Genomics and genome-wide association studies: an integrative approach to expression QTL mapping - PubMed (original) (raw)
Genomics and genome-wide association studies: an integrative approach to expression QTL mapping
James H Degnan et al. Genomics. 2008 Sep.
Abstract
Expression QTL mapping by integrating genome-wide gene expression and genotype data is a promising approach to identifying functional genetic variation, but is hampered by the large number of multiple comparisons inherent in such studies. A novel approach to addressing multiple testing problems in genome-wide family-based association studies is screening candidate markers using heritability or conditional power. We apply these methods in settings in which microarray gene expression data are used as phenotypes, screening for SNPs near the expressed genes. We perform association analyses for phenotypes using a univariate approach. We also perform simulations on trios with large numbers of causal SNPs to determine the optimal number of markers to use in a screen. We demonstrate that our family-based screening approach performs well in the analysis of integrative genomic datasets and that screening using either heritability or conditional power produces similar, though not identical, results.
Figures
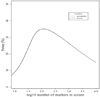
Figure 1
Average number (out of 100) of causal SNPs detected as a function of the log10 number of the top k marker in the PBAT screen, k = 1, …, 10, 000, based on 1000 simulations and using either heritability or power as the screening criterion.
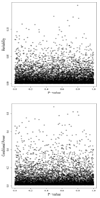
Figure 2
Heritability (top) and conditional power (bottom) plotted against p-values for one of the 1000 simulated data sets using noncausal SNPs only.
Similar articles
- A multi-trait Bayesian method for mapping QTL and genomic prediction.
Kemper KE, Bowman PJ, Hayes BJ, Visscher PM, Goddard ME. Kemper KE, et al. Genet Sel Evol. 2018 Mar 24;50(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12711-018-0377-y. Genet Sel Evol. 2018. PMID: 29571285 Free PMC article. - iGWAS: Integrative Genome-Wide Association Studies of Genetic and Genomic Data for Disease Susceptibility Using Mediation Analysis.
Huang YT, Liang L, Moffatt MF, Cookson WO, Lin X. Huang YT, et al. Genet Epidemiol. 2015 Jul;39(5):347-56. doi: 10.1002/gepi.21905. Epub 2015 May 22. Genet Epidemiol. 2015. PMID: 25997986 Free PMC article. - Integrative Transcriptome, Genome and Quantitative Trait Loci Resources Identify Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Candidate Genes for Growth Traits in Turbot.
Robledo D, Fernández C, Hermida M, Sciara A, Álvarez-Dios JA, Cabaleiro S, Caamaño R, Martínez P, Bouza C. Robledo D, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Feb 17;17(2):243. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020243. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26901189 Free PMC article. - The genetic dissection of immune response using gene-expression studies and genome mapping.
de Koning DJ, Carlborg O, Haley CS. de Koning DJ, et al. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2005 May 15;105(3-4):343-52. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2005.02.007. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2005. PMID: 15808311 Review. - Association mapping in plants in the post-GWAS genomics era.
Gupta PK, Kulwal PL, Jaiswal V. Gupta PK, et al. Adv Genet. 2019;104:75-154. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2018.12.001. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Adv Genet. 2019. PMID: 31200809 Review.
Cited by
- Matrix eQTL: ultra fast eQTL analysis via large matrix operations.
Shabalin AA. Shabalin AA. Bioinformatics. 2012 May 15;28(10):1353-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts163. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22492648 Free PMC article. - A systems-based framework for understanding complex metabolic and cardiovascular disorders.
Wu S, Lusis AJ, Drake TA. Wu S, et al. J Lipid Res. 2009 Apr;50 Suppl(Suppl):S358-63. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R800067-JLR200. Epub 2008 Nov 24. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 19033210 Free PMC article. Review. - SCeQTL: an R package for identifying eQTL from single-cell parallel sequencing data.
Hu Y, Xi X, Yang Q, Zhang X. Hu Y, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 May 11;21(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-3534-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32393315 Free PMC article. - Systems medicine: the future of medical genomics and healthcare.
Auffray C, Chen Z, Hood L. Auffray C, et al. Genome Med. 2009 Jan 20;1(1):2. doi: 10.1186/gm2. Genome Med. 2009. PMID: 19348689 Free PMC article. - Convergent functional genomics of schizophrenia: from comprehensive understanding to genetic risk prediction.
Ayalew M, Le-Niculescu H, Levey DF, Jain N, Changala B, Patel SD, Winiger E, Breier A, Shekhar A, Amdur R, Koller D, Nurnberger JI, Corvin A, Geyer M, Tsuang MT, Salomon D, Schork NJ, Fanous AH, O'Donovan MC, Niculescu AB. Ayalew M, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2012 Sep;17(9):887-905. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.37. Epub 2012 May 15. Mol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22584867 Free PMC article.
References
- Herbert A, Gerry NP, McQueen MB, Heid IM, Pfeufer A, Illig T, Wichmann HE, Meitinger T, Hunter D, Hu FB, Colditz G, Hinney A, Hebebrand J, Koberwitz K, Zhu XF, Cooper R, Ardlie K, Lyon H, Hirschhorn JN, Laird NM, Lenburg ME, Lange C, Christman MF. A common genetic variant is associated with adult and childhood obesity. Science. 2006;312:279–283. - PubMed
- Dina C, Meyre D, Samson C, Tichet J, Marre M, Jouret B, Charles MA, Balkau B, Froguel P. Comment on “A common genetic variant is associated with adult and childhood obesity”. Science. 2007;315:187. - PubMed
- Rosskopf D, Bornhorst A, Rimmbach C, Schwahn C, Kayser A, Krüger A, Tessmann G, Geissler I, Kroemer HK, Völzke H. Comment on “A common genetic variant is associated with adult and childhood obesity”. Science. 2007;315:187. - PubMed
- Herbert A, Gerry NP, McQueen MB, Heid IM, Pfeufer A, Illig T, Wichmann HE, Meitinger T, Hunter D, Hu FB, Colditz G, Hinney A, Hebebrand J, Koberwitz K, Zhu XF, Cooper R, Ardlie K, Lyon H, Hirschhorn JN, Laird NM, Lenburg ME, Lange C, Christman MF. Comment on “A common genetic variant is associated with adult and childhood obesity. Science. 2007;315:187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL086601A/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL074193/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MH59532/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059532-07/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059532/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086601/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources