Analytical strategies for LC-MS-based targeted metabolomics - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Analytical strategies for LC-MS-based targeted metabolomics
Wenyun Lu et al. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2008.
Abstract
Recent advances in mass spectrometry are enabling improved analysis of endogenous metabolites. Here we discuss several issues relevant to developing liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry methods for targeted metabolomics (i.e., quantitative analysis of dozens to hundreds of specific metabolites). Sample preparation and liquid chromatography approaches are discussed, with an eye towards the challenge of dealing with a diversity of metabolite classes in parallel. Evidence is presented that heated electrospray ionization (ESI) generally gives improved signal compared to the more traditional unheated ESI. Applicability to targeted metabolomics of triple quadrupole mass spectrometry operating in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode and high mass resolution full scan mass spectrometry (e.g., time-of-flight, Orbitrap) are described. We suggest that both are viable solutions, with MRM preferred when targeting a more limited number of analytes, and full scan preferred for its potential ability to bridge targeted and untargeted metabolomics.
Figures
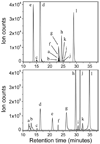
Figure 1
Chromatographic traces for selected metabolites in a cellular extract comparing the performance for the HILIC (top panel) and reversed-phase ion pairing chromatographic (bottom panel) methods in negative ionization mode, under identical mass spectrometry conditions. Selected metabolites are: glucose-6-phosphate and unresolved isomers thereof (a), glycerol-3-phosphate (b), orotate (c), NAD+ (d), pantothenate (e), succinate (f), malate (g), UDP-D-glucose (h), fructose-1,6-biphosphate (i), phosphoenolpyruvate (j), NADH (k), ATP (l). The LC condition for the HILIC mode (aminopropyl column with basic pH mobile phase, running time 50 minutes) has been reported previously [10],. The LC conditions for the ion pairing chromatography (reversed-phase Synergi Hydro column with acidic mobile phase, running time 50 minutes) can be found in the text. Note that metabolites a, b, f, and g are not separated in HILIC method while they are well separated in ion pairing chromatography method.
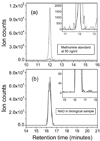
Figure 2
Chromatographic traces for methionine standard at 50 ng/mL in positive ionization mode (a) and NAD+ in a biological sample in negative mode (b), on identical TSQ Quantum Ultra (Thermo Fisher Scientific ) triple quadrupole instruments but with different ion sources, the unheated electrospray source (sold line) and the heated electrospray source (HESI, dashed line). The insets show the corresponding noise/background region. The LC method was HILIC as reported previously [10]. The source conditions for the unheated ESI were: spray voltage +3500 V or −3000 V, sheath gas 30 psi, auxiliary gas 10 psi. The source conditions for the HESI were: spray voltage +2555 V or −2555 V, vaporizer temperature 230 °C, sheath gas 22 psi, auxiliary gas 37 psi.
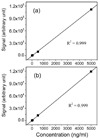
Figure 3
Linearity test results for glutamate standards on an Agilent TOF instrument (a) and a triple quadrupole instrument (b). Both show a linear response from 5 to 5000 ng/mL with a R2 > 0.999. The LC method was HILIC as reported previously [10].
Similar articles
- Strategies for large-scale targeted metabolomics quantification by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.
Zhou J, Yin Y. Zhou J, et al. Analyst. 2016 Nov 14;141(23):6362-6373. doi: 10.1039/c6an01753c. Analyst. 2016. PMID: 27722450 Review. - Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometric multiple reaction monitoring-based strategies for expanding targeted profiling towards quantitative metabolomics.
Guo B, Chen B, Liu A, Zhu W, Yao S. Guo B, et al. Curr Drug Metab. 2012 Nov;13(9):1226-43. doi: 10.2174/138920012803341401. Curr Drug Metab. 2012. PMID: 22519369 Review. - Metabolic profile of naringenin in the stomach and colon using liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization linear ion trap quadrupole-Orbitrap-mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS) and LC-ESI-MS/MS.
Orrego-Lagarón N, Vallverdú-Queralt A, Martínez-Huélamo M, Lamuela-Raventos RM, Escribano-Ferrer E. Orrego-Lagarón N, et al. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016 Feb 20;120:38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2015.10.040. Epub 2015 Dec 2. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016. PMID: 26698229
Cited by
- Sum of the parts: mass spectrometry-based metabolomics.
Milne SB, Mathews TP, Myers DS, Ivanova PT, Brown HA. Milne SB, et al. Biochemistry. 2013 Jun 4;52(22):3829-40. doi: 10.1021/bi400060e. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23442130 Free PMC article. Review. - Extraction of hydrophilic metabolites from Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes for metabolomic analysis.
Olszewski KL, Llinás M. Olszewski KL, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;923:259-66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-026-7_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 22990783 Free PMC article. - Chemical Evaluation of the Effects of Storage Conditions on the Botanical Goldenseal using Marker-based and Metabolomics Approaches.
Khin M, Cech NB, Kellogg JJ, Caesar LK. Khin M, et al. Yale J Biol Med. 2020 Jun 29;93(2):265-275. eCollection 2020 Jun. Yale J Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32607087 Free PMC article. - Quantifying the cellular NAD+ metabolome using a tandem liquid chromatography mass spectrometry approach.
Bustamante S, Jayasena T, Richani D, Gilchrist RB, Wu LE, Sinclair DA, Sachdev PS, Braidy N. Bustamante S, et al. Metabolomics. 2017 Dec 23;14(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s11306-017-1310-z. Metabolomics. 2017. PMID: 30830318 Free PMC article.
References
- Griffiths WJ, Karua K, Hornshaw M, Woffendin G, Wanga Y. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007;13:45. - PubMed
- Want EJ, Cravatt BF, Siuzdak G. Chembiochem. 2005;6:1941. - PubMed
- Want EJ, Nordstrom A, Morita H, Siuzdak G. J. Proteom. Res. 2007;6:459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AI078063-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM071508/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM071508-05/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM071508/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI078063/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI078063/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources