MAOA methylation is associated with nicotine and alcohol dependence in women - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
MAOA methylation is associated with nicotine and alcohol dependence in women
Robert A Philibert et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2008.
Abstract
In recent years, the role of epigenetic phenomenon, such as methylation, in mediating vulnerability to behavioral illness has become increasingly appreciated. One prominent locus at which epigenetic phenomena are thought to be in play is the monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) locus. In order to examine the role of methylation at this locus, we performed quantitative methylation analysis across the promoter region of this gene in lymphoblast lines derived from 191 subjects participating in the Iowa Adoption Studies (IAS). We analyzed the resulting data with respect to genotype and lifetime symptom counts for the more common major behavioral disorders in the IAS, antisocial personality disorder (ASPD), and substance use disorders (alcohol (AD) and nicotine dependence (ND)). We found that methylation status was significantly associated with lifetime symptom counts for ND (P < 0.001) and AD (P < 0.008) in women, but not men. Furthermore, a trend was found for women homozygous for the 3,3 allele to have a higher degree of overall methylation than women homozygous for the 4,4 allele (P < 0.10). We conclude that methylation of MAOA may play a significant role in common psychiatric illness and that further examination of epigenetic processes at this locus is in order.
Copyright 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
Figure 1
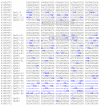
The sequence and structure of the MAOA promoter region. The first CpG island begins at bp 43398975 and contains 18 CpG residues. A second CpG island begins at bp 43399493 and contains 70 CpG residues. The position of each of the CpG residues is noted in the figure. The first exon of MAOA is denoted by small blue letters and is wholly contained within the second island. The positions of the primers used to amplify the MAOA VNTR are denoted by boxed letters. The transcription start site (TSS) is at bp43400353 between CpG residues 64 and 65.
Figure 2
The average methylation ratios (methyl CpG/total CpG) at each CpG residue for each sex. The bp position on the X chromosome is given on the X axis and corresponds to the position of each of the residues in Figure 1. The average values for female subjects are depicted by blue squares, while the average values for males are depicted by red circles. The position of MAOA exon 1 is denoted by the box with the direction of transcription being indicated by the line with arrows.
Figure 3
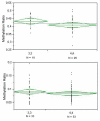
The relationship of MAOA VNTR genotype to methylation in females (above) and males (below). There was a trend for association for female 3,3 homozygotes to have higher average methylation (methyl CpG/total CpG) than female 4,4 homozygotes (43.3% ± 3.8 vs 40.9% ± 5.2; p<0.10). There was no significant difference between males hemizygous for the 3 repeat allele as compared to those with the 4 allele although the arithmetic difference was in the same direction (9.0 ± 3.7 vs 8.3 ± 2.6; p<0.32).
Similar articles
- Interaction between a functional MAOA locus and childhood sexual abuse predicts alcoholism and antisocial personality disorder in adult women.
Ducci F, Enoch MA, Hodgkinson C, Xu K, Catena M, Robin RW, Goldman D. Ducci F, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2008 Mar;13(3):334-47. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002034. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Mol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 17592478 - Monoamine oxidase A gene promoter methylation and transcriptional downregulation in an offender population with antisocial personality disorder.
Checknita D, Maussion G, Labonté B, Comai S, Tremblay RE, Vitaro F, Turecki N, Bertazzo A, Gobbi G, Côté G, Turecki G. Checknita D, et al. Br J Psychiatry. 2015 Mar;206(3):216-22. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.114.144964. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Br J Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25497297 - Possible interaction between MAOA and DRD2 genes associated with antisocial alcoholism among Han Chinese men in Taiwan.
Wang TJ, Huang SY, Lin WW, Lo HY, Wu PL, Wang YS, Wu YS, Ko HC, Shih JC, Lu RB. Wang TJ, et al. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Jan 30;31(1):108-14. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2006.08.010. Epub 2006 Sep 27. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17007976 - Epigenetic signature of MAOA and MAOB genes in mental disorders.
Ziegler C, Domschke K. Ziegler C, et al. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018 Nov;125(11):1581-1588. doi: 10.1007/s00702-018-1929-6. Epub 2018 Sep 21. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018. PMID: 30242487 Review. - Behavioral genetics in antisocial spectrum disorders and psychopathy: a review of the recent literature.
Gunter TD, Vaughn MG, Philibert RA. Gunter TD, et al. Behav Sci Law. 2010 Mar-Apr;28(2):148-73. doi: 10.1002/bsl.923. Behav Sci Law. 2010. PMID: 20422643 Review.
Cited by
- The impact of recent alcohol use on genome wide DNA methylation signatures.
Philibert RA, Plume JM, Gibbons FX, Brody GH, Beach SR. Philibert RA, et al. Front Genet. 2012 Apr 10;3:54. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00054. eCollection 2012. Front Genet. 2012. PMID: 22514556 Free PMC article. - Methylation of the MAOA promoter is associated with schizophrenia.
Yang H, Li J, Ji A, Hu L, Zhang X, Liu L, Qing L, Yan M, Nie S. Yang H, et al. Ann Transl Med. 2020 Jul;8(14):864. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-4481. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32793708 Free PMC article. Retracted. - DNA co-methylation modules in postmortem prefrontal cortex tissues of European Australians with alcohol use disorders.
Wang F, Xu H, Zhao H, Gelernter J, Zhang H. Wang F, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 14;6:19430. doi: 10.1038/srep19430. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26763658 Free PMC article. - Genetics and epigenetics of alcohol dependence.
Nieratschker V, Batra A, Fallgatter AJ. Nieratschker V, et al. J Mol Psychiatry. 2013 Jul 11;1(1):11. doi: 10.1186/2049-9256-1-11. eCollection 2013. J Mol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 25408904 Free PMC article. Review. - Genetically contextual effects of smoking on genome wide DNA methylation.
Dogan MV, Beach SRH, Philibert RA. Dogan MV, et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017 Sep;174(6):595-607. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32565. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017. PMID: 28686328 Free PMC article.
References
- Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, et al. Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science. 2003;301(5631):386–9. - PubMed
- Kim-Cohen J, Caspi A, Taylor A, et al. MAOA, maltreatment, and gene-environment interaction predicting children’s mental health: new evidence and a meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry. 2006;11(10):903–913. - PubMed
- Caspi A, McClay J, Moffitt TE, et al. Role of genotype in the cycle of violence in maltreated children. Science. 2002;297(5582):851–4. - PubMed
- Koller G, Bondy B, Preuss UW, Bottlender M, Soyka M. No association between a polymorphism in the promoter region of the MAOA gene with antisocial personality traits in alcoholics. Alcohol Alcohol. 2003;38(1):31–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical