: 10.1038/35024105. Nature. 2000. PMID: 10993081 - Attenuation of the Type IV Pilus Retraction Motor Influences Neisseria gonorrhoeae Social and Infection Behavior.
Hockenberry AM, Hutchens DM, Agellon A, So M. Hockenberry AM, et al. mBio. 2016 Dec 6;7(6):e01994-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01994-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27923924 Free PMC article. - Type IV pili and cell motility.
Wall D, Kaiser D. Wall D, et al. Mol Microbiol. 1999 Apr;32(1):1-10. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01339.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10216854 Review. - Type IV pili and twitching motility.
Mattick JS. Mattick JS. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2002;56:289-314. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160938. Epub 2002 Jan 30. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12142488 Review.
Cited by
- Multiscale modeling of bacterial colonies: how pili mediate the dynamics of single cells and cellular aggregates.
Pönisch W, Weber CA, Juckeland G, Biais N, Zaburdaev V. Pönisch W, et al. New J Phys. 2017 Jan;19(1):015003. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/aa5483. Epub 2017 Jan 10. New J Phys. 2017. PMID: 34017216 Free PMC article. - External Stresses Affect Gonococcal Type 4 Pilus Dynamics.
Kraus-Römer S, Wielert I, Rathmann I, Grossbach J, Maier B. Kraus-Römer S, et al. Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 25;13:839711. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.839711. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35283813 Free PMC article. - Influence of type IV pilus retraction on the architecture of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae-infected cell cortex.
Higashi DL, Zhang GH, Biais N, Myers LR, Weyand NJ, Elliott DA, So M. Higashi DL, et al. Microbiology (Reading). 2009 Dec;155(Pt 12):4084-4092. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.032656-0. Epub 2009 Sep 17. Microbiology (Reading). 2009. PMID: 19762436 Free PMC article. - DNA-uptake pili of Vibrio cholerae are required for chitin colonization and capable of kin recognition via sequence-specific self-interaction.
Adams DW, Stutzmann S, Stoudmann C, Blokesch M. Adams DW, et al. Nat Microbiol. 2019 Sep;4(9):1545-1557. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0479-5. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Nat Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31182799 Free PMC article. - Pili-Induced Clustering of N. gonorrhoeae Bacteria.
Taktikos J, Lin YT, Stark H, Biais N, Zaburdaev V. Taktikos J, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Sep 10;10(9):e0137661. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137661. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26355966 Free PMC article.
References
- Mattick JS, Whitchurch CB, Alm RA. The molecular genetics of type-4 fimbriae in Pseudomonas aeruginosa - a review. Gene. 1996;179:147–155. - PubMed
- Parge HE, Forest KT, Hickey MJ, Christensen DA, Getzoff ED, et al. Structure of the fibre-forming protein pilin at 2.6 A resolution. Nature. 1995;378:32–38. - PubMed
- Craig L, Volkmann N, Arvai AS, Pique ME, Yeager M, et al. Type IV pilus structure by cryo-electron microscopy and crystallography: implications for pilus assembly and functions. Mol Cell. 2006;23:651–662. - PubMed
- Burrows LL. Weapons of mass retraction. Mol Microbiol. 2005;57:878–888. - PubMed
- Merz AJ, So M. Interactions of pathogenic Neisseriae with epithelial cell membranes. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:423–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources