Disparate proteome reactivity profiles of carbon electrophiles - PubMed (original) (raw)
Disparate proteome reactivity profiles of carbon electrophiles
Eranthie Weerapana et al. Nat Chem Biol. 2008 Jul.
Erratum in
- Nat Chem Biol. 2008 Jul;4(7):following 407
Abstract
Insights into the proteome reactivity of electrophiles are crucial for designing activity-based probes for enzymes lacking cognate affinity labels. Here, we show that different classes of carbon electrophiles exhibit markedly distinct amino acid labeling profiles in proteomes, ranging from selective reactivity with cysteine to adducts with several amino acids. These data specify electrophilic chemotypes with restricted and permissive reactivity profiles to guide the design of next-generation functional proteomics probes.
Figures
Figure 1
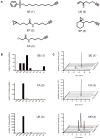
Proteome and solution reactivities of carbon electrophile probes. (a), Panel of probes utilized in this study. (b), Proteome reactivity profiles for SE, CA and UK probes demonstrating the number of assigned peptides with unique labeling sites on nine nucleophilic amino acid residues; top panel, SE, middle panel, CA, bottom panel, UK. (c), Solution reactivity profiles for SE, CA and UK probes; top panel, SE, middle panel, CA, bottom panel, UK. Representative extracted ion chromatograms are shown for product formation upon reacting the probes with 20 equivalents of each amino acid derivative in PBS for 12 hrs.
Figure 2
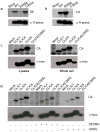
Labeling of ALDH, and the CLIC protein family with carbon electrophile probes. (a), Labeling of WT, E269A, and C303A ALDH1 enzymes with the CA probe. (b),. Labeling of WT, E269A, and C303A ALDH1 enzymes with the SE probe. Top panel, fluorescent gel images shown in grayscale demonstrating the selective labeling of the E269A and C303A mutants with the CA and SE probes, respectively. Bottom panel, western blots confirming equivalent expression of WT, E269A and C303A ALDH1 enzymes using α-X-press antibodies. (c), Labeling of CLICs with the CA probe in lysates and in whole cells. Top panel, fluorescent gel images shown in grayscale. Bottom panel, western blots confirming expression of CLICs using α-myc antibodies. (d), Nitric oxide and oxidized glutathione treatment of CLICs. Lysates were treated with either 5 mM of the nitric oxide donor, diethylamine nitric oxide, sodium salt (DEANO) or 2 mM of oxidized glutathione (GSSG). Top panel, fluorescent gel images shown in grayscale. Bottom panel, western blots confirming expression of CLICs using α-myc antibodies.
Comment in
- Proteomes take the electrophilic bait.
Kodadek T. Kodadek T. Nat Chem Biol. 2008 Jul;4(7):387-8. doi: 10.1038/nchembio0708-387. Nat Chem Biol. 2008. PMID: 18560426 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Proteomes take the electrophilic bait.
Kodadek T. Kodadek T. Nat Chem Biol. 2008 Jul;4(7):387-8. doi: 10.1038/nchembio0708-387. Nat Chem Biol. 2008. PMID: 18560426 No abstract available. - Activity-based probes as a tool for functional proteomic analysis of proteases.
Fonović M, Bogyo M. Fonović M, et al. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2008 Oct;5(5):721-30. doi: 10.1586/14789450.5.5.721. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2008. PMID: 18937562 Free PMC article. Review. - [Advances in applications of activity-based chemical probes in the characterization of amino acid reactivities].
Li J, Wang G, Ye M, Qin H. Li J, et al. Se Pu. 2023 Jan;41(1):14-23. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2022.05013. Se Pu. 2023. PMID: 36633073 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese. - Proteomics evaluation of chemically cleavable activity-based probes.
Fonović M, Verhelst SH, Sorum MT, Bogyo M. Fonović M, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007 Oct;6(10):1761-70. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M700124-MCP200. Epub 2007 Jul 5. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007. PMID: 17615255 - Investigating the proteome reactivity and selectivity of aryl halides.
Shannon DA, Banerjee R, Webster ER, Bak DW, Wang C, Weerapana E. Shannon DA, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2014 Mar 5;136(9):3330-3. doi: 10.1021/ja4116204. Epub 2014 Feb 24. J Am Chem Soc. 2014. PMID: 24548313
Cited by
- Novel inhibitors for PRMT1 discovered by high-throughput screening using activity-based fluorescence polarization.
Dillon MB, Bachovchin DA, Brown SJ, Finn MG, Rosen H, Cravatt BF, Mowen KA. Dillon MB, et al. ACS Chem Biol. 2012 Jul 20;7(7):1198-204. doi: 10.1021/cb300024c. Epub 2012 Apr 20. ACS Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22506763 Free PMC article. - Proteome-Wide Fragment-Based Ligand and Target Discovery.
Forrest I, Parker CG. Forrest I, et al. Isr J Chem. 2023 Mar;63(3-4):e202200098. doi: 10.1002/ijch.202200098. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Isr J Chem. 2023. PMID: 38213795 Free PMC article. - Methylsulfonyl benzothiazole (MSBT): a selective protein thiol blocking reagent.
Zhang D, Devarie-Baez NO, Li Q, Lancaster JR Jr, Xian M. Zhang D, et al. Org Lett. 2012 Jul 6;14(13):3396-9. doi: 10.1021/ol301370s. Epub 2012 Jun 8. Org Lett. 2012. PMID: 22681565 Free PMC article. - Reflecting on 20 years of progress.
Johnson R. Johnson R. Nat Chem Biol. 2025 Jan;21(1):3-5. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01792-1. Nat Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 39719498 No abstract available. - αβ,α'β'-Diepoxyketones are mechanism-based inhibitors of nucleophilic cysteine enzymes.
de Munnik M, Lithgow J, Brewitz L, Christensen KE, Bates RH, Rodriguez-Miquel B, Schofield CJ. de Munnik M, et al. Chem Commun (Camb). 2023 Oct 26;59(86):12859-12862. doi: 10.1039/d3cc02932h. Chem Commun (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37815791 Free PMC article.
References
- Evans MJ, Cravatt BF. Chem Rev. 2006;106:3279–301. - PubMed
- Kidd D, Liu Y, Cravatt BF. Biochemistry. 2001;40:4005–15. - PubMed
- Kato D, et al. Nat Chem Biol. 2005;1:33–8. - PubMed
- Patricelli MP, et al. Biochemistry. 2007;46:350–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources