Associations of adiponectin, resistin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with insulin resistance - PubMed (original) (raw)
Associations of adiponectin, resistin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with insulin resistance
Marie-France Hivert et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Aug.
Abstract
Context: Adipose tissue-derived adipokines may contribute to insulin resistance.
Objective: We tested the hypothesis that adipokines are associated with insulin resistance in a community-based cohort and that associations are maintained in people with and without the metabolic syndrome (high vs. low risk of diabetes).
Design, setting, and participants: We studied a cross-sectional sample of 2356 individuals attending the seventh examination (1998-2001) of the Framingham Offspring Study. We measured levels of glucose, insulin, adiponectin, resistin, and TNFalpha in fasting blood samples and defined metabolic syndrome by updated National Cholesterol Education Program criteria. We used ANOVA to test associations of adipokines with insulin resistance and multivariable logistic regression models to assess joint associations of adipokines and metabolic syndrome with insulin resistance.
Main outcome measure: Homeostasis model (HOMA-IR), with insulin resistance defined by HOMA-IR greater than the 75th percentile, was measured.
Results: Age- and sex-adjusted HOMA-IR levels were inversely related to adiponectin (r = -0.40, P < 0.0001) and positively related to resistin (r = 0.13, P < 0.0001) and TNFalpha (r = 0.12, P < 0.0001). The prevalence of insulin resistance increased with decreasing tertiles of adiponectin (from 10.9% in the third to 42.5% in the first tertile; P < 0.0001) and increasing tertiles of resistin (from 19.3 to 30.9%; P < 0.0001) and TNFalpha (from 18.8 to 32.0%; P < 0.0001). Results were similar after adjustment for body mass index. These associations were present in individuals with or without the metabolic syndrome. In multivariable regression models, metabolic syndrome and adipokines individually and jointly were significantly associated with insulin resistance.
Conclusion: Adverse levels of adipokines are associated with insulin resistance in individuals at low or high diabetes risk.
Figures
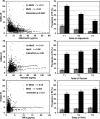
Figure 1
Adverse adipokine levels are associated with insulin resistance in individuals with metabolic syndrome (MetS) and without (no MetS). The left-hand column shows scatter plots (crude data) of plasma adiponectin (top), resistin (middle), and TNF-α (bottom) in relation to insulin resistance measured by HOMA-IR according to metabolic syndrome status (gray circle, no MetS; black circle, MetS; dashed line, no MetS; solid line, MetS). The right-hand column shows the prevalence (and
se
s) of insulin resistance (IR) (age-sex adjusted) defined by HOMA-IR greater than 75th percentile in relation to adipokines grouped into tertiles of increasing plasma concentration, according to metabolic syndrome status (light gray, no metabolic syndrome; dark gray, metabolic syndrome). For trends within metabolic syndrome categories, P < 0.0001 for decreasing prevalence of insulin resistance across adiponectin tertiles in both groups; for resistin (middle) and TNF-α (bottom), all P < 0.01 for trends in insulin resistance prevalence across tertiles in both groups.
Similar articles
- The association of tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor 2 and tumor necrosis factor alpha with insulin resistance and the influence of adipose tissue biomarkers in humans.
Hivert MF, Sullivan LM, Shrader P, Fox CS, Nathan DM, D'Agostino RB Sr, Wilson PW, Benjamin EJ, Meigs JB. Hivert MF, et al. Metabolism. 2010 Apr;59(4):540-6. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.08.017. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Metabolism. 2010. PMID: 19846171 Free PMC article. - Adipokines, inflammatory mediators, and insulin-resistance parameters may not be good markers of metabolic syndrome after liver transplant.
Anastácio LR, de Oliveira MC, Diniz KG, Ferreira AM, Lima AS, Correia MI, Vilela EG. Anastácio LR, et al. Nutrition. 2016 Sep;32(9):921-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2015.12.038. Epub 2015 Dec 31. Nutrition. 2016. PMID: 27189907 - Dynamics in insulin resistance and plasma levels of adipokines in patients with acute decompensated and chronic stable heart failure.
Schulze PC, Biolo A, Gopal D, Shahzad K, Balog J, Fish M, Siwik D, Colucci WS. Schulze PC, et al. J Card Fail. 2011 Dec;17(12):1004-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2011.08.010. Epub 2011 Oct 5. J Card Fail. 2011. PMID: 22123363 Free PMC article. - Adiponectin and resistin response in the onset of obesity in male and female rats.
Ribot J, Rodríguez AM, Rodríguez E, Palou A. Ribot J, et al. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008 Apr;16(4):723-30. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.113. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008. PMID: 18239591 - Association between obesity-related adipokines and colorectal cancer: a case-control study and meta-analysis.
Joshi RK, Kim WJ, Lee SA. Joshi RK, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jun 28;20(24):7941-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7941. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24976730 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Exploring Adiposity and Chronic Kidney Disease: Clinical Implications, Management Strategies, Prognostic Considerations.
Ozbek L, Abdel-Rahman SM, Unlu S, Guldan M, Copur S, Burlacu A, Covic A, Kanbay M. Ozbek L, et al. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Oct 11;60(10):1668. doi: 10.3390/medicina60101668. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39459455 Free PMC article. Review. - Nutritional assessment and medical dietary therapy for management of obesity in patients with non-dialysis chronic kidney disease: a practical guide for endocrinologist, nutritionists and nephrologists. A consensus statement from the Italian society of endocrinology (SIE), working group of the club nutrition-hormones and metabolism; the Italian society of nutraceuticals (SINut), club ketodiets and nutraceuticals "KetoNut-SINut"; and the Italian society of nephrology (SIN).
Annunziata G, Caprio M, Verde L, Carella AM, Camajani E, Benvenuto A, Paolini B, De Nicola L, Aucella F, Bellizzi V, Barberi S, Grassi D, Fogacci F, Colao A, Cicero AFG, Prodam F, Aimaretti G, Muscogiuri G, Barrea L. Annunziata G, et al. J Endocrinol Invest. 2024 Dec;47(12):2889-2913. doi: 10.1007/s40618-024-02446-8. Epub 2024 Sep 18. J Endocrinol Invest. 2024. PMID: 39292364 Review. - Heterogeneous response of estimated insulin sensitivity indices to metformin in young individuals with type 1 diabetes and different phenotypes.
Ramaldes LAL, Dos Santos SS, Dualib PM, de Sa JR, Dib SA. Ramaldes LAL, et al. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Sep 2;16(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01451-4. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 39218890 Free PMC article. - Adipokines-A Cohort Prospective Study in Children with Severe Burns.
Badoiu SC, Enescu DM, Tatar R, Miricescu D, Stanescu-Spinu II, Greabu M, Coricovac AM, Badoiu SE, Jinga V. Badoiu SC, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 11;25(14):7630. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147630. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062875 Free PMC article. - The role of selected adipokines in tumorigenesis and metabolic disorders in patients with adrenal tumors.
Babinska A, Kmieć P, Sworczak K. Babinska A, et al. Arch Med Sci. 2020 Mar 4;19(2):467-477. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2020.93486. eCollection 2023. Arch Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 37034534 Free PMC article.
References
- James PT, Leach R, Kalamara E, Shayeghi M 2001 The worldwide obesity epidemic. Obes Res 9:228S–233S - PubMed
- Kershaw EE, Flier JS 2004 Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2548–2556 - PubMed
- Hanley AJ, Bowden D, Wagenknecht LE, Balasubramanyam A, Langfeld C, Saad MF, Rotter JI, Guo X, Chen YD, Bryer-Ash M, Norris JM, Haffner SM 2007 Associations of adiponectin with body fat distribution and insulin sensitivity in nondiabetic Hispanics and African-Americans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:2665–2671 - PubMed
- Tschritter O, Fritsche A, Thamer C, Haap M, Shirkavand F, Rahe S, Staiger H, Maerker E, Haring H, Stumvoll M 2003 Plasma adiponectin concentrations predict insulin sensitivity of both glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetes 52:239–243 - PubMed
- Duncan BB, Schmidt MI, Pankow JS, Bang H, Couper D, Ballantyne CM, Hoogeveen RC, Heiss G 2004 Adiponectin and the development of type 2 diabetes: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes 53:2473–2478 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-HC-25195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK080140-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DZK080140/PHS HHS/United States
- K24 DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC25195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources