High-dose interleukin-2 for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma : a retrospective analysis of response and survival in patients treated in the surgery branch at the National Cancer Institute between 1986 and 2006 - PubMed (original) (raw)
High-dose interleukin-2 for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma : a retrospective analysis of response and survival in patients treated in the surgery branch at the National Cancer Institute between 1986 and 2006
Jacob A Klapper et al. Cancer. 2008.
Abstract
Background: The treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with high-dose interleukin-2 (HD IL-2) has resulted in durable tumor regression in a minority of patients. The current study presents the authors' 20-year experience administering this immunotherapeutic agent.
Methods: Patients with metastatic RCC (n = 259) were treated with HD IL-2 alone from January 13, 1986 through December 31, 2006 at the Surgery Branch of the National Cancer Institute. Potential predictive factors for response and survival, both pretreatment and treatment-related, were first subjected to univariate analysis and then to multivariate logistic regression or a Cox proportional hazards model. Finally, the authors investigated Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) prognostic factors for survival to assess their predictive value in the patient population in the current study.
Results: A total of 23 patients experienced a complete response and 30 patients achieved a partial response, for an overall objective response rate of 20%. All partial responders had developed disease recurrence at the time of last follow-up, but only 4 complete responders had experienced disease recurrence by that time. Despite toxicities, only 2 patients developed treatment-related mortalities over this same time period. A higher baseline weight (P = .05) and MSKCC prognostic factors (P = .02) were found to be the variables most associated with response. For survival >4 years and overall survival, several pretreatment and treatment-related factors maintained significance, but none more so than response (P < .0001).
Conclusions: HD IL-2 can induce complete tumor regression in a small number of patients, and many patients have experienced extended disease-free intervals. Given its relative safety, HD IL-2 should still be considered a first-line therapy in patients with metastatic RCC who have an overall good performance status.
Figures
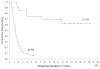
FIGURE 1
Response duration for patients with a complete response (CR) versus those with a partial response (PR).
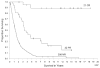
FIGURE 2
Overall survival for patients with a complete response (CR) versus those with a partial response (PR) versus nonresponders (NR).
Similar articles
- Dorsal Muscle Attenuation May Predict Failure to Respond to Interleukin-2 Therapy in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma.
Otemuyiwa B, Derstine BA, Zhang P, Wong SL, Sabel MS, Redman BG, Wang SC, Alva AS, Davenport MS. Otemuyiwa B, et al. Acad Radiol. 2017 Sep;24(9):1094-1100. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Acad Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28341412 - Treatment of 283 consecutive patients with metastatic melanoma or renal cell cancer using high-dose bolus interleukin 2.
Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Topalian SL, Schwartzentruber DJ, Weber JS, Parkinson DR, Seipp CA, Einhorn JH, White DE. Rosenberg SA, et al. JAMA. 1994 Mar 23-30;271(12):907-13. JAMA. 1994. PMID: 8120958 - Clinical efficacy and prognostic factors for overall survival in Japanese patients with metastatic renal cell cancer treated with sunitinib.
Yuasa T, Tsuchiya N, Urakami S, Horikawa Y, Narita S, Inoue T, Saito M, Yamamoto S, Yonese J, Fukui I, Nakano K, Takahashi S, Hatake K, Habuchi T. Yuasa T, et al. BJU Int. 2012 May;109(9):1349-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10534.x. Epub 2011 Aug 25. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 21883864 - Genomically annotated risk model for advanced renal-cell carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study.
Voss MH, Reising A, Cheng Y, Patel P, Marker M, Kuo F, Chan TA, Choueiri TK, Hsieh JJ, Hakimi AA, Motzer RJ. Voss MH, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Dec;19(12):1688-1698. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30648-X. Epub 2018 Nov 8. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30416077 Free PMC article. - Use of interleukin-2 in advanced renal carcinoma: meta-analysis and review of the literature.
Malaguarnera M, Ferlito L, Gulizia G, Di Fazio I, Pistone G. Malaguarnera M, et al. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2001 Jul;57(4):267-73. doi: 10.1007/s002280100321. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11549203 Review.
Cited by
- A 25 year perspective on the evolution and advances in an understanding of the biology, evaluation and treatment of kidney cancer.
Geynisman DM, Maranchie JK, Ball MW, Bratslavsky G, Singer EA. Geynisman DM, et al. Urol Oncol. 2021 Sep;39(9):548-560. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2021.04.038. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Urol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34092483 Free PMC article. Review. - Perspectives in drug development for metastatic renal cell cancer.
Basu B, Eisen T. Basu B, et al. Target Oncol. 2010 Jun;5(2):139-56. doi: 10.1007/s11523-010-0149-2. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Target Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20689997 Review. - Cancer Immunotherapy Beyond Checkpoint Blockade: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review.
Welty NE, Gill SI. Welty NE, et al. JACC CardioOncol. 2022 Dec 20;4(5):563-578. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2022.11.006. eCollection 2022 Dec. JACC CardioOncol. 2022. PMID: 36636439 Free PMC article. Review. - Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: From Biology to Treatment.
Kase AM, George DJ, Ramalingam S. Kase AM, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 21;15(3):665. doi: 10.3390/cancers15030665. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36765622 Free PMC article. Review. - Prognostic role of the innate immune signature CD163 and "eat me" signal calreticulin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Anno T, Tanaka N, Takamatsu K, Hakozaki K, Kufukihara R, Baba Y, Takeda T, Matsumoto K, Morita S, Kosaka T, Mikami S, Nishihara H, Mizuno R, Oya M. Anno T, et al. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023 Jun;72(6):1779-1788. doi: 10.1007/s00262-023-03369-8. Epub 2023 Jan 17. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023. PMID: 36646952 Free PMC article.
References
- SEER Database. Cancer of the Kidney and Renal Pelvis. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program; 2007.
- Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, et al., editors. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 6. Chapter 36. New York: Springer; 2002. pp. 323–328.
- Yang JC, Topalian SL, Schwartzentruber DJ, et al. The use of polyethylene glycol-modified interleukin-2 (PEG-IL-2) in the treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma and melanoma: a Phase I study and a randomized prospective study comparing IL-2 alone versus IL-2 combined with PEG-IL-2. Cancer. 1995;76:687–694. - PubMed
- Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Yang JC, et al. Combination therapy with interleukin-2 and alpha-interferon for the treatment of patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1989;7:1863–1874. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources