Developmental origins of childhood overweight: potential public health impact - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multicenter Study
Developmental origins of childhood overweight: potential public health impact
Matthew W Gillman et al. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008 Jul.
Abstract
Several modifiable pre- and postnatal determinants of childhood overweight are known, but no one has examined how they influence risk of overweight in combination. We estimated the risk of overweight at age 3 years according to levels of maternal smoking during pregnancy, gestational weight gain, breastfeeding duration, and infant sleep duration. We studied 1,110 mother-child pairs in Project Viva, a prospective prebirth cohort study. The main outcome measure was child overweight (BMI for age and sex >or=95th percentile) at age 3. We ran logistic regression models with all four modifiable risk factors as well as the covariates maternal BMI and education, child race/ethnicity, and household income. From the model, we obtained the estimated probability of overweight for each of the 16 combinations of the four risk factors. During pregnancy, 9.8% of mothers smoked and 50% gained excessive weight. In infancy, 73% mother-child pairs breastfed for <12 m, and 31% of infants slept <12 h/day. Among the 3-year-old children in the cohort, 9.5% were overweight. In the prediction model, the estimated probability of overweight ranged from 0.06 among children exposed to favorable levels of all four risk factors, to 0.29 with adverse levels of all four. Healthful levels of four behaviors during early development predicted much lower probability of overweight at age 3 than adverse levels. Interventions to modify several factors during pregnancy and infancy could have substantial impact on prevention of childhood overweight.
Figures
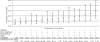
Figure 1
Predicted probability of overweight at 3 years for 16 combinations of four modifiable risk factors during pregnancy and infancy. Bars show 95% confidence limits. Also shown is prevalence in this cohort for each depicted combination of factors. Data from 1,110 mother–child pairs participating in Project Viva. Probabilities are adjusted for maternal education and BMI, household income, and child race/ethnicity. [Table: see text]
Similar articles
- Maternal smoking during pregnancy and childhood overweight and fat distribution: the KOALA Birth Cohort Study.
Timmermans SH, Mommers M, Gubbels JS, Kremers SP, Stafleu A, Stehouwer CD, Prins MH, Penders J, Thijs C. Timmermans SH, et al. Pediatr Obes. 2014 Feb;9(1):e14-25. doi: 10.1111/j.2047-6310.2012.00141.x. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Pediatr Obes. 2014. PMID: 23362054 - Short sleep duration in infancy and risk of childhood overweight.
Taveras EM, Rifas-Shiman SL, Oken E, Gunderson EP, Gillman MW. Taveras EM, et al. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2008 Apr;162(4):305-11. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.162.4.305. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2008. PMID: 18391138 Free PMC article. - Weight gain in the first week of life predicts overweight at 2 years: A prospective cohort study.
Feldman-Winter L, Burnham L, Grossman X, Matlak S, Chen N, Merewood A. Feldman-Winter L, et al. Matern Child Nutr. 2018 Jan;14(1):e12472. doi: 10.1111/mcn.12472. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Matern Child Nutr. 2018. PMID: 28636245 Free PMC article. - Systematic review and meta-analyses of risk factors for childhood overweight identifiable during infancy.
Weng SF, Redsell SA, Swift JA, Yang M, Glazebrook CP. Weng SF, et al. Arch Dis Child. 2012 Dec;97(12):1019-26. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2012-302263. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Arch Dis Child. 2012. PMID: 23109090 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The early life exposome and autism risk: a role for the maternal microbiome?
Di Gesù CM, Buffington SA. Di Gesù CM, et al. Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2385117. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2385117. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 39120056 Free PMC article. Review. - Effects of Screen Viewing Time on Sleep Duration and Bedtime in Children Aged 1 and 3 Years: Japan Environment and Children's Study.
Nishioka T, Hasunuma H, Okuda M, Taniguchi N, Fujino T, Shimomura H, Tanaka Y, Shima M, Takeshima Y, Japan Environment And Children's Study Group. Nishioka T, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 25;19(7):3914. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19073914. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35409594 Free PMC article. - Structured diet and exercise guidance in pregnancy to improve health in women and their offspring: study protocol for the Be Healthy in Pregnancy (BHIP) randomized controlled trial.
Perreault M, Atkinson SA, Mottola MF, Phillips SM, Bracken K, Hutton EK, Xie F, Meyre D, Morassut RE, Prapavessis H, Thabane L; BHIP Study team. Perreault M, et al. Trials. 2018 Dec 19;19(1):691. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-3065-x. Trials. 2018. PMID: 30567604 Free PMC article. - Maternal nutritional history predicts obesity in adult offspring independent of postnatal diet.
Howie GJ, Sloboda DM, Kamal T, Vickers MH. Howie GJ, et al. J Physiol. 2009 Feb 15;587(Pt 4):905-15. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.163477. Epub 2008 Dec 22. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19103681 Free PMC article. - Reduced carbohydrate diet to improve metabolic outcomes and decrease adiposity in obese peripubertal African American girls.
Casazza K, Cardel M, Dulin-Keita A, Hanks LJ, Gower BA, Newton AL, Wallace S. Casazza K, et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012 Mar;54(3):336-42. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31823df207. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22067112 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Kim J, Peterson KE, Scanlon KS, et al. Trends in overweight from 1980 through 2001 among preschool-aged children enrolled in a health maintenance organization. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2006;14:1107–1112. - PubMed
- Chen A, Pennell ML, Klebanoff MA, Rogan WJ, Longnecker MP. Maternal smoking during pregnancy in relation to child overweight: follow-up to age 8 years. Int J Epidemiol. 2006;35:121–130. - PubMed
- Power C, Jefferis BJ. Fetal environment and subsequent obesity: a study of maternal smoking. Int J Epidemiol. 2002;31:413–419. - PubMed
- von Kries R, Toschke AM, Koletzko B, Slikker W., Jr Maternal smoking during pregnancy and childhood obesity. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;156:954–961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 DK040561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL 68041/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HD 044807/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL068041/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064925-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075504-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD034568/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075504/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HD034568/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL068041-06/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 075504/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 64925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD034568-07/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD044807-05/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD 34568/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD044807/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK040561-13/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous