Brain derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism, the five factor model of personality and hippocampal volume: Implications for depressive illness - PubMed (original) (raw)
Brain derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism, the five factor model of personality and hippocampal volume: Implications for depressive illness
Russell T Joffe et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2009 Apr.
Abstract
Altered hippocampal volume, the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Val66Met polymorphism, and neuroticism have each been implicated in the etiology of psychiatric disorders, especially depression. However, the relationship between these variables is not well understood. Here, we determined the effects of the BDNF Val66met polymorphism on the five-factor personality dimensions (assessed using the NEO-FFI), trait depression (assessed with the DASS-21) in a cross-sectional cohort of 467 healthy volunteers. A large matched subset of this cohort was also assessed for grey matter volume of the hippocampus and contiguous temporal cortical regions using magnetic resonance imaging. In Met carriers, elevations in neuroticism and trait depression and stress were associated with lower mean hippocampal volume, but there were no such associations in Val homozygotes. Trait depression, in particular, was found to moderate the effects of BDNF genotypes on hippocampal volume. Met carriers with high trait depression showed a reduction in grey matter volume of the mean hippocampus compared with Val homozygotes. These findings suggest that even in otherwise healthy subjects, trait depression may contribute to the susceptibility of Met carriers to hippocampal grey matter loss.
2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
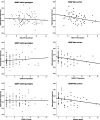
Figure 1
Scatter‐plots of associations between total hippocampal volume (mL) and behavioral measures, NEO‐FFI neuroticism and DASS‐21 depression and stress, within BDNF Met carriers and Val/Val homozygotes.
Figure 2
Line graphs depicting estimated marginal means from the multiple regression analysis, in which the interaction of BDNF Val66Met genotype status and DASS‐21 level of depression predicted grey matter volume for the left and right hippocampus. BDNF Met carriers (grey line) with higher depression scores showed reduced hippocampal volume compared with Val/Val genotypes (black line) with similarly high depression scores.
Similar articles
- Cognitive and magnetic resonance imaging brain morphometric correlates of brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met gene polymorphism in patients with schizophrenia and healthy volunteers.
Ho BC, Milev P, O'Leary DS, Librant A, Andreasen NC, Wassink TH. Ho BC, et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006 Jul;63(7):731-40. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.63.7.731. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16818862 Free PMC article. - Association study of a brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Val66Met polymorphism and personality trait and intelligence in healthy young females.
Tsai SJ, Hong CJ, Yu YW, Chen TJ. Tsai SJ, et al. Neuropsychobiology. 2004;49(1):13-6. doi: 10.1159/000075333. Neuropsychobiology. 2004. PMID: 14730195 - Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism on hippocampal volume change in schizophrenia.
Koolschijn PC, van Haren NE, Bakker SC, Hoogendoorn ML, Hulshoff Pol HE, Kahn RS. Koolschijn PC, et al. Hippocampus. 2010 Sep;20(9):1010-7. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20699. Hippocampus. 2010. PMID: 19714565 - Hippocampal volume and the brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism in first episode psychosis.
Smith GN, Thornton AE, Lang DJ, Macewan GW, Ehmann TS, Kopala LC, Tee K, Shiau G, Voineskos AN, Kennedy JL, Honer WG. Smith GN, et al. Schizophr Res. 2012 Feb;134(2-3):253-9. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2011.11.022. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Schizophr Res. 2012. PMID: 22192502 - BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and hippocampal volume in neuropsychiatric disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Harrisberger F, Smieskova R, Schmidt A, Lenz C, Walter A, Wittfeld K, Grabe HJ, Lang UE, Fusar-Poli P, Borgwardt S. Harrisberger F, et al. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Aug;55:107-18. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.04.017. Epub 2015 May 5. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015. PMID: 25956254 Review.
Cited by
- Emotional dysregulation, alexithymia and neuroticism: a systematic review on the genetic basis of a subset of psychological traits.
Castellini G, Merola GP, Baccaredda Boy O, Pecoraro V, Bozza B, Cassioli E, Rossi E, Bessi V, Sorbi S, Nacmias B, Ricca V. Castellini G, et al. Psychiatr Genet. 2023 Jun 1;33(3):79-101. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0000000000000335. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Psychiatr Genet. 2023. PMID: 36729042 Free PMC article. - "Nothing to see here": No structural brain differences as a function of the Big Five personality traits from a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Chen YW, Canli T. Chen YW, et al. Personal Neurosci. 2022 Aug 9;5:e8. doi: 10.1017/pen.2021.5. eCollection 2022. Personal Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35991756 Free PMC article. Review. - Associations of Brain-Derived Neurotropic Factor rs6265 Gene Polymorphism with Personality Dimensions among Athletes.
Humińska-Lisowska K, Chmielowiec J, Chmielowiec K, Niewczas M, Lachowicz M, Cięszczyk P, Masiak J, Strońska-Pluta A, Michałowska-Sawczyn M, Maculewicz E, Grzywacz A. Humińska-Lisowska K, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 7;19(15):9732. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159732. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35955088 Free PMC article. - The relationship between job stress and job burnout moderated by BDNF rs6265 polymorphism.
Jia H, He M, Zhang X, Li Y, He SC, Zhang XY. Jia H, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 Oct;238(10):2963-2971. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-05911-x. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021. PMID: 34245319 - Gray matter structures associated with neuroticism: A meta-analysis of whole-brain voxel-based morphometry studies.
Liu X, Lai H, Li J, Becker B, Zhao Y, Cheng B, Wang S. Liu X, et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021 Jun 15;42(9):2706-2721. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25395. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021. PMID: 33704850 Free PMC article.
References
- Antony MM,Bieling PJ,Cox BJ,Enns MW,Swinson RP ( 1998): Psychometric properties of the 42‐item and 21‐item versions of the depression anxiety stress scales in clinical groups and a community sample. Psychol Assess 10: 176–181.
- Ashburner J,Friston KJ ( 2000): Voxel‐based morphometry—The methods. Neuroimage 11: 805–821. - PubMed
- Beck AT,Ward CH,Mendelsohn M,Mock J,Erbaugh J ( 1961): An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4: 561–571. - PubMed
- Beck AT,Epstein N,Brown G,Steer RA ( 1988): An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: Psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol 56: 893–897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous