The RNA polymerase II core promoter - the gateway to transcription - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The RNA polymerase II core promoter - the gateway to transcription
Tamar Juven-Gershon et al. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008 Jun.
Abstract
The RNA polymerase II core promoter is generally defined to be the sequence that directs the initiation of transcription. This simple definition belies a diverse and complex transcriptional module. There are two major types of core promoters - focused and dispersed. Focused promoters contain either a single transcription start site or a distinct cluster of start sites over several nucleotides, whereas dispersed promoters contain several start sites over 50-100 nucleotides and are typically found in CpG islands in vertebrates. Focused promoters are more ancient and widespread throughout nature than dispersed promoters; however, in vertebrates, dispersed promoters are more common than focused promoters. In addition, core promoters may contain many different sequence motifs, such as the TATA box, BRE, Inr, MTE, DPE, DCE, and XCPE1, that specify different mechanisms of transcription and responses to enhancers. Thus, the core promoter is a sophisticated gateway to transcription that determines which signals will lead to transcription initiation.
Figures
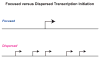
Figure 1
Focused versus dispersed core promoters. In focused core promoters, transcription initiates at a single site or in a cluster of sites in a narrow region of several nucleotides. Dispersed core promoters are typically found in CpG islands in vertebrates and usually yield multiple weak start sites over a region of 50 to 100 nucleotides. Focused core promoters are more ancient and widespread throughout nature than dispersed core promoters. In vertebrates, however, dispersed promoters are more common than focused promoters. There may be fundamental differences in the basic mechanisms of transcription from focused versus dispersed core promoters.
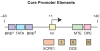
Figure 2
Core promoter motifs. This diagram, which is drawn roughly to scale, shows some of the known core promoter elements for transcription by RNA polymerase II. There are no universal core promoter elements. Each of these elements is found in only a fraction (typically estimated to be from 1% to 30%, depending on the motif) of all core promoters. The Inr is probably the most commonly occurring core promoter motif. There are additional core promoter elements that remain to be discovered. The TATA box, Inr, MTE, DPE, and DCE are recognition sites for the binding of transcription factor TFIID. It should be noted, however, that there are multiple forms of TFIID and TFIID-related protein complexes that could potentially interact with the core promoter. BREu and BREd interact with TFIIB.
Similar articles
- Regulation of gene expression via the core promoter and the basal transcriptional machinery.
Juven-Gershon T, Kadonaga JT. Juven-Gershon T, et al. Dev Biol. 2010 Mar 15;339(2):225-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.08.009. Epub 2009 Aug 13. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 19682982 Free PMC article. Review. - Characterization of transcription from TATA-less promoters: identification of a new core promoter element XCPE2 and analysis of factor requirements.
Anish R, Hossain MB, Jacobson RH, Takada S. Anish R, et al. PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5103. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005103. Epub 2009 Apr 1. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19337366 Free PMC article. - TSS seq based core promoter architecture in blood feeding Tsetse fly (Glossina morsitans morsitans) vector of Trypanosomiasis.
Mwangi S, Attardo G, Suzuki Y, Aksoy S, Christoffels A. Mwangi S, et al. BMC Genomics. 2015 Sep 22;16(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1921-6. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26394619 Free PMC article. - Perspectives on the RNA polymerase II core promoter.
Kadonaga JT. Kadonaga JT. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012 Jan-Feb;1(1):40-51. doi: 10.1002/wdev.21. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 23801666 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Inactivated RNA polymerase II open complexes can be reactivated with TFIIE.
Čabart P, Luse DS. Čabart P, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 6;287(2):961-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.297572. Epub 2011 Nov 27. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22119917 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide analysis of Pax8 binding provides new insights into thyroid functions.
Ruiz-Llorente S, Carrillo Santa de Pau E, Sastre-Perona A, Montero-Conde C, Gómez-López G, Fagin JA, Valencia A, Pisano DG, Santisteban P. Ruiz-Llorente S, et al. BMC Genomics. 2012 Apr 24;13:147. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-147. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22531031 Free PMC article. - Defining the status of RNA polymerase at promoters.
Core LJ, Waterfall JJ, Gilchrist DA, Fargo DC, Kwak H, Adelman K, Lis JT. Core LJ, et al. Cell Rep. 2012 Oct 25;2(4):1025-35. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.08.034. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Cell Rep. 2012. PMID: 23062713 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide identification and characterization of transcription start sites and promoters in the tunicate Ciona intestinalis.
Yokomori R, Shimai K, Nishitsuji K, Suzuki Y, Kusakabe TG, Nakai K. Yokomori R, et al. Genome Res. 2016 Jan;26(1):140-50. doi: 10.1101/gr.184648.114. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Genome Res. 2016. PMID: 26668163 Free PMC article. - The Fuchs corneal dystrophy-associated CTG repeat expansion in the TCF4 gene affects transcription from its alternative promoters.
Sirp A, Leite K, Tuvikene J, Nurm K, Sepp M, Timmusk T. Sirp A, et al. Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 28;10(1):18424. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75437-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33116252 Free PMC article.
References
- Smale ST, Kadonaga JT. The RNA polymerase II core promoter. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:449–479. - PubMed
- Thomas MC, Chiang CM. The general transcription machinery and general cofactors. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2006;41:105–178. Comprehensive review on basal transcription by RNA polymerase II. - PubMed
- Juven-Gershon T, Hsu JY, Kadonaga JT. Perspectives on the RNA polymerase II core promoter. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34:1047–1050. Review on core promoter motifs. - PubMed
- Müller F, Demény MA, Tora L. New problems in RNA polymerase II transcription initiation: matching the diversity of core promoters with a variety of promoter recognition factors. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:14685–14689. Review on core promoters. - PubMed
- Sandelin A, Carninci P, Lenhard B, Ponjavic J, Hayashizaki Y, Hume DA. Mammalian RNA polymerase II core promoters: insights from genome-wide studies. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:424–436. Review on the generation and use of CAGE (cap analysis of gene expression) tag data for the study of mammalian RNA polymerase II core promoters. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM041249/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM041249/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM041249-19S1/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM041249-19/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM041249-20/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources