IAPs: what's in a name? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
IAPs: what's in a name?
Srinivasa M Srinivasula et al. Mol Cell. 2008.
Abstract
Originally described in insect viruses, cellular proteins with Baculoviral IAP repeat (BIR) motifs have been thought to function primarily as inhibitors of apoptosis. The subsequent finding that a subset of IAPs that contain a RING domain have ubiquitin protein ligase (E3) activity implied the presence of other functions. It is now known that IAPs are involved in mitotic chromosome segregation, cellular morphogenesis, copper homeostasis, and intracellular signaling. Here, we review the current understanding of the roles of IAPs in apoptotic and nonapoptotic processes and explore the notion that the latter represents the primary physiologic activities of IAPs.
Figures
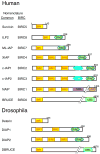
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of the human and Drosophila IAP family of proteins
The number of residues in each IAP is shown, as well as the functional motifs that they contain. The BIRC nomenclature equivalents are provided. ILP2, ML-IAP, and Deterin are shown in this figure but not discussed in the review because little information about their function is available. NCBI GenBank (
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank
) accession numbers are survivin: O15392; ILP2 : Q96P09; ML-IAP : Q96CA5; XIAP : P98710; c-IAP1 : Q13490; c-IAP2 : Q13489; NAIP : Q13075; Bruce : Q9NR09; Deterin : NM_142351; DIAP1 : Q24306; DIAP2 : Q24307: DBruce : NP_649995. CARD, caspase-associated recruitment domain; UBC, ubiquitin-conjugation; NOD, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain; LRR, leucine-rich repeats.
Similar articles
- Insect inhibitor-of-apoptosis (IAP) proteins are negatively regulated by signal-induced N-terminal degrons absent within viral IAP proteins.
Vandergaast R, Mitchell JK, Byers NM, Friesen PD. Vandergaast R, et al. J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4481-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03659-14. Epub 2015 Feb 4. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25653450 Free PMC article. - Inhibitors of apoptosis catch ubiquitin.
Rajalingam K, Dikic I. Rajalingam K, et al. Biochem J. 2009 Jan 1;417(1):e1-3. doi: 10.1042/BJ20082215. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19061481 - IAPs: Modular regulators of cell signalling.
Budhidarmo R, Day CL. Budhidarmo R, et al. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Mar;39:80-90. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25542341 Review. - IAPs: more than just inhibitors of apoptosis proteins.
Dubrez-Daloz L, Dupoux A, Cartier J. Dubrez-Daloz L, et al. Cell Cycle. 2008 Apr 15;7(8):1036-46. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.8.5783. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18414036 Review. - Smac mimetics activate the E3 ligase activity of cIAP1 protein by promoting RING domain dimerization.
Feltham R, Bettjeman B, Budhidarmo R, Mace PD, Shirley S, Condon SM, Chunduru SK, McKinlay MA, Vaux DL, Silke J, Day CL. Feltham R, et al. J Biol Chem. 2011 May 13;286(19):17015-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.222919. Epub 2011 Mar 10. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21393245 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Significance of survivin expression: Prognostic value and survival in stage III non-small cell lung cancer.
Wang M, Liu BG, Yang ZY, Hong X, Chen GY. Wang M, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2012 Jun;3(6):983-988. doi: 10.3892/etm.2012.512. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Exp Ther Med. 2012. PMID: 22970003 Free PMC article. - PTK7 regulates radioresistance through nuclear factor-kappa B in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Park M, Yoon HJ, Kang MC, Kwon J, Lee HW. Park M, et al. Tumour Biol. 2016 Oct;37(10):14217-14224. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5288-3. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27557627 - Phenethyl isothiocyanate suppresses inhibitor of apoptosis family protein expression in prostate cancer cells in culture and in vivo.
Sakao K, Desineni S, Hahm ER, Singh SV. Sakao K, et al. Prostate. 2012 Jul 1;72(10):1104-16. doi: 10.1002/pros.22457. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Prostate. 2012. PMID: 22161756 Free PMC article. - Survivin - The inconvenient IAP.
Altieri DC. Altieri DC. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Mar;39:91-6. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.12.007. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25591986 Free PMC article. Review. - Novel Polypyridyl chelators deplete cellular zinc and destabilize the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) prior to induction of apoptosis in human prostate and breast cancer cells.
Zuo J, Schmitt SM, Zhang Z, Prakash J, Fan Y, Bi C, Kodanko JJ, Dou QP. Zuo J, et al. J Cell Biochem. 2012 Aug;113(8):2567-75. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24132. J Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22415943 Free PMC article.
References
- Altieri DC. Validating survivin as a cancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:46–54. - PubMed
- Altieri DC. The case for survivin as a regulator of microtubule dynamics and cell-death decisions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:609–615. - PubMed
- Arora V, Cheung HH, Plenchette S, Micali OC, Liston P, Korneluk RG. Degradation of survivin by the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP)-XAF1 complex. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:26202–26209. - PubMed
- Brown JM, Wilson G. Apoptosis genes and resistance to cancer therapy: what does the experimental and clinical data tell us? Cancer Biol Ther. 2003;2:477–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials