Diabetes complications in 1952 type 2 diabetes mellitus patients managed in a single institution in Saudi Arabia - PubMed (original) (raw)
Diabetes complications in 1952 type 2 diabetes mellitus patients managed in a single institution in Saudi Arabia
Jamal S Alwakeel et al. Ann Saudi Med. 2008 Jul-Aug.
Abstract
Background and objectives: Because there is no recent update on the state of diabetes and its concomitant complications in Saudi Arabia, we undertook a study of the prevalence of health complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus admitted to our institution.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of medical records of adult Saudi patients with type 2 diabetes who were seen in clinics or admitted to the Security Forces Hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, between January 1989 and January 2004.
Results: Of 1952 patients, 943 (48.3%) were males. For the whole study population the mean age at enrollment was 58.4+/-14.2 years, the mean age at onset of diabetes was 48.1+/-12.8 years, the mean duration of diabetes was 10.4+/-7.5 years, and the mean duration of follow-up was 7.9+/-4.6 years. Nephropathy was the most prevalent complication, occurring in 626 patients (32.1%). Acute coronary syndrome occurred in 451 (23.1%), cataracts in 447 (22.9%), retinopathy in 326 (16.7%), and myocardial infarction in 279 (14.3%), Doubling of serum creatinine was seen in 250 (12.8%) and 79 (4.0%) went into dialysis. Hypertension was present in 1524 (78.1%) and dyslipidemia in 764 (39.1%). Overall mortality was 8.2%. Multiple complications were frequent. Males had higher prevalence of complications than females (P<.05). Mortality was significantly higher in males 92 (9.8%) than females 69 (6.8%) (P=.024). The prevalence of complications significantly increased with duration of diabetes and age (P<.05).
Conclusion: Among Saudis, the prevalence of concomitant diabetic complications is high, with cardiovascular and renal complications the most frequent. Many patients had multiple complications. Early and frequent screenings in the patients with type 2 diabetes are desirable to identify patients at high risk for concomitant complications and to prevent disabilities.
Figures
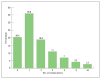
Figure 1
Number of complications among patients with type 2 diabetes (including nephropathy, background retinopathy, proliferative retinopathy, acute coronary syndrome, diabetic foot, neuropathy, stroke and hypertension).
Similar articles
- Concomitant macro and microvascular complications in diabetic nephropathy.
Alwakeel JS, Al-Suwaida A, Isnani AC, Al-Harbi A, Alam A. Alwakeel JS, et al. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2009 May;20(3):402-9. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2009. PMID: 19414942 - Microvascular and macrovascular complications in diabetic nephropathy patients referred to nephrology clinic.
Al-Wakeel JS, Hammad D, Al Suwaida A, Mitwalli AH, Memon NA, Sulimani F. Al-Wakeel JS, et al. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2009 Jan;20(1):77-85. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2009. PMID: 19112222 - The association of diabetes with ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attacks in a tertiary center in Saudi Arabia.
Homoud B, Alhakami A, Almalki M, Shaheen M, Althuabiti A, AlKhathaami A, Khatri IA. Homoud B, et al. Ann Saudi Med. 2020 Nov-Dec;40(6):449-455. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2020.449. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Ann Saudi Med. 2020. PMID: 33307739 Free PMC article. - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Saudi Arabia: Major Challenges and Possible Solutions.
Robert AA, Al Dawish MA, Braham R, Musallam MA, Al Hayek AA, Al Kahtany NH. Robert AA, et al. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017;13(1):59-64. doi: 10.2174/1573399812666160126142605. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017. PMID: 26813972 Review. - Microvascular complications among patients with diabetes: An emerging health problem in Saudi Arabia.
Alwin Robert A, Al Dawish MA. Alwin Robert A, et al. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2019 May;16(3):227-235. doi: 10.1177/1479164118820714. Epub 2019 Jan 1. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2019. PMID: 30599757 Review.
Cited by
- Incremental Healthcare Resource Utilization and Expenditures Associated with Cardiovascular Diseases in Patients with Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study.
Ebrahimoghli R, Janati A, Sadeghi-Bazargani H, Hamishehkar H, Khalili-Azimi A. Ebrahimoghli R, et al. Iran J Med Sci. 2022 Jan;47(1):53-62. doi: 10.30476/ijms.2020.87284.1742. Iran J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35017778 Free PMC article. - Awareness of Diabetic Retinopathy Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Attending the Outpatient Clinic in the General Hospital in Rabigh, Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study.
Wahby I, Albeladi F, Abukhudair A, Alyoubi S, Alyoubi S, Alotaibi A, Albeladi A. Wahby I, et al. Cureus. 2022 Aug 21;14(8):e28235. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28235. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36158427 Free PMC article. - Incidence of Cardiovascular Complications and Nephropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in a Primary Care Setting in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Alsaidan M, Alkhenizan A, Amber ST, Alsoghayer S, AlFakhri L, Abudaia J. Alsaidan M, et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 Apr 15;14:1663-1667. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S301933. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 33883915 Free PMC article. - Incidence and prevalence rates of diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia: An overview.
Alotaibi A, Perry L, Gholizadeh L, Al-Ganmi A. Alotaibi A, et al. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2017 Dec;7(4):211-218. doi: 10.1016/j.jegh.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 7. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2017. PMID: 29110860 Free PMC article. Review. - DiabCare survey of diabetes management and complications in the Gulf countries.
Omar MS, Khudada K, Safarini S, Mehanna S, Nafach J. Omar MS, et al. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Mar-Apr;20(2):219-27. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.176347. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27042419 Free PMC article.
References
- Al-Nozha MM, Al-Maatouq MA, Al-Mazrou YY, Al-Harthi SS, Arafah MR, Khalil MZ, et al. Diabetes Mellitus in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 2004;25(11):1603–10. - PubMed
- Al-Nuaim AR, Al-Mazrou Y, Al-Attas O, et al. National Chronic Metabolic Diseases Survey Part I. Ministry of Health and King Saud University; Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: 1995. p. 63.
- AlWakeel JS, Mitwalli AH, Abu-Aisha H, Tarif N, Memon N, Sulimani F, et al. Single center experience with pre-dialysis patients. Saudi J Kidney Dis Tranplant. 2002;13(3):363–70. - PubMed
- El-Hazmi MA, Al-Swailem A, Warsy AS, Al-Sudairy F, Sulimani R, Al-Swailem A, et al. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance in the population of Riyadh. Ann Saudi Med. 1995;15(6):598–601. - PubMed
- Warsy AS, El-Hazmi MA. Diabetes mellitus, hypertension and obesity-related common multifactorial disorders in Saudis. East Mediterr Health J. 1999;5(6):1236–42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical