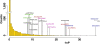Genomic and epigenetic alterations deregulate microRNA expression in human epithelial ovarian cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2008 May 13;105(19):7004-9.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801615105. Epub 2008 May 5.
Stefano Volinia, Tomas Bonome, George Adrian Calin, Joel Greshock, Nuo Yang, Chang-Gong Liu, Antonis Giannakakis, Pangiotis Alexiou, Kosei Hasegawa, Cameron N Johnstone, Molly S Megraw, Sarah Adams, Heini Lassus, Jia Huang, Sippy Kaur, Shun Liang, Praveen Sethupathy, Arto Leminen, Victor A Simossis, Raphael Sandaltzopoulos, Yoshio Naomoto, Dionyssios Katsaros, Phyllis A Gimotty, Angela DeMichele, Qihong Huang, Ralf Bützow, Anil K Rustgi, Barbara L Weber, Michael J Birrer, Artemis G Hatzigeorgiou, Carlo M Croce, George Coukos
Affiliations
- PMID: 18458333
- PMCID: PMC2383982
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0801615105
Genomic and epigenetic alterations deregulate microRNA expression in human epithelial ovarian cancer
Lin Zhang et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008.
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are an abundant class of small noncoding RNAs that function as negative gene regulators. miRNA deregulation is involved in the initiation and progression of human cancer; however, the underlying mechanism and its contributions to genome-wide transcriptional changes in cancer are still largely unknown. We studied miRNA deregulation in human epithelial ovarian cancer by integrative genomic approach, including miRNA microarray (n = 106), array-based comparative genomic hybridization (n = 109), cDNA microarray (n = 76), and tissue array (n = 504). miRNA expression is markedly down-regulated in malignant transformation and tumor progression. Genomic copy number loss and epigenetic silencing, respectively, may account for the down-regulation of approximately 15% and at least approximately 36% of miRNAs in advanced ovarian tumors and miRNA down-regulation contributes to a genome-wide transcriptional deregulation. Last, eight miRNAs located in the chromosome 14 miRNA cluster (Dlk1-Gtl2 domain) were identified as potential tumor suppressor genes. Therefore, our results suggest that miRNAs may offer new biomarkers and therapeutic targets in epithelial ovarian cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
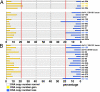
Fig. 1.
Numerous miRNAs are down-regulated in late-stage or high-grade ovarian cancer. (A) Heat map showing the 44 miRNAs significantly down-regulated in late-stage relative to early-stage EOC. (B) Heat map showing the 13 miRNAs significantly down-regulated in high-grade relative to low-grade EOC. (C) Heat map showing the miRNAs significantly down-regulated in late-stage or high-grade serous EOC. (D) Venn diagrams of down-regulated miRNAs in different analyses.
Fig. 2.
DNA copy number deletions contribute to down-regulation of miRNAs. (A) DNA copy number status of 17 genomic loci containing miRNAs differentially expressed between IOSE cells and EOC cell lines. (Upper) Four up-regulated miRNAs. (Lower) Thirteen down-regulated miRNAs. Red lines indicate the designated cut-off for significant alterations (20%). (B) DNA copy number status of 16 genomic loci containing miRNAs significantly down-regulated in late-stage EOC. Red lines indicate the designated cut-off for significant alterations (20%).
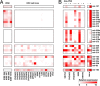
Fig. 3.
Epigenetic alterations silence miRNA expression in ovarian cancer. (A) Heat map depicts expression of 24 miRNAs in IOSE cells and EOC cell lines analyzed by real-time RT-PCR. (B) Expression of the same 24 miRNAs in five EOC cell lines and HeLa cells after treatment with demethylating agent 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-Aza-CdR) and the histone deacetylase inhibitor 4-phenylbutyric acid (PBA) for 6 days.
Fig. 4.
miRNA deregulation affects mRNA transcripts. Histograms of negative natural logarithms of 4,096 P values derived from one-tailed Wilcoxon rank sum test applied to the distributions of each hexamer occurrence in the 3′ UTRs of all up-regulated versus unchanged mRNA transcripts.
Fig. 5.
Down-regulation of miRNA cluster at the Dlk1-Gtl2 domain is associated with poor survival. (A) Nonsupervised clustering of the eight Dlk1-Gtl2 domain miRNA expression signatures classifies 73 late-stage EOC in two distinct clusters (cluster 1, n = 38; cluster 2, n = 35). (B) Five-year survival of patients with advanced stage EOC whose tumors belong to cluster 1 (blue) or cluster 2 (green). (C) Summary of clinicopathologic characteristics of patients in the two clusters. (D) Examples of high and low proliferation index based on Ki67 immunohistochemistry staining in late-stage EOC. (E) Summary of proliferation index in tumors from the two clusters.
Similar articles
- Novel miRNA genes deregulated by aberrant methylation in ovarian carcinoma are involved in metastasis.
Loginov VI, Pronina IV, Burdennyy AM, Filippova EA, Kazubskaya TP, Kushlinsky DN, Utkin DO, Khodyrev DS, Kushlinskii NE, Dmitriev AA, Braga EA. Loginov VI, et al. Gene. 2018 Jul 1;662:28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.04.005. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29631007 - Clinically relevant microRNAs in ovarian cancer.
Zhang S, Lu Z, Unruh AK, Ivan C, Baggerly KA, Calin GA, Li Z, Bast RC Jr, Le XF. Zhang S, et al. Mol Cancer Res. 2015 Mar;13(3):393-401. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0424. Epub 2014 Oct 10. Mol Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25304686 Free PMC article. Review. - Mechanisms of microRNA deregulation in human cancer.
Deng S, Calin GA, Croce CM, Coukos G, Zhang L. Deng S, et al. Cell Cycle. 2008 Sep 1;7(17):2643-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.17.6597. Epub 2008 Sep 12. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18719391 Review. - Integration of microRNA signatures of distinct mammary epithelial cell types with their gene expression and epigenetic portraits.
Pal B, Chen Y, Bert A, Hu Y, Sheridan JM, Beck T, Shi W, Satterley K, Jamieson P, Goodall GJ, Lindeman GJ, Smyth GK, Visvader JE. Pal B, et al. Breast Cancer Res. 2015 Jun 18;17(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0585-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26080807 Free PMC article. - Prognostic significance of Dicer expression in ovarian cancer-link to global microRNA changes and oestrogen receptor expression.
Faggad A, Budczies J, Tchernitsa O, Darb-Esfahani S, Sehouli J, Müller BM, Wirtz R, Chekerov R, Weichert W, Sinn B, Mucha C, Elwali NE, Schäfer R, Dietel M, Denkert C. Faggad A, et al. J Pathol. 2010 Feb;220(3):382-91. doi: 10.1002/path.2658. J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 19960504
Cited by
- Non-coding RNAs as therapeutic targets in cancer and its clinical application.
Leng X, Zhang M, Xu Y, Wang J, Ding N, Yu Y, Sun S, Dai W, Xue X, Li N, Yang Y, Shi Z. Leng X, et al. J Pharm Anal. 2024 Jul;14(7):100947. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.02.001. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Pharm Anal. 2024. PMID: 39149142 Free PMC article. Review. - The microRNA Let-7 and its exosomal form: Epigenetic regulators of gynecological cancers.
Wang F, Zhou C, Zhu Y, Keshavarzi M. Wang F, et al. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Jun 5;40(1):42. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09884-3. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38836981 Free PMC article. Review. - Current strategies for early epithelial ovarian cancer detection using miRNA as a potential tool.
Bhadra M, Sachan M, Nara S. Bhadra M, et al. Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Apr 16;11:1361601. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1361601. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38690293 Free PMC article. Review. - Drug resistance in ovarian cancer: from mechanism to clinical trial.
Wang L, Wang X, Zhu X, Zhong L, Jiang Q, Wang Y, Tang Q, Li Q, Zhang C, Wang H, Zou D. Wang L, et al. Mol Cancer. 2024 Mar 28;23(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01967-3. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38539161 Free PMC article. Review. - miRNA on the Battlefield of Cancer: Significance in Cancer Stem Cells, WNT Pathway, and Treatment.
Bhagtaney L, Dharmarajan A, Warrier S. Bhagtaney L, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 27;16(5):957. doi: 10.3390/cancers16050957. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473318 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–866. - PubMed
- Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–269. - PubMed
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical